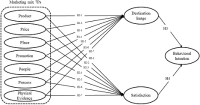
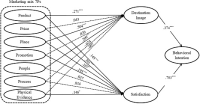
Purpose Limited research has investigated the marketing mix of international sporting events empirically. This study filled this gap by identifying the marketing mix and examined the structural relationships among marketing mix, destination image, satisfaction and revisit intention focusing on foreign spectators of 2019 Gwangju FINA World Championships. Methods The questionnaire was structured in four sections: sporting event marketing mix (seven dimensions and 21 items), host city image (three items), satisfaction (three items) and revisit intention (three items). Analysis of data from 396 foreign spectators in FINA Championships indicated that the proposed model fit the data well. Within a attitude-behavior theoretical framework, this study proposed and tested a structural relationships among the constructs. Results The results of this study presented that (1) product, place, and people in sporting event marketing mix significantly impacted foreign spectators’ destination image, (2) product, price, place, promotion, and physical evidence were appeared to be significant predictors of satisfaction, and (3) destination image and satisfaction had a significant effect on foreign spectators’ revisit intention. Conclusion The findings suggest marketing mix for the international sporting event and its influential mechanism on foreign spectators’ revisit intention. Practically, this study provides important implications for event organizers that can be utilized to develop strategic marketing mix in sporting events to enhance spectators’ destination image, satisfaction, and revisit intention.

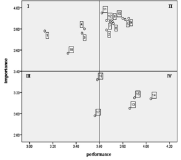
Purpose The purpose of this study was to find out what young amateur golfers consider the most when purchasing golf apparel and to find out the Importance-Performance attributes when choosing golf apparel. Methods Amateur golfers in their 20s through 40s who have purchased golf clothing directly were selected as the subject. A total of 350 questionnaires were distributed using the purposive sampling method, and 331 copies as a final validity sample. For data analysis exploratory factor analysis Cronbach’α, frequency analysis, and Importance-Performance analysis by using SPSS 21.0. Results First, except for ‘fancy design’, ‘water-proof function’, ‘elasticity comfort’, ‘brand name’ there were significant differences between importance and satisfaction of selection attribute. Second, ‘harmonic colors’, ‘has its own characteristics’, ‘expressing beauty’, ‘elasticity comfort’ were analyzed to be situated in quadrant Ⅰ. Third, ‘fancy design’, ‘water-proof function’, ‘temperature maintenance function’, ‘elasticity and durability’, ‘brand name’, ‘high-priced yet popular brand’, ‘popular brand’ were analyzed to be situated in quadrant Ⅱ. Fourth, ‘comfortable to wear’, ‘convenient for physical activity’ were analyzed to be situated in quadrant Ⅲ. Fifth, ‘can be also worn for outdoor wear’, ‘wear for gathering’, ‘wear as daily attire’ were analyzed to be situated in quadrant Ⅳ. Conclusions The results will be the basis for effective target marketing on young amateur golfers who are rapidly emerging and will be able to grasp the characteristics of golf apparel that they really want.


The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of congruence type between sporting event and corporate sponsor as well as the effects of advertisement exposure frequencies (1, 3 or 5 times) on advertisement attitude and advertisement effectiveness, including brand attitude and advertisement wear-in and wear-out effects. Data (N=150) were collected using a convenience sampling method and 3-group random assignment. The collected data were analyzed by means of frequency analysis, reliability analysis based on factor rho coefficient, correlation analysis, one-way ANOVA, confirmatory factor analysis, and latent mean analysis. The results were as follows; firstly, in case of higher functional congruence condition, advertisement attitude was most positive in a 3-time exposure situation and it decreased as advertisement exposure frequency further increased. However, in the lower functional congruence situation, advertisement attitude was continuously decreased as advertisement exposure frequencies increased. Secondly, in the higher image similarity situation, advertisement attitude was increased as advertisement exposure frequencies increased. On the other hand, in the lower image congruence situation, advertisement attitude was decreased as advertisement exposure frequencies increased. Lastly, advertisement attitude, brand attitude, and wear-in effects were statistically higher in the high functional and image congruence situations than did in the low functional and image congruence situations.

