PURPOSE This study aimed to compare and analyze the game content of the “3-rounds, 2-win system” matches before and after the rule revision implemented in 2022. METHODS This study covered 72 matches from the 2019 Rome World Championships Grand Prix, 92 matches from the Sofia World Championship Grand Prix, and 173 matches from the 2022 Rome World Championships Grand Prix. In total, 337 game videos were analyzed to assess the players‘ game content before and after the rule revision. RESULTS Analyzing the basic skills before and after the revision shows that the frequency of round kicks and pushes was high. Notably, while the frequency of round kicks, which are primarily used by players, decreased after the revision, the scoring success rate increased. CONCLUSIONS Based on the research findings, it is believed that post-revision, players are focusing more on game management aimed at scoring rather than attempting preliminary movements or connecting kicks to deceive their opponents.
PURPOSE By analyzing trends in Taekwondo demonstrations, specifically in breaking and performances, to date, this study aims to offer timely insights and set the groundwork for future research. METHODS We used Korean abstracts from a total of 425 papers containing the keyword “Taekwondo demonstrations” spanning 20 years from April 2004 to April 2023. We employed Python 3.5.2 to conduct dynamic topic modeling (Latent Dirichlet Analysis, LDA) and to examine the correlation between the topic distribution by section and the publication year. RESULTS The main findings from the LDA are as follows. Topic 1 (10%): “The development of demonstrations: performance in culture and art, ” Topic 2 (11%): “The development of formalized rules and judgments in a demonstration event,” Topic 3 (08%): “A study on the educational courses and professionalism of Taekwondo coaches,” Topic 4 (11%): “Technical movements and kinematic characteristics,” Topic 5 (09%): “A study on marketing perspectives of demonstration performances,” and Topic 7 (33%): “Global exchange: the development and rise of internationalization.” In the correlation analysis between the topic share by section and the publication year, Topics 1 to 5 exhibited no statistically significant correlation. However, Topic 6, “A study on the attainment of events, training, and the psychological factors influencing athletes” and Topic 7, “Global exchange: the development and rise of internationalization,” also displayed a very statistically significant but negative correlation. CONCLUSIONS Future research should focus on studies on the psychological management of athletes during the performance of specific techniques and training methods. Further research considering the global characteristics of Taekwondo may be required.
PURPOSE The ethical leadership of Taekwondo instructors plays a crucial role in enhancing the value of Taekwondo. Therefore, this study explores the elements of ethical leadership among Taekwondo instructors by drawing on the insights from Lao Tzu's Tao Te Ching. METHODS Through the Tao Te Ching, an oriental classic containing the ideas of Lao Tzu, we have extracted and discussed the elements of ethical leadership that Lao Tzu conveys to Taekwondo leaders in this era. RESULTS The ethical leadership of taekwondo leaders in the Tao Te Ching was presented as the virtues of inaction and humility as behavioral norms. Inaction as a code of conduct was discussed about a leader who practices inaction in a changing world through subjective thought rather than a meaningful Taekwondo leader who leads Taekwondo with an existing pattern and looks at ethics. A Taekwondo instructor must possess the virtue of humility. A Taekwondo instructor with humility must be glazed, soft, and humble as water. CONCLUSIONS In a Taekwondo culture that follows the Confucian ideology of extreme austerity, Lao Tzu's ethic of non-action and the virtue of humility can be like wearing an ill-fitting robe. However, standing on the edge, outside the frame of reference of the ideologies and values we have come to believe in and follow, and seeing the world as it is, not as it should be, according to the laws of nature, provides a new discourse for Taekwondo philosophy.
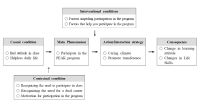
Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the process of participation in the PEAK program of collegiate athletes based on grounded theory. Methods In-depth interviews were conducted with 12 athletes from Y University who were registered in Korea Taekwondo Association. The collected data were analyzed by using the open coding, axis coding, and selective coding of the grounded theory, completed the paradigm model among the extracted concepts, and extracted the core categories through the story outline. Results As the result of data analysis, 'participating in the PEAK program' was found as the central phenomenon, and the causal situation was 'bad attitude in class' and 'helpless daily life'. The contextual conditions were 'recognition of the need for class participation and dual career' and 'motivation to participate in the program', and the intervening conditions were 'factors that hinder participation in the program' and 'factors that help program participation'. The action/interaction strategies were ‘caring climate’ and ‘promoting transfer’, and depending on the consequence, ‘learning attitude change’ and ‘life skill change’ appeared. Conclusion Participants improved their learning attitude through the PEAK program and confirmed the possibility of life skills transfer. It is hoped that this study can lead to implementation of various studies and discussions about life skills and transfer.


