This study was to identify the perception on retirement for professional soccer players as a basic study for the development of career transition program, Professional soccer K-League(K-League Classic, K-League Challenge), N-League(Club League), K3-League(Challenger League) league players registered in 2013 were selected as a population. Structured questionnaire surveys were utilized for the research, total of 1000 questionnaires(250 per league) were distributed and gathered. Final sample of 548 questionnaires were analyzed excluding people which do not respond properly. SPSS was used to identify the characteristics of the responder in frequency analysis. One-way ANOVA was used to find the difference in retiring causes among the leagues, Pearson Correlation analysis was used to examine the correlations among the variables. Multiple regression analysis was used to find the effect of economic and psychological preparation on plans after retirement. The results were as follows. First, among the causes of retirement, 'contract suspended', 'seek other life', 'family issues such as marriage' showed the difference in perception of retirement according to the leagues. Second, psychological preparation was more focused than economic preparation to prepare for retirement planning among players, respectively.
This study aims to provide an in-depth study on K-League players' perception and preparation process on retirement. In order to achieve the purpose, data collection was conducted in two major ways; face-to-face interviews and questionnaires from 10 currently working players. The result of study is based on inductive analysis. First of all, sense of expectation and concern, limited scope of secondary job, and necessity for career education are appeared in terms of players' perception. Second, preparation process on retirement is concluded in two categories; personal development activities(non-professional and inefficiency) and financial preparation. Thirdly, difficulties in the procedures of retirement preparation are categorized into ‘limited time and isolated lifestyle caused by staying in club house ’ and ‘lack of educational programs regarding retirement’. Depending on the results of this study, opportunities confined to retired players are supposed to be enlarged to currently working players. In addition, football club and K-League federation need to support players not only to enhance performance but also to prepare retirement.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the differences between the three simple control models of Hayes (2012) and to determine whether there were Moderating Effects depending on the level of self-esteem, willpower and belief that are psychological factors in the relationship between athlete's retirement and Athlete's period. Methods To achieve this objective, a total of 259 retirees were collected from data on retirement and psychological factors. The data processing method presented the reliability and feasibility of the measuring instrument through technical statistics, frequency analysis, confirmation factor analysis, and reliability analysis. In addition, we conducted a hierarchical regression analysis using the PROCESS command statement in IBM 20 to examine the regulatory effects. Results The results of the study are as follows: The first was the significant model of Hayes (2012)'s three simple control models. It is up to the researcher to choose which model to choose, but when selecting the model, the justification of the variables must be established on the basis of theoretical basis, and the reliability of the variables must be put in to produce reliable and reasonable results. The second was to verify that the relationship between the retirement factor(10) and the Athlete's period has an adjustment effect based on self-esteem, willpower and belief. Among the psychological factors, the Moderating Effects was greatest in the influence of belief on the Athletes' period, and the more reasons for retirement, the longer the Athletes' period than the weaker. The combined mental strength of all three psychological factors combined shows that the combined effect of control also significantly increases the player's ability to survive by combining with the retirement factor. In particular, sportsmanship has resulted in a better mix of retirement factors than the sense of Self-esteem and will, resulting in a longer increase in the capacity. Conclusions Therefore, players who long for a player always keep their dreams of becoming a big star in mind, and ask me to always keep the belief in hope that I will enjoy my career for a long time.






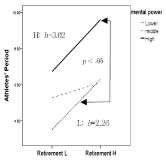
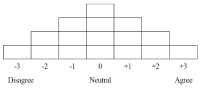
Purpose The purpose of this study is to classify the subjectivity of re-socialization barriers among retired footballers. Methods Q methodology was conducted to identify constraint factors contributing to social adjustment and reemployment perceived by 28 P-samples. Results Re-socialization barriers were classified as ‘Type I: Internal-constraint’, ‘Type II: External-constraint’, ‘Type III: Internal-conflict’, and ‘Type IV: External-conflict’. These types provided a variety of academic and practical discussions, depending on where the barriers are taken from (internal and external) and what depends on them (objective conditions and subjective ideas). Conclusions This study focused on the subjective structure of retired footballers and complemented traditional methodology focusing on hypothesis testing. Therefore, each type found in this study provides useful information not only in follow-up study on retired athletes, but also in policy-making decision such as support projects.


