
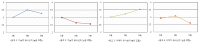
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of congruence type between sporting event and corporate sponsor as well as the effects of advertisement exposure frequencies (1, 3 or 5 times) on advertisement attitude and advertisement effectiveness, including brand attitude and advertisement wear-in and wear-out effects. Data (N=150) were collected using a convenience sampling method and 3-group random assignment. The collected data were analyzed by means of frequency analysis, reliability analysis based on factor rho coefficient, correlation analysis, one-way ANOVA, confirmatory factor analysis, and latent mean analysis. The results were as follows; firstly, in case of higher functional congruence condition, advertisement attitude was most positive in a 3-time exposure situation and it decreased as advertisement exposure frequency further increased. However, in the lower functional congruence situation, advertisement attitude was continuously decreased as advertisement exposure frequencies increased. Secondly, in the higher image similarity situation, advertisement attitude was increased as advertisement exposure frequencies increased. On the other hand, in the lower image congruence situation, advertisement attitude was decreased as advertisement exposure frequencies increased. Lastly, advertisement attitude, brand attitude, and wear-in effects were statistically higher in the high functional and image congruence situations than did in the low functional and image congruence situations.

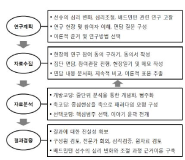
This study was purposed to explore psychological change and regulation process during badminton competition. The data were conducted using group interviews and participation observations who 18 K college badminton players. The data were analyzed using open, axial, and selective coding based on grounded theory method (Strauss & Corbin, 1998). The results were as follows: Open coding results, 89 concepts, 44 subcategories, and 18 categories emerged as psychological change and regulation process during badminton competitions. Axial coding results, the categories are showed structural relationships such as performance, score, psychological momentum, the importance of competition, court environment, physical condition, competition strategy, psychological preparation, past experience, outcome expectation, psychological disturbance, psychological skills, game situation-changing strategy, support-seeking strategy, significant others' behavior, the opponents' behavior, psychological resilience, and maintenance psychological disturbance. Selective coding results, core category of this study was revealed to maintain psychological homeostasis. Environmental context during badminton competitions causes specific situations and events that evoke psychological disturbance. In turn, a player seeks mental and behavioral strategies to maintain psychological homeostasis. There is psychological homeostasis mechanism during badminton competitions for peak performance. Development of proper interest for psychological homeostasis will be improved through this research approach in sport psychology.

PURPOSE This study investigated the effects of moderate-intensity continuous exercise (MICE) and high-intensity interval exercise (HIIE), performed postprandially, on blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lactate levels in men aged 40–50 with prediabetes and prehypertension. METHODS Twelve men with prediabetes and prehypertension were selected. After consuming a liquid meal, the participants participated in three trials: MICE, HIIE, and a non-exercise condition, with a one-week washout period between each trial. The trials were conducted in a counter-balanced manner to ensure equal energy expenditure across conditions. The intensity of the MICE trial was set at 70% of the heart rate reserve (HRR), whereas the HIIE trial alternated between 50% and 90% of HRR for 30 minutes. Blood glucose, blood pressure, and blood lactate levels were measured at various time points during each trial, and a two-way repeated-measures ANOVA was used for analysis. RESULTS 1) In the MICE trial, significant reductions were observed in blood glucose (at 15 and 30 minutes during exercise), systolic blood pressure (SBP) (at 50 minutes post-exercise), and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) (at 20, 40, 50, and 60 minutes post-exercise). 2) In the HIIE trial, significant reductions in blood glucose (at 15 and 30 minutes during exercise), SBP (at 40 minutes post-exercise), and DBP (at 40 minutes post-exercise) were observed. Blood lactate levels significantly increased. 3) When comparing the two exercise trials, blood glucose in the HIIE trials showed a recovery trend post-exercise, and blood lactate levels increased to a greater extent. CONCLUSIONS These findings suggest that both MICE and HIIE effectively lower blood glucose during exercise, but HIIE causes a more rapid post-exercise increase in blood glucose compared to MICE. In addition, MICE results in a smaller rise in blood lactate. Therefore, MICE is recommended for improving prediabetes and prehypertension. Future research should compare these effects in healthy individuals and examine long-term adaptations to repeated exercise.