Purpose The purpose of this study was to verify their effectiveness as we develop and apply worksheets for improving life skills and resilience of collegiate Taekwondo athletes. Methods The study went through three stages: developing, applying, and evaluating. In the developing stage, literature review, expert meeting, and pilot test (n=25) were conducted to develop the worksheets. In the applying stage, 37 athletes participated in life skills program using the worksheets. Data were collected by survey and in-depth interview. In the evaluating stage, paired t-test, word cloud analysis, and inductive content analysis used to identify the effect of worksheets. Results First, the worksheets were composed of 3 stages (plan, acquisition, implementation) and 15 sessions including 12 factors of life skills. Second, the worksheets were applied in each phases such as planning, acquiring, and implementing. In the planning phase, they understood life skills knowledge and set goals. In the acquisition phase, students learned specific life skills’ strategies. In the practice phase, the acquired life skills were applied and practiced in real life and relationships. Third, the result of paired t-test showed that all the factors of life skills and 6 factors of resilience were significantly improved. In addition, word cloud and in-depth interviews revealed that the participants' cognitive and psychological changes were most prominent. Conclusions The life skills worksheets consists of 12 factors in 15 sessions and can be considered as an effective intervention tool for improving the resilience and life skills of collegiate Taekwondo athletes.

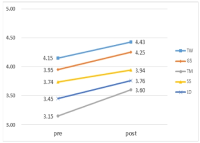
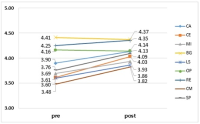









Purpose The purpose of this study was to provide basic data for spectators group of Taekwondo performance efficient marketing activities through market segmentation from characteristics, perceived values of the Taekwondo performance spectators. Methods The subjects of this research were Kukkiwon, Taekwondowon and 1,021 questionnaires were finally used for the analysis. The results of this research were drawn by frequency analysis, CFA(confirmatory factor analysis), reliability analysis, cluster analysis (hierarchical and K-means), cross-tabulation analysis and One-way ANOVA were used for data processing through SPSS 22.0 and AMOS 22.0. Results As results of the analysis, It was subdivided into three clusters (such as group of male college students, man group of low perceived value and high degreed women group of low pragmatism). Conclusions The significant differences of the characteristics and perceived value appeared from each cluster. Cluster 1: A group of male college students, and the highest perceived value for Taekwondo performance. Cluster 2: A group of male, and a low perceived value for Taekwondo performance. Cluster 3: A group of high degreed women and a low pragmatism of perceived value. Therefore, a practical marketing strategy was needed for each groups.

Purpose This study has been conducted to explore the factors that ignite the mental toughness of Taekwondo players and to compare report ratios concerning the explored factors between training and competition. Methods An open-ended questionnaire conducted 123 Taekwondo players offered raw data that stemmed the from 379 training and 369 competition situation. The raw data was categorized by an inductive approach, and the report ratios of both general and specific domain mental toughness in training and competition were compared. Results The results of this categorization were as follows. First, the mental toughness ignition factors of Taekwondo players are commonly categorized as willing to goal, external pressure, reward expectation, challenge, and social support. Second, factors were prioritized into reward expectation, challenge, willing to goal, social support, and external pressure. Third, willing to goal and external pressure were often reported in training, while reward expectation and challenge were more often reported in a competition. Social support showed similar ratios in both settings. Conclusion This study is expected to offer interesting results in the context of the ignition of mental toughness, while being utilized as a fundamental database for the development of mental social support strategies the help Taekwondo players ignite their mental toughness in competition.



