This study aims to find the alternative to increase the participation rates of physical activities and to analyze socio-demographic factors that determine sporting participation in Korea. We estimates the sporting participation model with ʼ2012 national sport participation survey in Korea' and binary logit analysis. The results are as follows: sporting participation is positively related to gender(male), age, education level, household income, health status, leisure time in weekday, proximity to public and private sports facilities. The most significant factors influencing the raising the participation rates of physical activities factors are age and proximity to sports facilities. Therefore, to make many people to participate in sports activities, we need to supply the public sports facilities that in proximity to house and the facilities needs to be taken into participant's age such as elderly group. Also, we make effort to improve the accessibility to sports facilities of poor and unhealthy people.
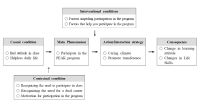
Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the process of participation in the PEAK program of collegiate athletes based on grounded theory. Methods In-depth interviews were conducted with 12 athletes from Y University who were registered in Korea Taekwondo Association. The collected data were analyzed by using the open coding, axis coding, and selective coding of the grounded theory, completed the paradigm model among the extracted concepts, and extracted the core categories through the story outline. Results As the result of data analysis, 'participating in the PEAK program' was found as the central phenomenon, and the causal situation was 'bad attitude in class' and 'helpless daily life'. The contextual conditions were 'recognition of the need for class participation and dual career' and 'motivation to participate in the program', and the intervening conditions were 'factors that hinder participation in the program' and 'factors that help program participation'. The action/interaction strategies were ‘caring climate’ and ‘promoting transfer’, and depending on the consequence, ‘learning attitude change’ and ‘life skill change’ appeared. Conclusion Participants improved their learning attitude through the PEAK program and confirmed the possibility of life skills transfer. It is hoped that this study can lead to implementation of various studies and discussions about life skills and transfer.

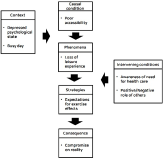
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the alienation and the overcoming process of the physical activity participation of people with Adventitious Visual Impairment(AVI) Methods 21 Adults with AVI were recruited and one on one semi-structured interview was conducted. Ground theory was used to analyze the data. Member check, peer debriefing was conducted to enhance the trustworthiness of this study. Results As a result, a total of 203 concepts were derived. This consisted of 21 subcategories and the common themes of the subcategories were categorized into nine categories. Specific results are as follows. First, the physical activity of people with AVI was directly affected by the sports facilities, physical activity programs, and professional instructor. This causal condition resulted in the loss of leisure experience in the context of the busy daily life and the depressed psychological state. Second, due to the perceived need of health care and the positive involvement of others, people with AVI came to expect the effect of exercise. Third, people with AVI participated in physical activity again as a tool to achieve the purpose of health improvement. This type of physical activity has a limitation that it can not guarantee the continuity of physical activity due to the limitation that it does not contain autonomy and interest of people with AVI. Conclusions Based on these results, the following suggestions were made. First, it is necessary to improve the environment for ensuring participation in physical activity of people with AVI. Moreover education and promotion of the effects and values of the exercise should be carried out for people with AVI and their guardians. Second, it is necessary to diversify physical activity types and reconstruct existing exercise programs.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine students’ perceptions of girls’ participation in physical education(PE) in elementary schools and examine the impacts of a girl-friendly integrated program on children’s participation in PE classes. Methods The participants were 10 fifth graders (5 girls and 5 boys) and their teacher in an elementary school. Data which were collected from in-depth interviews with students, students’ journal entries, field observation, and teacher’s reflective journal entries were analyzed inductively. Results Findings revealed that boys perceived girls’ participation as passive, possessing a low level of skills, and staying at the peripheral position. Meanwhile girls expressed their desire to demonstrate their strengths in PE classes and were afraid of boys’ criticism regarding their lack of skills. There were also misconceptions and misunderstanding on girls’ PE participation between boys and girls. In order to resolve these issues, a girls-friendly integrative program was designed. based on the four guiding principles drawn from students’ perception: (1) from ignorance to interest, (2) from misunderstanding to understanding, (3) from sport skills to sport values, and (4) from competition to cooperation. The program integrated boys and girls for promoting active interaction and also integrated competence, knowledge, and dispositions to accommodate students’ various ways of PE participation. Findings revealed that the program had: (1) diversified students’ perceptions of PE participation, (2) promoted students’ diverse and active participation, and (3) established classroom atmosphere which emphasized positive values.


