
The purpose of this study was to verify the effect on elementary school students in the exercise start stage by performing a sport psychological skill training to improvement of psychological skill and life skill. Participants were eight elementary school boys volleyball player. The program consisted of psychological skills and life skills in educational counseling model of Visek et al(2009). It was conducted 40-50 minutes a session in total for 22 sessions. Data was collected through a psychological test, worksheet and participant observation, in-depth interviews. The collected data was analyzed to verify difference by paird t-test after pre-middle-post test and to extract meaningful data category. Quantity analysis showed that a result of sport psychological skill test proved a significant difference in willingness to overcome, confidence, concentration, anxiety regulation. Life skill test were no significant differences in all factors. However, the rise of scores was observed on result of the pre-middle paired t-test of life skill during season. Quality analysis showed possibility of goal setting, concentration on the routine, decrease of competitive anxiety, increase of positive thinking, self-understanding and understanding of others, promotion of communication among team members. This sport psychology skill training had a significant effect on the psychological skills of elementary players change. But it seems to be necessary life skills in a more through review of the information.



Purpose The purpose of this studied to improve athletes’ performance through sports psychological skills training and counseling of a male canoe player in high school. Methods One male high school athlete in J area was interviewed for sports psychological skills training and counseling, and interviewed athletes and coaches diagnosed the potential psychological problems of athletes. Through this process, the athlete gained the ability to control anxiety about the game and strengthened the attention-focused ability to increase his confidence and set a goal for improving concentration. For effective training, sports psychological counselors, athletes, and coaches met once a week to create a routine. and participated in direct training on a boat with the coach every week. Sports psychological skills, anxiety about competition, and self-management of athletes were measured before and after to confirm the effectiveness of training of athletes' psychological skills. Results As a result, athletes' psychological skills and anxiety decreased, their confidence increased, and their concentration, which was diagnosed as an urgent problem of athletes, improved. Conclusions psychological skills of athletes, psychological shortcomings of players were reinforced, thus enhancing the athletes' performance. This suggests the effectiveness and necessity of training in sports psychological skills. It is hoped that continued support will serve as an opportunity to diagnose potential psychological problems of student athletes and apply them to training to contribute to improving their performance.
PURPOSE This study compares the effects of video group and metaverse group counseling for student athletes to analyze differences in immersion, sychological skills learning effects, and each approach’s participation experiences. METHODS Twenty-four high school archery students were divided into three groups: a metaverse experimental, a video comparison, and a control group. For the experimental and comparative groups, 10 non-face-to-face psychological skills training sessions were conducted. With the control group, results were compared and analyzed by measuring psychological skills and social presence pre- and post-training. Additionally, analysis of the qualitative effects of psychological skills training was performed. RESULTS The psychological skill test’s quantitative analysis of the video comparison group showed a more significant effect in anxiety control factors than the metaverse experimental and the control groups. Moreover, in the social presence test, both the metaverse and the video groups showed significant differences in social presence and satisfaction; furthermore, Scheff post-verification results showed that the two environments’ satisfaction was significantly higher than that of the control group. Qualitative analysis confirmed that the metaverse and video groups experienced psychological, technical, and relational changes in common. CONCLUSIONS Although the metaverse group using avatars was likely to increase immersion, both the video and the metaverse groups were effective in psychological skills training, suggesting that the training effect may vary depending on the non- face-to-face environment’s stability and participation method. Future studies should examine effects of applying the metaverse platform to sports psychological skills training and various psychological support activities by solving the metaverse environment’s technical limitations.

Sport Imagery Questionnaire of Hall et al.(1998) was developed to investigate the imagery type of athletes objectively. The purpose of this research is to verify validity and reliability of Korean SIQ by using Rasch Model, in order to make up for complement drawback of SIQ which was developed only using factorial analysis. This research conducted first and second questionnaire survey. Second survey was conducted targeting different study participants from those of first survey. The participants of first survey was 265 athletes of Chungcheong Province, and the participants of second survey was 169 athletes of Chungcheong Province. SPSS 21, Winstep 3.62, and AMOS 18 was used for date analysis. The result of Rasch Model verification for the data of first survey revealed that 8 items of SIQ were unfit. Thus, 5 factors and 22 items were determined. 7 point Likert scale was revealed to be a good fit. The result of Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data of second survey revealed that Construct Validity of 5 factors and 22 items was valid and reliability was high by recording Cronbach’α value .954. External Validity was revealed to be high by showing that correlation between sport confidence and MG-M imagery was high.

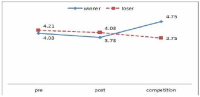
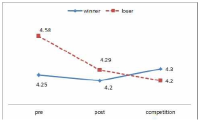
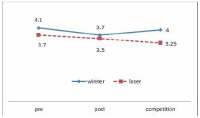
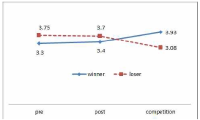
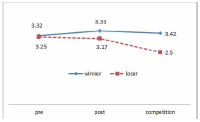
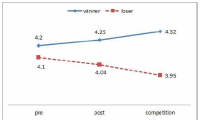
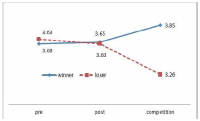
The purpose of this study was to confirm the differences between winner and loser groups of national team participated in the World Taekwondo Championships statistically and trends of psychological status according to applying mental coaching. In order to achieve the purpose it was the selection of 16 national members participated in the 2013 World Taekwondo Championships in Puebla. Data was selected by TOPS(test of performance strategy). The survey was conducted before and after applying the mental coaching and the game soon after. Data processing results were calculated utilizing Excel and SPSS 21.0 version. Based on the findings issue the conclusions were as follows. First, the psychological state of the winner and loser groups showed a different trend in the self-talk, emotion control, performed automatically, imagery, struggle, negative thinking, relaxation, condition factor. Winner group was shown maintenance or better trends of psychological state in the three times measurements on the other hand, loser group was shown decrease in the game soon after. Secondly, winner and loser groups are statistically significant differences in the psychological state of competition in self-talk, struggle, negative thinking, solving tension factors. In other words, The winner group had higher score in the four factors than loser group in the competition.