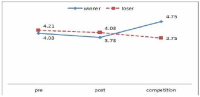
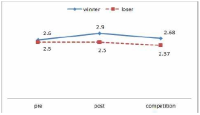
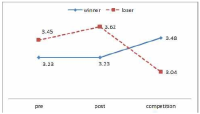
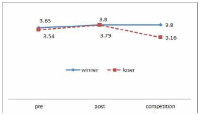
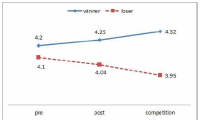
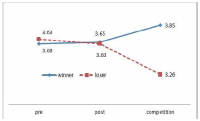
The purpose of this study was to confirm the differences between winner and loser groups of national team participated in the World Taekwondo Championships statistically and trends of psychological status according to applying mental coaching. In order to achieve the purpose it was the selection of 16 national members participated in the 2013 World Taekwondo Championships in Puebla. Data was selected by TOPS(test of performance strategy). The survey was conducted before and after applying the mental coaching and the game soon after. Data processing results were calculated utilizing Excel and SPSS 21.0 version. Based on the findings issue the conclusions were as follows. First, the psychological state of the winner and loser groups showed a different trend in the self-talk, emotion control, performed automatically, imagery, struggle, negative thinking, relaxation, condition factor. Winner group was shown maintenance or better trends of psychological state in the three times measurements on the other hand, loser group was shown decrease in the game soon after. Secondly, winner and loser groups are statistically significant differences in the psychological state of competition in self-talk, struggle, negative thinking, solving tension factors. In other words, The winner group had higher score in the four factors than loser group in the competition.

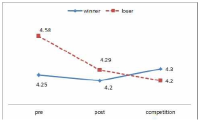
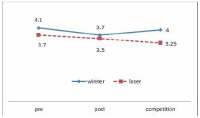
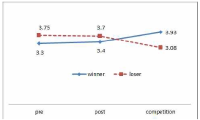
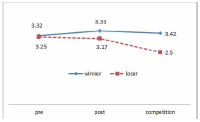
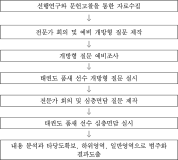
The purpose of this study was to develop and validity Competitive State Anxiety Scale for Taekwondo Form athlete(CSATF). The participants were composed of the 48 Taekwondo Form athlete to explore sub-factors of Competitive State Anxiety for Taekwondo Form athlete. The data were collected by an open-ended questionnaire and interview. The participants were composed of 257 national Taekwondo Form athlete to develop Competitive State Anxiety Scale for Taekwondo Form athlete. This 157 athlete data were used for items analysis, reliability analysis and exploratory factor analysis. And 100 athlete data were utilized for confirmatory analysis. Also convergent validity, discriminant validity, predictive validity latent mean analysis of CSATF were performed The results of this study were as follows. Firstly, the results revealed that the four general dimensions were identified such as cognitive anxiety, somatic anxiety, state of confidence, environmental anxiety. Secondly, CSATF comprised cognitive anxiety(5 item), somatic anxiety(5 item), state of confidence(5 item) and environmental anxiety(6 item). Thirdly, convergent validity, discriminant validity and predictive validity, the multi-group analysis according to gender examined validity of CSATF.

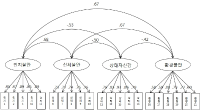
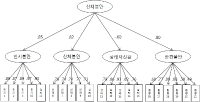
PURPOSE This study assessed elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness and developed reference standards for both their basic and specialized physical fitness. METHODS Data for analysis were collected from 870 athletes: from national teams, 123 elite Taekwondo athletes from the Performance Analysis and Assessment System (PAAS) administrator website (1999–2020); from regional sports centers, 731 collegiate and general division elite Taekwondo athletes (2015–2019); and from Y University, 16 elite Taekwondo athletes. Through measurement items’ selection and categorization, 20 physical fitness items were selected for the reference standards’ development, including 9 for basic fitness and 11 for specialized fitness. Taekwondo weight classes were divided into two: light + middle (fin, fly, bantam, feather) and middle + heavy (light, welter, middle, heavy). RESULTS Descriptive statistics for basic and specialized physical fitness items were categorized by gender and athletes’ fitness level. The reference standards’ development was aligned with existing standards, integrating the Cajori physical fitness 5-levels. It also introduced minimum physical fitness reference standards and target achievement reference standards for evaluating elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness. CONCLUSIONS The reference standards proposed here can serve as objective indicators in selection of national representative athletes and also provide foundational data to establish fitness goals and evaluate future elite athletes’ physical fitness.