PURPOSE This study sought to explore elementary school (ES) teachers' avoidance of teaching model-based instruction (MBI) in physical education (PE) lessons. METHODS An open-ended questionnaire (n=93) and three focus group interviews (FGI ) were conducted with seven ES teachers. The collected data were analyzed using grounded theory analysis procedures (Strauss & Corbin, 1997). RESULTS Accordingly, we derived a grounded theory paradigm model composed of the core phenomenon (ES teacher’s avoidance of MBI in PE lessons), causal conditions (traditional difficulties of Elementary PE lessons, mismatch between MBI and ES teachers/PE lessons, lack of experience and teacher knowledge for/in MBI), contextual conditions (complex instructor organization, powerful trend of play), intervening conditions (value orientation for fun-focused PE, misunderstanding about PE curriculum), interactive strategies (focus on screening physical activities, preparing for PE lessons with YouTube rather than teacher guide book), and results (learner inclusive effects and de-curricularization). CONCLUSIONS ES teachers’ avoidance of MBI in PE lessons is a result of several reported problems with elementary PE lessons and is likely to be a recurring problem in the future. To encourage ES teachers’ MBI in PE lessons, efforts should be made to build practical knowledge of model use in pre- and in-service teacher education.
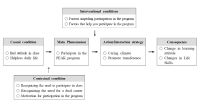
Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the process of participation in the PEAK program of collegiate athletes based on grounded theory. Methods In-depth interviews were conducted with 12 athletes from Y University who were registered in Korea Taekwondo Association. The collected data were analyzed by using the open coding, axis coding, and selective coding of the grounded theory, completed the paradigm model among the extracted concepts, and extracted the core categories through the story outline. Results As the result of data analysis, 'participating in the PEAK program' was found as the central phenomenon, and the causal situation was 'bad attitude in class' and 'helpless daily life'. The contextual conditions were 'recognition of the need for class participation and dual career' and 'motivation to participate in the program', and the intervening conditions were 'factors that hinder participation in the program' and 'factors that help program participation'. The action/interaction strategies were ‘caring climate’ and ‘promoting transfer’, and depending on the consequence, ‘learning attitude change’ and ‘life skill change’ appeared. Conclusion Participants improved their learning attitude through the PEAK program and confirmed the possibility of life skills transfer. It is hoped that this study can lead to implementation of various studies and discussions about life skills and transfer.

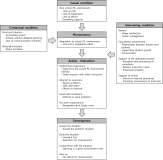
Purpose The purpose of this study is to explore the Instructor’s adaptation process of school P.E. environment in middle school sports club and to develop substantive level theory. Methods For this purpose, 17 sports instructors who had worked for more than 3 years at the middle school in Seoul were selected as research participants. The method of this study is the Grounded theory(Strauss & Corbin, 1990). Results The results of this study are as follows. First, as a result of open coding, the instructor's adaptation process of the school P.E. environment was organized into 104 concepts, 30 sub-categories, and 15 categories. Second, as a result of axial coding, a paradigm model for the adaptation process of the school P.E. environment was formed. Third, as a result of the selective coding, created the storyline of the adaptation process and made the core category, ‘instructor's adaptation process of the school P.E. environment in middle school’. Four types of adaptation process such as 'Acceptance type', 'Effort type', 'Compromising type' and 'Abandoning type' are derived through the formalization applied to the hypothesis of the core category. Conclusions Based on these results, the developed substantive level theory was evaluated and summarized.