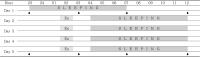
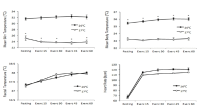
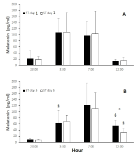
Whether a nocturnal exercise with concomitant increase of body temperature (Tb) would intensify circadian phase delay compare to exercise with a suppressed Tb increase was examined. Seven healthy men (20.57 ± 2.88 yrs, 174.43 ± 4.05 cm, 70.13 ± 6.07 kg, 10.74 ± 1.92% fat) participated in two tests. Each lasted 5-days. On the day of 1 of each test, subjects maintained habitual sleep time (23:00-07:00, 0.2 lux) in laboratory. From day 2 thru 5, they biked for 60 min at 55% of maximal capacity beginning at 01:30 (15 lux). Then they went to bed at 04:00 and woke at 12:00. During test, they exercised either at 26℃ with elevating Tb (ET) or at 17℃ with cooling devices for suppressing Tb (ST). Two tests were counter balanced and separated by 2 weeks. During exercise, rectal (Tre) and skin (Tsk) temperatures, and heart rate were continuously recorded. Body weight changes during exercise were measured. Urine volume and saliva sample were collected. Blood samples were taken at 23:00, 03:30, 07:00, and 12:00 on day 1 and 5 of tests and analyzed for melatonin. The average weight loss for 4 days of exercise in ET and ST was 0.62 ± 0.09 and 0.22 ± 0.07 kg, respectively (p<.001). Tre increased during exercise but not different between conditions. Tsk maintained at 32℃ in ET and 24℃ in ST (p<.001). Tb were higher in ET than ST during exercise (p<.05). The average total urine volume passed was 0.07 ± 0.07 in ET and 0.11 ± 0.07 liter in ST (p<.05). The melatonin concentration at day 1 was 23 ± 26, 107 ± 45, 98 ± 46, and 14 ± 5 in ET and 18 ± 10, 108 ± 65, 103 ± 75, and 14 ± 12 pg/ml in ST for each time period. At day 5, it was 9 ± 3, 64 ± 41, 122 ± 73, and 54.1 ± 17.8 in ET and 8 ± 1, 68 ± 21, 111 ± 52, and 32 ± 14 pg/ml in ST. Differences of melatonin between ET and ST at day 5 of 12:00 as well as between day 1 and 5 at 12:00 of both conditions were noticed (p<.05). Salivary cortisol and immunoglobulin-A were not different. A nocturnal exercise induced a circadian phase delay in both conditions. However, body temperature increase during exercise intensified the shift indicating the importance of thermal load during exercise for circadian shift.

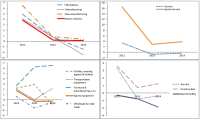
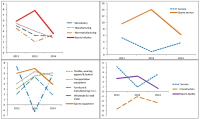
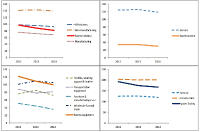
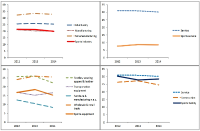
In this paper, we analyzed financial ratio of Sports Industry Enterprises in Korea from 2011 until 2014. We use Kis-Value data and extract 195 enterprise from it. And we compared the results with other industries which data were analyzed from the Bank of Korea. The results of the analysis are that the financial ratios of the sports industry is higher than other industries. This shows that the management conditions in sports industry are better than the other industries. In particular, among the sports industries, the management condition in sports service industry shows better states than other sports industries and other industries. This indicates that the sports service industry is a high value-added industry and growth rate of this industry is much faster than other industries. Growth rate of sales of Sports industry in 2014 was 0.1% whereas growth rate of sales of all industries was –1.5%. Also, growth rate of total assets of Sports industry in 2014 was 3.5% while growth rate of sales of all industries was 3.0%. So, growth ratio of the sports industry was higher than all industries. On the other hand, growth rate of tangible asset which represents the investment in fixed assets was 1.9%, which was lower than that of all industries 2.5%. Through operating income to sales, we can know the profitability of company from operating activities. Operating income to sales of sports industry in 2014 was 9.5% whereas operating income to sales of all industries was 4.3%. Especially sports service industry increased 24.6% in 2014. Income before income taxes to sales was 10.1%, which was higher than all industries 3.9%. In particular sports service industry was 28.3%. It shows that the sports service companies have issued a profit through strong corporate activities. Debt ratio of the sports industry in 2014 was 80.9% while it was 91.9% for all industries. Debt ratio of sports facilities industry was 166.9% that is higher than the average of all industries. But the debt ratio of the sports service industry was 29.9%, it can be seen considerably