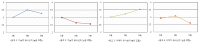
PURPOSE This study examines how fitness centers’ care services affect the MZ generation’s perceived value, exercise attitude, and exercise commitment and how perceived value mediates this impact. METHODS Patrons aged 20–30 who used fitness centers in the Seoul and Gyeonggi regions participated in a questionnaire survey from January to February 2024, providing a total of 233 responses. Using SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0, the data underwent frequency analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling. RESULTS First, perceived caring services had a significant effect on perceived value. Second, perceived value had a substantial influence on exercise attitude. Third, perceived value had no significant effect on exercise commitment. Fourth, exercise attitude significantly drives exercise commitment. Fifth, perceived caring services did not significantly affect exercise attitude or commitment. Sixth, perceived value fully mediates the relation between perceived caring services and exercise attitude. Seventh, perceived value had a full mediating effect on the association between perceived caring services and exercise commitment. Finally, tailored services and emotional support were identified as key factors in fostering MZ individuals’ positive exercise experiences and commitment. CONCLUSIONS Fitness centers should develop strategic services reflecting their customers’ goals and values to enhance their exercise attitudes and commitment and ultimately secure long-term customer loyalty.
PURPOSE This study examined levels of safety knowledge and practice among recreational sports participants, focusing particularly on impacts of gender, age, injury experience, and exercise-level profile. In sports environments, understanding these factors is essential for developing targeted strategies to promote safe behaviors. METHODS Survey data from 7725 participants engaged in regular recreational sports activities were analyzed. Latent Profile Analysis was employed to categorize participants based on their injury experience and exercise levels, resulting in two profiles: Group 1 (moderate or severe injury experience with intermediate exercise levels) and Group 2 (mild injury experience with beginner exercise levels). Three-way ANOVA was then used to evaluate relationships between these profiles and safety knowledge and practice levels. RESULTS Results revealed significant differences across sex, age, and profile groups. Compared with women, men demonstrated higher levels of safety knowledge and practice, which were likely influenced by greater exposure to high-intensity sports and risk-taking tendencies. Adolescents exhibited the highest levels of safety knowledge and practice linked to structured safety education, but these levels declined in early adulthood and then increased again in middle age due to growing health awareness and preventive motivations. Furthermore, participants in Group 1 consistently showed higher levels of safety knowledge and practice than those in Group 2, highlighting injury experience’s role in shaping safety behaviors. CONCLUSIONS These findings underscore the importance of developing gender-specific safety education programs, age-appropriate interventions, and training initiatives tailored to beginning participants. Future research should evaluate these strategies’ long-term impact on safety practices and injury prevention in diverse sports settings.
PURPOSE This study aimed to analyze the moderating effect of physical fitness on the relationship between abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome (MetS) in older women. METHODS A total of 190 participants were categorized based on waisthip ratio (WHR) into high (50%) and low (50%) groups, as well as based on Z-score of fitness into high (25%; high fit), moderate (50%; moderate fit), and low (25%; low fit) groups. Logistic regression was used to assess the relative risk of MetS based on abdominal obesity and fitness levels, and moderation analysis using the Process macro was conducted to explore the moderating effect of fitness on the relationship between abdominal obesity and MetS risk factors. RESULTS After adjusting forcovariates, logistic regression showed that high WHR (odds ratio (OR)=2.721, p=0.004) led to a significantly higher risk of MetS compared with low WHR; the high fit group (OR=0.360, p=0.044) had a significantly lower risk of MetS compared wih the low fit group. Moderation analysis revealed that the impact of abdominal obesity on MetS risk factors varied depending on the level of fitness (β=-0.495, p=0.037), and the results remained significant after covariate adjustment (β=-0.458, p=0.049). CONCLUSIONS This study suggests that the risk of MetS from abdominal obesity can be mitigated by higher levels of physical fitness. These findings highlight the need for participation in regular physical activity to maintain a high level of fitness, along with proper nutritional intake, to prevent MetS in older women.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the influence of certain factors on spectators' spectating behavior through the analysis of spectator-type Taekwondo spectators’ spectating behavior by applying the extended theory of planned behavior and embodied cognition theory and considering spectators’ desire to stay. METHODS A total of 305 surveys were used as the final sample. SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 26.0 were used for frequency , correlation, confirmatory factor, and structural equation model analyses. RESULTS First, attitudes, subjective norms, perceived behavioral control, and prior knowledge, which are predictors of the extended theory of planned behavior, had a statistically significant effect on the spectators’ desire to stay. Second, the spectators’ desire to stay had a statistically significant effect on the spectators’ content , environment, and behavior. Third , the spectators’ content and environment, which are sub-factors of the embodied cognition theory, had a statistically significant effect on the spectators’ behavior. CONCLUSIONS The study results suggest that attitudes, subjective norms, perceived behavior control, and prior knowledge, which are predictors of the extended theory of planned behavior, have a positive effect on the embodied cognition and spectator behavior of spectator-type Taekwondo spectators.