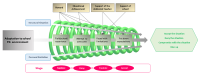

PURPOSE This study comprehensively compared the perception and interaction of player–coach in the development of mental toughness in soccer. METHODS Data were collected through semi-structured individual interviews from 12 participants (6 athletes and 6 coaches), analyzed using the grounded theory by Strauss and Corbin, and they were compared to the group of athletes and coaches, respectively. RESULTS The following results were obtained: (1) Both athletes and coaches recognized that the experience of coping with the pressure present in competition was a central phenomenon in the development of mental toughness. (2) Regarding the situation and condition that lead to coping with pressure, the athletes emphasized the individual's goal orientation in the context of competitive situations and environmental conditions, while the coaches emphasized the athletic attitude toward competition and development in childhood. (3) The athlete–coach interaction was identified as an intervening condition affecting the experience of coping with pressure. (4) As the action–reaction strategy for the development of mental toughness, the optimistic thinking was emphasized for athlete and achievement-oriented thinking for coach; thus, it differed in the characteristics of mental toughness. CONCLUSIONS This study presented the results of an integrated comparison of mental toughness, which can vary depending on the contextual specificity (soccer) and the subject of perception (athlete– coach), especially indicating the importance of the player–coach interaction, which can contribute to the strategy to be used in mental toughness development.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop the theory of child abuse of children with disabilities in Adapted Physical Education (APE). METHODS A grounded theory study was conducted based on a constructivist approach. Data were collected via in-depth interviews. Participants were 20 instructors selected based on theoretical sampling. The collected data were analyzed in the order of open coding, axial coding, and selective coding. RESULTS First, the direct causal conditions of abuse of children with disabilities in APE were the instructors’ and guardians’ distorted perception towards the disabled children along with the individual vulnerability of children with developmental disabilities. Second, the contextual conditions that form the background of the abuse of children with disabilities in APE included the burden of the instructor due to the unjust demands of the guardian of the child, the growth background of the instructor, and the repressive atmosphere of APE. Third, abuse of children with disabilities can be divided into three types: ‘active abuse’ based on the instructor’s distorted viewpoint of the child with a developmental disability, ‘passive abuse’ due to the unjust demands of the guardian, and ‘passive abuse’ due to the structural problems in the APE field. Fourth, the abuse of children with disabilities in APE, which can be distinguished by different characteristics, affects the instructor’s inner conflict and self-reflection. CONCLUSIONS This study approached the phenomenon of abuse of children with disabilities in Korean adapted physical education as a grounded theory, and the theory generated is expected to contribute to the establishment of strategies necessary to design adapted physical education in keeping with human rights.
PURPOSE Players’ nonverbal behavior during a game may be expressed through selfregulatory and intentional processes, where nonverbal cues are strategically used to achieve specific outcomes. This study aimed to observe and explore the strategic and intentional nonverbal behaviors utilized by table tennis players. METHODS The study utilized a grounded theory methodology and involved purposeful sampling of ten adult table tennis players. Semi-structured face-to-face interviews were conducted. The collected data were analyzed using open, axial, and selective coding techniques. RESULTS The findings revealed that players’ intentional nonverbal behaviors are influenced by their confidence levels, physical condition, and perceptions of others’ nonverbal cues. Throughout this process, players underwent various emotional experiences, worked to maintain a positive mental state, and experienced changes in both their behaviors and psychological states, which impacted the flow of the game. CONCLUSIONS This study’s results provide valuable insights into the role of intentional nonverbal behaviors utilized by athletes during competitions. This suggests that understanding and incorporating intentional nonverbal behavior should be a key consideration in sports psychology counseling and psychological skills training.
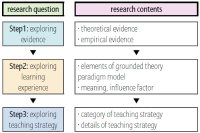
Purpose The purpose of this study was to understand learning experiences deeply and to prepare practical teaching strategies by reflecting the voices of the field. Methods For this, I used the logic and techniques of 'the grounded theory'. In particular, I used ‘the grounded theory paradigm model', which enables a holistic and systematic analysis of specific experiences to explore learning experiences and teaching strategies. I selected 10 male and female students who participated in art and physical activities as research participants. I collected data through literature review, in-depth interviews, and expert meetings, and analyzed using open coding, axial coding, and selective coding. Results First, I explored “the learning experience of art and physical activities in free-semester system", according to the elements of grounded theory paradigm model. It is composed of the ’causal condition’, ‘contextual condition’, ‘central phenomenon’, ‘interventional condition’, ‘interaction strategy’, and ‘results’. Second, based on this, I conducted "the teaching strategies for art and physical activities in free-semester system". These are composed of 'expansion strategy', 'diversity strategy', 'spontaneity strategy', and 'immersion strategy'. Conclusions The results of this study suggest that art and physical activities in free-semester system are leading to a positive change extended from the planned goals. In addition, various variables are structurally intertwined, and thus, it is considered that more strategic and systematic efforts are required in various dimensions for the successful application.


