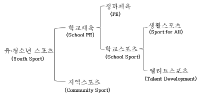
Purpose and Methods The purpose of this study is to clarify the concepts of ‘youth sport policy’ and policy areas as an alternative to school physical education concept and to provide a core conceptual framework for the development and implementation of youth sports policy in the future. Results The notion of youth sport policy is a process of seeking rational decision-making and optimal alternatives to solve the social problems associated with sports participation of youth in elementary school(aged 6 years) to high school(aged 18 years). The concept of 'youth sport' can reflect modern culture rather than 'school physical education' and it can be seen as more future oriented for lifelong participation in sports. The areas of youth sport policy are classified into physical education, school sport, and community sport. Physical education refer to the physical education classes operated by the Ministry of Education, and the school sport refers to the sports activities that take place throughout the school. Community sport is sports activities that are carried out outside the school by the choice of youth, which is the area where cooperation between the public sector and the private sector is needed. Conclusion In conclusion, healthy and active life for youth is required to establish cooperative governance of related organizations in order to ensure proper linkage between youth sport policy areas. Through this, it is necessary to solve the social problems of youth and promote their lifelong enjoyment of sport more consistently, efficiently and effectively.

The purpose of the study is to find the impact of social and economic factors in physical activity of children and youth. This study utilized the data from 4th Korean Children and Youth Panel Study(KCYPS), and the analysis were carried out based on the starting sample of 2,009 from ‘the elementary 4 panel’ and 1,978 from the ‘middle school 1 panel’ and 1,984 from the ‘high school 1 panel’, 5,971 full data were used in the final analysis. Data were processed using hierarchical regression analysis and it was statistically validated at the significance level of 0.05. First, Pearson r and Spearman ρ showed that all variables are statistically significant correlations. Second, among the first factors of personal and family characteristics, household income level(B=.113), family composition(B=-.049) and parental education (B=.060) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, parental education (B=.027) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Third, among the second factors of community-level characteristics, Gini coefficient (B=-.810), wealth concentrating (B=.120) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, the Gini coefficient (B=-0.315) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Additional factors that determine the coefficient of variation in the level 2 were found to be 0.623 and 0.001 respectively. Therefore, second factors of community-level characteristics are added such as Gini coefficient, wealth concentrating were explained to children and youth exercise time during physical activity 62.3%(p<.01) and subjective evaluation of physical education in grades 0.1%(p<.01). predictive power to
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a model for life skills transfer in sport. METHODS A literature review of research on life skills transfer was conducted. The prior representative studies on sport life skills and transfer models were selected and discussed to improve the validity of this study. RESULTS First, based on the basic psychological needs of the internalization and generalization of life skills, the model for life skills transfer should consider the influence of the explicit and implicit climate and environment. Furthermore, access to cognitive processes is required based on the conceptualization and integration of transfer. Second, the concept of a transfer was defined, and key issues of the cognitive processes that support the connection between the sport domain and out of the sport domain were discussed. Third, the model for life skills transfer in sport was presented. In this model, life skills transfer occur through sport context, cognitive process, promoting factors, and out of sport context. CONCLUSIONS Since the 2000s, research on life skills and transfer in sport has developed quantitatively based on positive youth development theory. Unfortunately, research on this area in South Korea is very insufficient. This study suggests a model for life skills transfer in sport based on an extensive and systematic analysis of the prior research, and this model can be used for future research.
PURPOSE Sport pedagogy (SP) has established itself as a subdiscipline in Human Movement Studies since the 1970s. It has become an academic labyrinth as a result of its rapid flourishing. Most researchers are extremely confused about this disorderly research complex. This study aimed to evaluate the characteristics of SP in stages in the western (mostly English speaking) countries. METHODS Analysis of literature published in English from 1990 to 2022. RESULTS The developmental versions were divided as follows: SP1.0 is positivistic in nature, SP2.0 is multi-paradigmatic as it includes all paradigms, and SP3.0 (current version). Many academic journals have been launched, and a variety of books on divergent topics are being published. Currently, research has exploded. In SP3.0, research performed by British scholars are notable in terms of number and quality, overpowering those by scholars in the USA and other countries. Youth sport and sport coaching are regarded as new legitimate areas. Additionally, signs for SP4.0 have been indicated. CONCLUSIONS In order to find way outs in the SP labyrinth, it is necessary to recognize the current research trends in international SP.
Purpose Incidence and prevalence of Korean teenager cheerleading injuries were surveyed. Methods A total of 769 junior cheerleaders who participated in National Sport Cheerleading Competitions responded to a questionnaire, and 435 reported experiences of injuries. Results Risk factors for injury included older age (p<0.001), increased experience (p<0.001), and higher BMI (p<0.05). The most frequent injury occurred at wrist, ankle, knee, shoulder and waist. And the most responded types of injury were muscular pain and contusion. Cheerleading experience affected on injury prevalence. They were injured when they perform Elevator (<0.5 yrs), Cradle (0.5-1 yrs), Cradle and Basket toss (1-2 yrs), Cradle and Pyramid (2-3 yrs). These techniques involved in bodily movements of going up and cradle. About 56% of injury was treated at home or not treated at all, and 60% of injury was either self-treated or not intervened. And only 32% of cheerleaders practiced on a formal mattress. Conclusion Safety measures for these youth cheerleaders are necessary and guidelines for securing safety and preventing and treating injuries for these population are urgent.