The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.
The purpose of this study was to examine the current status of school sport club(SSC) participation and to explore relationship between school sport participation and positive youth development. In order to do this, a survey was conducted with 403 elementary, middle, and high school teachers who are currently taking charge of SSCs, and also individual interviews were conducted with 22 students. In addition, the youths' developmental asset questionnaire was administered with 412 middle school students. The survey results from 403 teachers showed that SSCs have potential to contribute to positive youth development because teachers are placing an emphasis on character development as well as physical and social development through SSC activities. In addition, participants who regularly participate in physical activities had higher internal and external developmental assets than non-participants or irregular participants. Specifically, students participated in SSC more than twice a week had higher internal and external assets than students participate once a week. In addition, participants who engage more than one hour per session had higher internal and external assets except constructive use of time and social competence. Discussion and implications for organizing SSCs to provide developmental contexts and contents for positive youth development were provided.
This study measured the accessibility of public exercise facilities within a residental area of a metropolitan community and examined how the accessibility can affect physical activity participation of residents. Initially, a total of 639 residents, who were aged between 19-70, visited Metabolic Syndrome Management Center of the Community Public Health Center, and registered for a Obesity Clinic Program, was listed as potential subjects. And those who responded to Physical Activity Questionnaire were selected for the analyses (n=92, 14.3% of 639). The relationships between physical activity level and accessibility to public exercise facilities were analyzed. Objective distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous physical activity(r=.209)’, 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.206)’. And perceived distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.235)’. perceived transport time to public facility was related to ‘duration of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.239)’, ’volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.306)’, and ‘volume of participation to total physical activity(r=.273)’. In contrast, the difference between objective distance to public facility and perceived subjective distance to the facility was negatively related to ‘duration of participation to moderate-intensity physical activity(r=-.221)’. The perceived numbers of public facility was positively related to ‘frequency of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.237)’, ‘frequency of participation to walking(r=.273)’, ‘volume of participation to walking(r=.251)’ and 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.252)’. The predictor of 'total volume of participation to physical activity was perceived numbers of public facility(R2=.153, p=.046). The results revealed that the subjective accessibility to public health facilities was more influential to physical activity participation than the objective accessibility. Further research was warranted while using diverse populations as well as considering a inclusion of environmental factors.


PURPOSE This study aimed to prove the mediator effect of skill level on participation frequency and injury level of leisure sports players with the highest injury rate. METHODS Raw data of the “2019 Sports Safety accident data” conducted by the Korea Sports Safety Foundation were used for this study. We analyzed 857 leisure sports players participating in events with the top four highest injury rates (Basketball, Soccer, Baseball/Softball, Foot Volleyball). Frequency, descriptive statistics, and correlation analyses using SPSS version 27.0 and Process macro model 4 were employed for analysis. RESULTS The results regarding participation frequency, injury severity, and skill level among recreational athletes are as follows. First, a positive correlation was established between the participation frequency of recreational athletes and their skill levels. Second, the correlation between participation frequency and injury severity was observed only in soccer and basketball. Third, skill level plays a mediating role in the relationship between participation frequency and injury level. The results indicate that as the participation frequency among leisure sports players who participate in ball sports with a high injury rate increases, this affects the degree of injury. CONCLUSIONS Skill level appears to play a mediating role in the relationship between participation frequency and injury level. Based on the results, we recommend safety education not only on the relationship between participation frequency and injury level, but also the intermediary role of skill level.
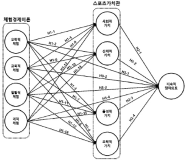
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the structural relationship between the sport values and continuous participation intention of the dance for all participants based on the 4 experience economy theory. Methods Frequency analysis, correlation analysis, confirmatory factor analysis and structural equation modeling using SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 18.0 were conducted to analyze the survey materials. Results First, the entertainment experience was a significant effect on all factors of sports value. Second, educational experience was a significant effect on all factors except sports entertainment value. Third, escapist experiences have a significant effect on all factors except physical value. Fourth, aesthetic experience has a significant effect on all factors of sports value. Fifth, social value and entertainment value was a significant influence on the continuous participation intention. Sixth, entertainment experience and aesthetic experience was a significant influence on the continuous participation intention. Conclusions Through these study results, it was confirmed that 4 experience, sport values and continuous participation intention of dance for all participants had a significant influence on each other.

This article analyzes and compares the methodologies used in physical activity participation surveys from England, Australia, and South Korea. Specifically, it examines the “2021–22 Active Lives Adult Survey” from England, the “2021–22 AusPlay (15+)” from Australia, and the “2022 National Sports Participation Survey” from South Korea, highlighting both similarities and differences in their approaches. The analysis led to two key insights. First, there is a need to expand the scope of respondents in South Korea’s National Sports Participation Survey. Currently, the survey targets only 0.02% of the population aged ≥10 years, whereas the surveys in England and Australia gather data from a wider age range and more diverse regions. Therefore, South Korea should adopt online, postal, and mobile survey methods to widen the respondent pool and enhance the representativeness and reliability of the data collected. Second, South Korea needs to update its physical activity participation standards. The current benchmarks fall below international recommendations. Establishing new criteria that specify activity duration, intensity, and type is essential for effectively improving public health policies. The results of this study emphasize the importance of accurately assessing and enhancing physical activity participation in South Korea. These findings are expected to contribute to the development of effective sports policy standards in line with the World Health Organization’s global action plan.