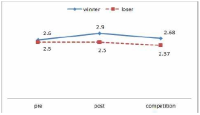
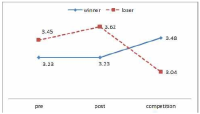
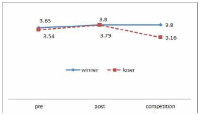
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to develop a period-based psychological support model for athletes and to establish a system after deducing a psychological support model foreach time period. METHODS In this study, 5 psychological support practitioners were selected as research participants to explore requirements and 4 athletes were selected for the field application of the psychological support model. The requirements for developing the psychological support model were collected through in-depth interviews by the psychological support practitioners. Literature reviews and interviews were conducted to develop the psychological support model. RESULTS The period-based psychological support model consists of orientation, problem exploration, problem clarification, intervention, effect evaluation, and termination. The period of psychological support for athletes was divided into the following: A single-session psychological support, brief psychological support, and seasonal psychological support. The system of period-based psychological support model for athletes is a flow chart that applies the period-based psychological support model from the initiation till the termination of psychological support. CONCLUSIONS The phase of the psychological support model is expected to contribute to the enhancement of the effectiveness of psychological support by establishing a psychological support system for athletes.
The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.
Purpose : The purpose of this study was to investigate coaching information with which coaches provided players during badminton competition. Methods : To this end, we generated an open-ended questions and presented it to 88 high school athletes registered in the Badminton Korea Association. The survey was conducted during a tournament and immediately after the tournament to collect the data. The collected data were categorized through inductive content analysis. Results : As a result of this study, a total of 480 raw data points collected through the open-ended survey were categorized into four general areas: psychological information, technical information, tactical information, and game operation information. Specifically, psychological information was divided into six subdivisions: concentration, confidence, relaxation/stabilization, mental toughness, play thought, and passion; technical information was broken into four subdivisions: strokes, footwork, swing and posture, and position preparation; tactical information had four subdivisions: coping to opponents, play changes, rotation, and manipulation of opponents; and, game operation information was divided into two subdivisions: taking the lead in a game and changing atmosphere. Conclusions : In other words, in badminton competition, the coaches strengthened psychological skills that promote psychological stability to attain the athletes’ peak performance and modified the athletes’ motion into the action necessary for achieving accurate techniques. Furthermore, they provided a variety of coaching information so that the athletes will respond appropriately to their opponents’ play, take the lead in games and induce a positive mood. The psychological, technical, tactical and game operation information offered by badminton coaches are the main factors influencing the performance of badminton players and suggest a need for the proper management and control of the coaches as well as athletes for the peak performance.
PURPOSE This study aimed to extract football coaches’ categories of performance evaluation factors (PEF) and examine the reflective characteristics of the football coaches’ player and casting judgments. METHODS PEF were extracted through an open-ended questionnaire and categorization from 80 AFC C or higher football coaches. Reflection was calculated in player and casting judgments through an analytic hierarchy process. The difference between the football coaches’ player and casting judgments was examined using SPSS 21.0. RESULTS First, the PEF of football coaches were categorized into four general categories: physical intelligence, psychological intelligence, growth potential, and competition intelligence. Second, the importance of football coaches’ player judgments were reflected by the PEF as football intelligence, situation judgment, football talent, tactical understanding, tactical operation, etc. The importance of the casting judgment were reflected by the PEF as tactical understanding, mediative skills, fitness, tactical operation, situation judgment, etc. Third, a statistically significant difference was noted between player and casting judgments. Football coaches tended to value growth potential and talent as sub-factors in the player evaluations. Football coaches’ PEF were aligned with the importance of player and casting judgments in psychological and competition intelligence as sub-factors such as skills, physical, attitude, passion, etc., but differed from physical intelligence and growth potential as sub-factors including mediative skills, physical, football talent, and tactical understanding. CONCLUSIONS In the football coaches’ player evaluations, the idealistic principle centered on growth potential. However, in the casting evaluation, the realistic principle centered on victory takes effect.
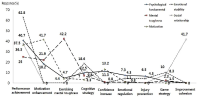
This study aimed to explore the psychological factors affecting sports performance and their purposes as perceived by adolescent athletes. Study data were collected by conducting an open-ended survey with 232 student athletes from adolescent athletes in S city. The collected data were categorized using content analysis, which was conducted twice to explore the psychological factors affecting sports performance and their purposes. From 537 answers, 30 performance-affecting psychological factors—including confidence, endurance, effort/dedication, optimal tension, and social support—were identified, and they were classified into five categories: psychological fundamental, mental toughness, motivation, emotional stability, and social relationships. From 588 answers, the purposes of the psychological factors were identified, including performance achievement, motivation enhancement, demonstrating mental toughness, cognitive strategy, confidence increase, emotional regulation, injury prevention, game strategy, and reinforcement cohesion. These performance-affecting psychological factors and their purposes may serve as a reference to understand how secondary school students perceive the relationships among various psychological factors and the relationship between the psychological factors and performance. This study is expected to inform goal setting and content organization in psychological skills training.