lower than the average of all industries. Total borrowings and bonds payable ratio of the sports industry was 19.8%, it can be seen lower than the 25.3 percent for all industries. Cash flow coverage ratio which represents the ability to afford the interest and debt to cash income. Sports industry rate was 25.4%. It was lower than the all industry's 62.7% and it indicates sports industry is financially not good. So, we know that sports service industry was financially not healthy. Business analysis results of sports industry of Korea appeared better than other industries. But business conditions are getting worse and, like any other industry. Thus, through the business analysis, we should prepare substantiality of management. And we should plan productivity improvement and business strategies for the changing business environment.




PURPOSE This study examined the biomechanical differences in running shoes with two midsole materials, ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) and polyether block amide (PEBA), and carbon fiber plate insertion. METHODS Ten recreational runners participated in the study and performed running trials on a 12m runway at a controlled speed of 3.89 m/s ± 5%. Biomechanical data were obtained for time-continuous variables of the metatarsophalangeal (MTP) joint (angle, moment, and power), as well as for discrete variables (push-off time, peak vertical impact force, peak anterior propulsion force, and timing of joint power transition). Data were analyzed using statistical parametric mapping for continuous data and the Wilcoxon signed-rank test for discrete variables (α = .05). RESULTS Compared with no-plate conditions, the EVA sole with plate significantly reduced push-off time, MTP joint range of motion, positive joint power, and peak anterior propulsion force, with an earlier timing of joint power transition (p < .05). In contrast, the PEBA sole with plate decreased MTP joint range of motion but increased plantar flexion moment, negative joint power, and push-off time (p < .05). Furthermore, under plate-inserted conditions, PEBA significantly increased plantar flexion moment, negative joint power, and push-off time, as well as exhibited a delayed timing of joint power transition compared with EVA (p < .05). CONCLUSIONS The interaction between midsole material and plate insertion causes complex variations in MTP joint energy management. Specifically, EVA shoes with a plate may facilitate rapid roll-off and promote swift turnover, thereby enhancing acceleration. In contrast, PEBA shoes with a plate may promote prolonged energy absorption, which could potentially reduce joint fatigue during long-distance running.
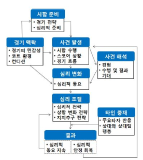
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop the theory of child abuse of children with disabilities in Adapted Physical Education (APE). METHODS A grounded theory study was conducted based on a constructivist approach. Data were collected via in-depth interviews. Participants were 20 instructors selected based on theoretical sampling. The collected data were analyzed in the order of open coding, axial coding, and selective coding. RESULTS First, the direct causal conditions of abuse of children with disabilities in APE were the instructors’ and guardians’ distorted perception towards the disabled children along with the individual vulnerability of children with developmental disabilities. Second, the contextual conditions that form the background of the abuse of children with disabilities in APE included the burden of the instructor due to the unjust demands of the guardian of the child, the growth background of the instructor, and the repressive atmosphere of APE. Third, abuse of children with disabilities can be divided into three types: ‘active abuse’ based on the instructor’s distorted viewpoint of the child with a developmental disability, ‘passive abuse’ due to the unjust demands of the guardian, and ‘passive abuse’ due to the structural problems in the APE field. Fourth, the abuse of children with disabilities in APE, which can be distinguished by different characteristics, affects the instructor’s inner conflict and self-reflection. CONCLUSIONS This study approached the phenomenon of abuse of children with disabilities in Korean adapted physical education as a grounded theory, and the theory generated is expected to contribute to the establishment of strategies necessary to design adapted physical education in keeping with human rights.