PURPOSE This study presents policy proposals based on literature review and document analysis in relation to sport concussion. METHODS Online documents were collected from sports organizations of the United States, the United Kingdom, and South Korea that either supervise sports concussion management policies or govern specific sports at different levels. RESULTS The results and implications of the study were as follows. First, safety education on sports concussion should be strengthened quantitatively and qualitatively, be required by all sports stakeholders, and will need to be executed by utilizing new technology platforms. Second, sports governing bodies must present a concussion safety policy tailored to each sport by distinguishing between youth and professional sports. Finally, discussions regarding the legalization of domestic sports concussion safety policies should take place in a timely manner. CONCLUSIONS These precautionary approaches would contribute to raising awareness on concussions in sports and help build a safer environment for sports.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the sport 5C scale of the Korean version. Methods The participants were 772 high school students from 17 to 19 who participated in sport regularly. The validation of Sport K-5C followed a three-step validation procedure through substantive stage, structural stage, and external stage. Results First, In the substantive stage, Sport K-5C consisted of 50 items with 5 factors. Second, in the structural stage, although Sport K-5C was explored as 24 items with 4 factors by EFA, but as a result of CFA, Sport K-5C was confirmed as 24 items with 5 factors. Third, the external stage provided additional validity through correlations of tests with other questionnaires which are similar concept and opposite concept, and group differentiation. Conclusions Sport K-5C is composed of 5 factors and 24 items. The factors are Caring, Character, Confidence, Competence, Connection. This scale can be used to provide an objective evaluation of positive development of youth in sport and physical education context.

The purpose of this study was to examine the current status of school sport club(SSC) participation and to explore relationship between school sport participation and positive youth development. In order to do this, a survey was conducted with 403 elementary, middle, and high school teachers who are currently taking charge of SSCs, and also individual interviews were conducted with 22 students. In addition, the youths' developmental asset questionnaire was administered with 412 middle school students. The survey results from 403 teachers showed that SSCs have potential to contribute to positive youth development because teachers are placing an emphasis on character development as well as physical and social development through SSC activities. In addition, participants who regularly participate in physical activities had higher internal and external developmental assets than non-participants or irregular participants. Specifically, students participated in SSC more than twice a week had higher internal and external assets than students participate once a week. In addition, participants who engage more than one hour per session had higher internal and external assets except constructive use of time and social competence. Discussion and implications for organizing SSCs to provide developmental contexts and contents for positive youth development were provided.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to apply a life skills program to student-athletes and statistically verify the changes in life skills of the experimental and control group. METHODS Participants were 34 high school Taekwondo athletes (Mage=17.71). They were divided into 18 in the experimental group and 16 in the control group. For eight weeks, the experimental group participated in the life skills program after training and the control group participated in only training as usual. Data were collected by using Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA), and the participants of two groups filled out the LSSSA before and after the program application. The collected data were analyzed by using repeated measure analysis of variance (ANOVA), and partial η2 (eta squared) was calculated to present the effect size. RESULTS The interaction between time and group was statistically significant in goal setting, coping with stress, positive thinking, and managing emotion among sub-factors of life skills. Partial η2 was interpreted as having a large effect size as it revealed the range of .22 to .51. Therefore, comparing before and after participating in the program, the life skills score of the experimental group among the two groups was significantly improved. CONCLUSIONS Student-athletes who participated in the program experienced positive changes in life skills than those who did not participate in the program.
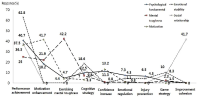
This study aimed to explore the psychological factors affecting sports performance and their purposes as perceived by adolescent athletes. Study data were collected by conducting an open-ended survey with 232 student athletes from adolescent athletes in S city. The collected data were categorized using content analysis, which was conducted twice to explore the psychological factors affecting sports performance and their purposes. From 537 answers, 30 performance-affecting psychological factors—including confidence, endurance, effort/dedication, optimal tension, and social support—were identified, and they were classified into five categories: psychological fundamental, mental toughness, motivation, emotional stability, and social relationships. From 588 answers, the purposes of the psychological factors were identified, including performance achievement, motivation enhancement, demonstrating mental toughness, cognitive strategy, confidence increase, emotional regulation, injury prevention, game strategy, and reinforcement cohesion. These performance-affecting psychological factors and their purposes may serve as a reference to understand how secondary school students perceive the relationships among various psychological factors and the relationship between the psychological factors and performance. This study is expected to inform goal setting and content organization in psychological skills training.