PURPOSE This study developed and applied a group counseling program for university athletes’ career development. METHODS Following Kim’s (2002) procedure for developing group counseling, this program was based on social cognitive career theory and finalized by using two preliminary studies and expert validation evaluation. Afterward, Taekwondo players from University A in Chungcheongnam-do and University B in Seoul were assigned to experimental and control groups, respectively, and then a nonequivalent control group design was conducted. The experimental group was provided with a six-step career group counseling program, including introduction, understanding personal and distal context, enhancing self-efficacy and outcome expectations, developing career interest, deciding on a career, and closing, for ten 45-minute sessions, twice a week. RESULTS First, results of two-way repeated measures ANOVA showed statistically significant changes in career decision self-efficacy (self-appraisal, occupational information, goal selection, planning, and problem-solving) and career attitude maturity (determination, certainty, and independence). Second, analysis of the outcome assessment by session showed the following positive results: consideration about the future after sports retirement, self-understanding, identification of jobs that fit aptitude, improvement of self-efficacy, having a positive mindset when switching careers, confidence in one’s preferred career, exploration into solutions to career barriers, understanding of preferred career, setting specific career goals, and deeper understanding of careers. CONCLUSIONS In sum, these findings indicate that the career counseling program had a positive effect on university athletes’ career development. We hope this study will serve as a catalyst to expand the discussion on retirement from sports and career development.
Purpose This study seeks to explore the process where drop-out elite athletes collect their life skills obtained during their sports career and transfer them to their daily lives. Methods An open-ended questionnaire survey was conducted on a total of ninety retired elite athletes and the responses were analyzed. Based on the results of inductive analysis, five subjects were selected for a follow-up in-depth interview. The responses to the open-ended questionnaire were analyzed by the inductive content analysis method and the results from in-depth interviews by the deductive content analysis method. Results A total of 478 life skills were collected from the drop-out elite athletes and structuralized into four general categories: psychological skill, social skill, self-management skill, and goal-setting skill. The results of this study have revealed that life skills positively transferred to their future courses of lives and daily lives. Conclusion It is believed that the results of this study will be helpful to understanding the concept of sports life skills, studying the possibility of transfer, and provide the basic data for helping drop-out elite athletes with re-socialization and positive adaptation.

Purpose This study aimed to investigate the psychological capitals created by the experience of winning an Olympic medal by using the photovoice method. Methods Data were collected on the way the participants-five Bronze medalists in the Women's volleyball in 1976 Montreal Olympics-take and send photographs. The interviews were conducted by phone based on the collected data. The photographs were placed into the parent category after conducting inductive content analysis, and their validity was confirmed from the expert meetings. Results The results of the study, indicate that the participants have earned psychological capitals such as my matter volleyball for diligence, the gift of a Bronze medal to gratitude, the source of achievement, challenges, and key of relationship tenderness from the experience of winning an Olympic medal. Conclusion In this regard, this study provides an opportunity to extend the study on the lives of retired athletes who won an Olympic medal to various perspectives, as well as the impact of sports experience on everyday life.










Purpose The purpose of this study is to look into the life of MTB college athletes before and after their college entrances through long-term longitudinal narrative inquiry and investigate how the career exploration after graduation is conducted in a contextual way. Methods For this study, four MTB college athletes who entered the university as specialists are selected as research participants, and their life and career are examined through a long-term longitudinal narrative inquiry. Results As a result, the life and career of MTB college athlete appear as follows. First, MTB college athletes entered MTB because of 'self - will' or 'influence of family and acquaintances' and the motivation is 'extension of hobbies', 'college entrance', etc. Second, the MTB college athletes' training and goals are set in the 'college entrance examination', which means the entrance to higher college. Third, MTB college athletes' college life is closely related to 'management and support system for college athletes', and the career search for them is based on 'the prospect as a player' and 'professional prospect of MTB athletes’. However, MTB college athletes showed their plan B to prepare for their uneasy future or to retire. Conclusions In the end, the MTB college athletes came to think about life and career on the narrow stage of unpopular sports and was seen coming down from the narrow stage of unpopular sports. Based on these results, this study presents critical discussions about their life and career of MTB college athletes and seeks implications for the school elite sports in Korea.

PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to section the stages of performance development based on the track and field athletes' performance records, derive the performance development span, which was a continuum of the development stages, and extract the psychological experience of the performance development span. METHODS In this study, 56 retired track and field athletes were provided with competition records, and 10 athletes participated in in-depth interviews. With the stage of performance development partitioned using long and short-term moving averages and regression slope in PRR, a continuous of performance development span was derived. To extract psychological experiences in the performance development span, a subject analysis was conducted after an in-depth interview. RESULTS First, the track and field athletes' performance development stage calculated short and long-term moving averages in the PRR. Based on the average difference in the regression slope of the initial 20% CPR in which the long-term moving average was not calculated, it was divided into beginning, rising, peak, and decline periods. Second, the performance development span was a continuum of the stage was of performance development, and the beginning period was 0 < PRR ≤ 7, it was a time when the competition record rises sharply. The rising period was 7 < PRR ≤ 60, which was a virtuous cycle time of growth athlete. The peak period was 60 < PRR ≤ 74, which was a time when the peak record was maintained. The decline period was 74 < PRR ≤ 100, which was a time when the competition record was downward. Third, throughout the performance development span physical intelligence of track and field athletes was based on their natural physical superiority, the technical skills rises and remains at its peak and then enters a downward trend. Competitional Intelligence aims to become personalization as it matures gradually while its competition management capability and game knowledge are immature. Psychological intelligence overcomes the initial psychological atrophy to form confidence, and after experiencing psychological burden at the peak, confidence decreases. In the environmental context, the competition record rises in the early stages, continues to rise, peaks, and enters a downward trend. CONCLUSIONS Track and field athletes' performance development span was implemented as a continuum of beginning, rising, peak, and decline periods, and the psychological experience of the performance development span formed a span of physical intelligence, competitional intelligence, psychological intelligence, and environmental context.