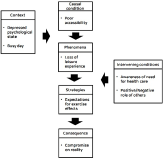
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the alienation and the overcoming process of the physical activity participation of people with Adventitious Visual Impairment(AVI) Methods 21 Adults with AVI were recruited and one on one semi-structured interview was conducted. Ground theory was used to analyze the data. Member check, peer debriefing was conducted to enhance the trustworthiness of this study. Results As a result, a total of 203 concepts were derived. This consisted of 21 subcategories and the common themes of the subcategories were categorized into nine categories. Specific results are as follows. First, the physical activity of people with AVI was directly affected by the sports facilities, physical activity programs, and professional instructor. This causal condition resulted in the loss of leisure experience in the context of the busy daily life and the depressed psychological state. Second, due to the perceived need of health care and the positive involvement of others, people with AVI came to expect the effect of exercise. Third, people with AVI participated in physical activity again as a tool to achieve the purpose of health improvement. This type of physical activity has a limitation that it can not guarantee the continuity of physical activity due to the limitation that it does not contain autonomy and interest of people with AVI. Conclusions Based on these results, the following suggestions were made. First, it is necessary to improve the environment for ensuring participation in physical activity of people with AVI. Moreover education and promotion of the effects and values of the exercise should be carried out for people with AVI and their guardians. Second, it is necessary to diversify physical activity types and reconstruct existing exercise programs.


Purpose This study confirmed the historical significance of the First World War US Combat Strength Training Fitness System for contributing in the ROK military sports development. Methods This research method is literature analysis to be focused by the previous US Army Field Manuals. Results Concretely, The meaning of US Army fitness training was divided into four stages. First, this study confirmed the actual condition of the US Army fitness before First World War. Since 1916, US Army has developed a group physical training program applied the items suitable for the war and has systematically reflected the program in the recruitment training. Second, this study confirmed the process of operating military fitness program during the First World War. US Army physical fitness program provided an effective method to suit soldier fitness for war. Third, this study observed the fitness training changes of US Army after the First World War. At that time, US Army focused on maintaining health and basic physical strength for civilians and reserve forces, but US Army ran parallel with basal physical fitness and combat physical fitness after the Korean War. Fourth, this study compared military strength training between First World War and current US Army. Since First World War, the training of US Army has been developed around doctrine and manuals to be maintained the consistency of the system. In conclusion, US Army physical training system of First World War meant to be provided the basis of current military physical education and physical training. In other words, current fitness training is not dogmatic but has evolved, and it accommodated the basics of soldier physical training course from the past.








Recently, there have been diverse types of physical activities supported by government policy in S. Korea. However, these activities may not be effective if they do not reach to moderate to vigorous level. This study designed school physical education system based on SPARK program, which include traditional physical education, sports club based physical activity, after school physical activity, and Saturday physical activity, to evaluate its effectiveness associated with physical fitness and empirical meanings of physical activity. This study employed a mixed method research paradigm for better understanding. Among various mixed method paradigm stances, this study employed "blending strategy" for complementary analysis. First of all, the effectiveness in health condition was evaluated by quantitative data. Specifically, physical fitness and lifestyle were analyzed by Helmas, IPAQ, and Accelerometer respectively. Second, empirical meanings of physical activity were analyzed by both Photovoice and in-depth interview which are qualitative research method. The result of this study first showed that a specially designed school physical activity program based on the SPARK contributed to improve students' physical fitness and lifestyle as well, however, there were important differences between male and female students. Second, physical achievement, alteration of spatiotemporal meaning, and change of societal relationship emerged as important themes. Further, these themes showed that they played an important role to maintain students' motivation in physical activity and consequently physical activity promotion was invigorated in school. Based on these results, we synthesized investment factors and process factors and outcome factors respectively. Finally, we suggested alternative teaching methods and suggestions for following research to overcome gender issues.