Purpose The current study reexamined the financial value of National Fitness Award. Methods To determine the economic value of National Fitness Award, we incorporated 6 willingness to pay(WTP) models using contingent valuation method(CVM). The data were collected from 250 members and 250 non-members of National Fitness Award(NFA) who were over 19 years old. Out of 500 completed questionnaires, total of 489 usable questionnaires were used for data analyses. Among 489, the WTP were calculated after 125 protest responses were discarded. The data were analyzed with SPSS 24.0 for frequency analysis, descriptive statistics, reliability test, and exploratory factor analysis. Stata 14.0 and R programs were used for calculating WTP. Results First, WTP was positively influenced by household income. Second, WTP was positively influenced by satisfaction level among members. Third, willingness to pay (WTP) for the National Fitness Award were 30,877won (Mean WTP), 29,455won (Median WTP), 25,829won (Truncated WTP). The average WTP was 28,720won. Conclusions Although National Fitness Award has been provided as free service to Korean people, previous study noted problems in facility and promotion. For the National Fitness Award to possess sustainability with proper service quality, it may need to be changed to fee based service. The current study suggested that, should it be changed to fee-based service, the proper price for the service is 25,000won.
PURPOSE This study investigated the perceptions and experiences of collegiate student-athletes with mental health concerns who are receiving sport psychology services. METHODS A total of 196 college student-athletes (98 male, 98 female) were recruited for the quantitative phase, while 14 athletes from 7 sports participated in the qualitative phase. This integrated approach sought to provide a comprehensive perspective on the research subject. The quantitative participants answered scales for depression (CES-D), anxiety (GAD-7), social support (NCAA RSSS), and mental help-seeking attitude (MHSAS), and the qualitative participants underwent in-depth interviews using a semistructured questionnaire based on a socioecological model. Quantitative data were examined using confirmatory factor analysis, reliability measures, independent t-test, and one-way analysis of variance via SPSS 28.0 and AMOS 28.0, and qualitative data were inspected through content analysis and expert meetings. RESULTS First, higher levels of depression, anxiety, and perceived social support were reported by female athletes as opposed to male athletes. Second, athletes in individual sports reported higher levels of social support than those in team sports. Third, athletes who planned to undergo future psychological counseling reported higher anxiety, social support, and helping attitudes than those with no plans to do so. Fourth, athletes who slept for more than seven hours reported lower levels of depression and anxiety and higher levels of perceived social support than those who slept for six hours or less. Fifth, freshman athletes reported higher depression levels than sophomore athletes. Sixth, student-athletes with no scholarships had higher anxiety levels than those with partial scholarships, who then reported higher perceived social support than those with full scholarships. Seventh, a lack of accessibility was the primary barrier to psychological service access for student-athletes. Eighth, engagement in interpersonal relationships was identified as a major stressor among student-athletes. CONCLUSIONS Differences in collegiate student-athletes’ mental health status as well as perceptions of and experiences in sport psychology services depend on various factors. These findings may serve as foundational data for improving sport psychology support services for collegiate student-athletes.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to provide information for improving the performance and skills of 500 m speed skaters by analyzing the kinematic and kinetic changes in their slide board movements over time. METHODS The subjects were 10 male short-distance skaters in their 20s to 30s who were registered as professional athletes with the Korea Sports Council. The changes in joint angle, joint moment, and joint power over time in the subjects’ slide board motion were measured and analyzed. RESULTS It was found that during phase 2 of the skater’s slide board movement, there was an increase in plantar flexion and a decrease in flexion of the lower extremity joint and extension of the knee and hip joint, with decrease in positive power of the knee joint. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study are expected to provide practical information to skating coaches and athletes by quantifying the biomechanical factors observed over time during slide board movements. In addition, this study is expected to contribute to the field of speed skating by presenting scientific training methods and proposing new analysis techniques to improve performance in the future.