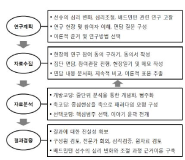
This study was purposed to explore psychological change and regulation process during badminton competition. The data were conducted using group interviews and participation observations who 18 K college badminton players. The data were analyzed using open, axial, and selective coding based on grounded theory method (Strauss & Corbin, 1998). The results were as follows: Open coding results, 89 concepts, 44 subcategories, and 18 categories emerged as psychological change and regulation process during badminton competitions. Axial coding results, the categories are showed structural relationships such as performance, score, psychological momentum, the importance of competition, court environment, physical condition, competition strategy, psychological preparation, past experience, outcome expectation, psychological disturbance, psychological skills, game situation-changing strategy, support-seeking strategy, significant others' behavior, the opponents' behavior, psychological resilience, and maintenance psychological disturbance. Selective coding results, core category of this study was revealed to maintain psychological homeostasis. Environmental context during badminton competitions causes specific situations and events that evoke psychological disturbance. In turn, a player seeks mental and behavioral strategies to maintain psychological homeostasis. There is psychological homeostasis mechanism during badminton competitions for peak performance. Development of proper interest for psychological homeostasis will be improved through this research approach in sport psychology.

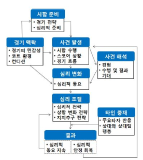
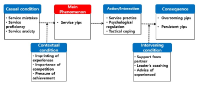
Purpose This study aims to investigate the experience of service yips in badminton players in depth through using grounded theory method. Methods We collected data from in-depth interviews with 14 participants in total, consisting of badminton players who experienced service yips, their doubles partners and coaches. The collected raw data were analyzed base on derive transcription, coding and paradigm models through grounded theory method. Results First, as a result, 59 concepts, 31 subcategories and 15 categories in regard to badminton service yips were deduced from open coding. Second, in axial coding, it was structured in a paradigm model by categories such as service yips, service mistakes, service proficiency, service anxiety, the imprinting experiences, the importance competition, the pressure of achievement, service practice, psychological control, tactical handling, support from partners, leaders’ coaching, advice from experienced ones, overcoming yips and persistent yips. Third, selective coding resulted in ‘Badminton service yips’ as the core category of this study. ‘Badminton service yips’ is a chronic performance impairment associated with badminton players making severe errors in swing motion on a service not intended by them that it is due to physiological or psychological symptoms such as hand tremors, overall body stiffness, arms stiffness, overstress, overanxiety, and concern over service mistakes. Conclusions We expect our study can be a theoretical foundation for understanding and explanation of ‘Badminton service yips’ and a useful reference for badminton players suffering from psychological difficulties caused by their service yips. The findings in this study should be considered for the development of potential strategies for overcoming the badminton service yips.

Purpose Lock and Heere (2017) argued that two different theories of social identity theory(SIT) and role identity theory have been used in previous studies of team identification. However, they failed to provide why such phenomenon existed in the literature of team identification. Thus, the first purpose of the study is to provide the possible reasons why the two theories were used as the ground of team identification in the previous literature. In addition, the current study examined whether team identification was properly developed from SIT by incorporating the cases of organizational identification and consumer-company identification in business literature. Results & Conclusion There are two possible explanations on why the two theories have been used in team identification studies. First, in the initial studies of team identification, theoretical ground of team identification was lacking. Thus, without a firm theoretical guidelines, authors might have used the two theories as the ground of team identification. Second, as previous literature noted, the two theories are like the two different sides of a single theory. Thus, authors may have not recognized the need of differentiating the two theories and used the two theories as the ground of team identification. This study also examined whether team identification was properly developed from SIT. The social category in team identification includes two different social identities(team members and fans), which is quite different from a social category with single identity in it. The locus of social category of team was arbitrarily expanded to include fans in the same category. This case is quite similar with consumer-company identification in marketing literature. Future study needs to examine whether the locus of social category can be expanded to include two different social identities.