
[Purpose] The purpose of this study was to investigate the process of Jang Changsun’s winning gold medal in the 1966 Toledo World Amateur Wrestling Championship and its meaning. [Methods] Jang Changsun and Katsumura Yasuo who had competed with Jang Changsun for the gold medal were selected as participants, a player and an executive who had participated in the Championship were selected as informants. Data had been collected by in-depth interview were analyzed firstly by using the Patton(1991)’s data analysis method, and the following conclusions were obtained by comparing with preceding studies, press releases, reports etc. [Results] Jang Changsun won a gold medal through the three stages of desperate struggles. The first struggle was to loose weight. Jang Changsun lost three times more weight than other players through fasting treatment, intensive training and dehydration in order to secure an advantageous position in the competition. His second struggle was the sparring itself. He made his mind to win gold medal 2 years before the Championship and started to strengthen his physical fitness and polish up his techniques to fight with strong players from powerful nation of wrestling. He finished the sparring by winning 4 games and tieing 2 games resulting in the same deduction points with Katsumura. It was inevitable for him to fight desperately to lose weight again to get gold medal. He eventually won the gold medal by losing his weight until he fainted because of injuries and serious dehydration. [Conclusion] The first gold medalist Jang Changsun contributed a lot to development of Korean sports by offering chance to consider significance of improving elite player’s exercising environment, scientific coaching, gaining self-confidence to win medal, and realizing the importance of sports informations.



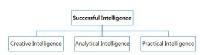
This study was to analyze the hierarchical importance of successful intelligence in Football coaches and players. In order to explore the hierarchical importance of successful intelligence 24 football coaches(under AFC A course) and 20 Korea Football Association U15 Players were responded to analytic hierarchy process questionnaires. In the Analytic Hierarchy Process, football coaches and players completed the AHP Questionnaire with creative intelligence, analytical intelligence and practical intelligence. The hierarchical importance order of successful intelligence for coach and player were analytical intelligence, practical intelligence, and creative intelligence respectively. Evaluation of hierarchical importance of successful intelligence for coach is analytical intelligence(.542), practical intelligence(.278), creative intelligence(.181) in order. Evaluation of hierarchical importance of successful intelligence for coach was analytical intelligence(.684), practical intelligence(.161), creative intelligence(.155) in order. The hierarchical importance of successful intelligence for coach and player were similar each other. Analytical intelligence, was evaluated most important factor for coach and player in successful intelligence. Successful intelligence is important issue for sport performance. More consider needs to Successful intelligence for sport psychology researchers.




PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to explore the effects of the student-athlete and student peer mentoring program as a collegiate class. METHODS The peer mentoring program, conducted at A University in the first semester of the 2023 school year, was evaluated using practical action research (Zuber-Skeritt, 1996). RESULTS In the introduction stage, ‘relative and absolute evaluation’, ‘member ratio’, and ‘definition of professor role’ were categorized as challenge issues. In the progress stage, ‘de-formalized lecture method’, ‘student athlete’s coaching experience’, and ‘student’s experience of football culture’ were discovered as possibilities, while ‘vacancy and absence of mentor-mentee’, ‘limited group activities and limitations of team sports’, and ‘lack of objective evaluation’ required improvement. At the end stage, student-athletes experienced changes in values such as self-identity, football, and human relationships, as well as quantitative and qualitative changes in sports participation. CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the potential of the peer mentoring program as a collegiate class as well as its practical significance for guaranteeing student-athletes' learning rights and for forming sports culture on collegiate campuses.
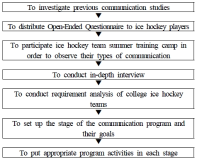
This study was designed to develop a communication training program for college ice hockey teams and examine the effects of this program. College ice hockey players and coaches participated in this study. The various types of data were collected and analyzed to assess the needs of the program and to develop the program with expert meetings. To analyze the effects of the developed program, questionnaires, experience reports, and in-depth interviews were conducted as measures. The results of this study are as follows. First, ice hockey team communication consisted of eight factors (i.e., sympathy, respect, trust, two-way verbal communication, firm expression of opinion, training program communication, developing rapport, and cohesion). Thus, the program developed based on eight factors and consisted of three stages of total 12 sessions which was 90 min to 100 min long. Second, this program increased communication satisfaction, coach-athlete interaction, group cohesion and exercise effectiveness, and these quantitative results were statistically significant. Moreover, qualitative analysis revealed that this program enhanced sympathy, social cohesion, and task cohesion among participants as well as positively changed their communication skills better than before. The communication training program which was developed through this study could provide basic information of a communication training program in the sports domain and positively influence overall sports team effectiveness and performance.


Purpose This study was designed to develop a team building program that helps freshmen student-athletes to adapt to college life and enhance team function and process and to examine the effects of this program. It could provide basic information of a team building program that effectively accelerates team function in the college team sports domain. Methods The program was developed through this process. First, an open-ended questionnaire was utilized to discover the needs of the program. Second, the results of needs of the program and important factors of team-building program were taken into consideration. Third, expert meetings were conducted. Consequently, the program consisted of three stages of total 10 sessions which was 90 min long. The questionnaires(Group Cohesion Questionnaire and Coach-Athlete Relationship Questionnaire), experience report, and program evaluation form were used as measures to identify the effects of the developed program. SPSS version 24.0 and inductive analysis were used to analyze the data. Results The results of this study are as follows. First, there was no statistically significant influence between developed program and the level of group cohesion. In contrast, the level of coach-athlete interaction was significantly increased. Second, the analysis of experience report revealed that this program reduced interpersonal conflict between team members and formed positive interpersonal relationship by mind of respect and consideration. Conclusion In conclusion, the hierarchical culture was strongly formed and team member suffered from the dual role of athlete and student in Korean college team sports. Thus, these should be resolved in order to enhance team function and process. As a results, this process could increase team performance as well as offer psychological stability to college student-athletes.

PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the nature of human rights violations experienced by semi-professional athletes in semi-professional sports teams and explored the relevant cases. METHODS For this purpose, 35 semi-professional athletes (20 men and 15 women) from the semi-professional sports teams participated in the study, and data collection was conducted through in-depth interviews and focus group interviews (FGI). The collected data were analyzed using the phenomenological research method proposed by Colaizzi (1978). RESULTS The study summarized the results into five categories, 14 theme clusters and 41 themes. Its inherent structures include ‘first step to becoming a semi-professional athlete: disadvantageous contracts for players,’ ‘unavoidable absolute power: obedience to the coach,’ ‘forced training camp: autonomy and privacy infringement,’ ‘structural problems of the semi-professional sports federation: tyrannized power’ and ‘female players who are in male-oriented society: gender-focused than performance.’ CONCLUSIONS The results of this study provided an understanding of athletes’ human rights violations experienced in semi-professional sports teams. Understanding athletes in semi-professional sports teams through phenomenological research was conducted based on previous studies discussing practical and policy intervention measures.

The purpose of this study was (1) to develop instructional contents for teaching and learning sportsmanship and (2) to examine the perceptions of sports instructors on that contents. Instructional contents based on sympathy was constructed from Youtube clips. Final version was developed to apply situated learning in class and was comprised of twenty-sportsmanship video clips and worksheets. Participants were sports instructors (N=208) in elementary and middle schools. Open-ended question and interview on call were used to collect the data. Qualitative content analysis was used to analyze the instructors’ perception regarding instructional contents. Results of this study showed that sports instructors responded to the contents as thoughtful experience (1) making myself realize the value of opponent, (2) making myself realize the value of sports, (3) making myself realize the value of judge, (4) making myself realize the value of coach/athlete. This study concluded that instructional contents was touching and emotional. Implication of instructional contents for teaching and learning sportsmanship, pros and cons of the contents and teaching tips were discussed.




PURPOSE This study was conducted to estimate the tendency of psychological factors influencing cycling performance by analyzing the characteristic factors of athlete reputation in the news big-data. METHODS To explore the psychological factors influencing cycling performance, an open questionnaire was conducted on 82 cyclists, and Inductive Content Analyses was performed. Overall, 89,520 news articles were collected through BIGKinds, and forming factors of athlete reputation were derived through LDA topic modeling analysis and inductive categorization. Through regression analysis, time series tendency of the factors of athlete reputation was calculated. Finally, the tendency of psychological factors to influence cycling performance was estimated based on the previously derived results in this study. RESULTS The psychological factors influencing cycling performance were found to be; emotion control, trust capital, cognitive control, motivation and communications with the coach. The forming factors of athlete reputation was found to be; reporting of the sports event, infrastructure creation, analysis to performance, moral issue, social environmental changes and sports gossip. The time series tendency of the forming factors of athlete reputation was found to include the categories of Hot, Warm, Cool and Cold. The psychological factors influencing cycling performance are estimated to expand to exercise performance and moral intelligence. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study suggest that the discussion of psychological factors influencing cycling performance extends not only to exercise performance, but also to moral intelligence, reflecting the socio-cultural context in the discussion of performance.
The purpose of this study was to examine psychological capital acquisition through Asian Games Participation. 17 of national women football players were completed Psychological Capitals Questionnair. The psychological capital consists of optimism, psychological skills, self-management, collective efficacy, and performance perception was investigated after the team call-ups and before the team-release. The data was analyzed by paired t-test. As results, Korean women football players’ collective efficient and performance perception showed a statistical significance at the beginning of the team call-ups but optimism, psychological skills, and self-direction did not show statistic significances. The team-harmony, interpersonal-management, team-power, sufficient training, trust in coach, efficient communication, and psychological football factors, which were subfactor of football players’ psychological capital, showed statistical significances. However, confidence, concentration, goal-setting, imagery, willpower, anxiety-control, mental-management, life-management, training-management, innate-behavior management, physical-management, football skills, mediative skills, and football intelligence factors did not have statistic significances. These results demonstrate that effects of mega sporting events-like experiences and psychological factors’ variability and inflexibility according to weather changes should be considered when it comes to discussion of psychological factors regarding players’ performance. It is expected that this study would be a fundamental resource for understanding of psychological influences through participations in mega sporting events and discussions about further psychological interventions for teams with environmental consideration as well as methodological developments which could measure effects of the psychological interventions.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to provide information for improving the performance and skills of 500 m speed skaters by analyzing the kinematic and kinetic changes in their slide board movements over time. METHODS The subjects were 10 male short-distance skaters in their 20s to 30s who were registered as professional athletes with the Korea Sports Council. The changes in joint angle, joint moment, and joint power over time in the subjects’ slide board motion were measured and analyzed. RESULTS It was found that during phase 2 of the skater’s slide board movement, there was an increase in plantar flexion and a decrease in flexion of the lower extremity joint and extension of the knee and hip joint, with decrease in positive power of the knee joint. CONCLUSIONS The results of this study are expected to provide practical information to skating coaches and athletes by quantifying the biomechanical factors observed over time during slide board movements. In addition, this study is expected to contribute to the field of speed skating by presenting scientific training methods and proposing new analysis techniques to improve performance in the future.