The frailty, characterized by reduced physiological function is closely related to a fall, disability, institutionalization, hospitalization, and mortality in the elderly. A reduced physical fitness is a major phenotype of the frailty. The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship among pre-frailty, physical activity (PA) and functional fitness in the community dwelling elderly women. The study participants were elderly women (n=338, 70.6±4.2years) aged over 65 who took part in the Korean Healthy Fitness Criteria study for the National Fitness Award Project in 2015. The pre-frailty was defined using the Cardiovascular Health Study frailty criteria. PA was assessed using the International PA Questionnaire (IPAQ). The participants were classified as regular PA participants if they meet the World Health Organization (WHO) PA recommendation for the elderly. Functional fitness was assessed using the composite of the National Fitness Award fitness testing for the elderly. Quality of life was evaluated using EuroQoL visual analogue scale and WHO quality of life assessment. As the results, the pre-frail elderly women were significantly older and obese (body mass index, percent body fat, waist circumference) than the healthy elderly. The pre-frail elderly presented significant decreases in walking, moderate intensity, and total PA compared to the healthy elderly even after adjusted for age and percent body fat. However, no significant difference was found in vigorous-intensity activity between the pre-frail and healthy elderly. Also, the pre-frail elderly women showed the decrease in functional fitness and quality of life compared to the healthy elderly. Regular PA was associated with high levels of muscular endurance and coordination in healthy and pre-frail elderly. In pre-frail elderly, high levels of cardiorespiratory endurance was associated with PA. In conclusion, regular PA is inversely associated with fitness decline in healthy and pre-frail community-dwelling elderly women. Regular PA might attenuate fitness decline in pre-frail elderly women.
The purpose of present study is to develop the'Golf Mental Scale'that measures and assesses golf players' cognitive, emotional, behavioral response per golf mental factor experienced while competing in depth. In order to achieve this research purpose, Researcher collected raw data of golf mental question through literature review and interview with 8 members of Korean male national golf team and gathered questions per factor through Deductive-Inductive Content Analysis for the raw data. Then, Researcher conducted first and second questionnaire survey targeting 253 of elite & pro golf players and conducted Rasch Model and Confirmatory Factor Analysis for the data collected using SPSS 21.0, Winsteps Ver. 3.65 Program, AMOS 18. The conclusion reasoned out through these research process was as follows: First, golf players' psychological factor structure identified was revealed as Concentration, Self-confidence, Anxiety and Arousal control, Emotion control, Thought control. Total 37 questions were determined. Second, 5 point scale was revealed to be a good fit for Golf Mental Scale. Third, the result of Construct Validity Verification of CFA showed that Golf Mental Scale model was a good fit. Fourth, Reliability of Golf Mental Scale showed high level by recording Cronbach' α value .936. Fifth, Internal Consistency of Convergent Validity and Discriminant Validity was revealed to be satisfied. Eventually, Golf Mental Scale is expected to be used practically as a functional test tool that provides participant's response toward each situation-specific questions concretely and an objective evaluation of participant's golf mental ability per factor considering questions'level of difficulty and participants'characteristic.

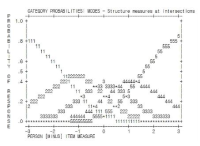
PURPOSE This study aims to investigate the effects of three perceived benefits of physical activity classes on class satisfaction, college satisfaction, well-being, and workout intention, as well as the moderating effects of sports characteristics on the relationships between the benefits and outcomes. METHODS A total of 282 questionnaires were collected from university students enrolled in physical activity classes during the semester. Confirmatory factor analysis, structural equation modelling (SEM), measurement invariance testing, and multi-group SEM were conducted using the Mplus 7.0. RESULTS Euphoric and social benefits positively affected class satisfaction. Class satisfaction, in turn, influenced college satisfaction, well-being, and workout intention. Sports characteristics moderated this relationship between the benefits of physical activity class and class satisfaction. CONCLUSIONS These findings offer practical insights for promoting student engagement and long-term participation in physical activity.
PURPOSE This study aims to provide policy recommendations for the development of women’s football and the enhancement of the Women’s University Football League (WUFL) by examining participant satisfaction and meaningfulness of football. METHODS To achieve this goal, we distributed survey questionnaires, including 5-point Likert scale and open-ended questions, and subsequently analyzed 153 responses using qualitative data analysis software, N-vivo. RESULTS Our findings reveal that female students actively engaged in the WUFL express high overall satisfaction. Furthermore, participants perceive football as a source of happiness, an energy booster, and a platform for new experiences. Their involvement in football goes beyond typical leisure; it is regarded as a form of serious leisure. DISCUSSION AND CONCLUSIONS Based on these results, we propose actions such as fostering and elevating amateur women’s competitions, promoting female students’ participation in football, and developing a comprehensive strategy for increasing women’s enjoyment of playing football.
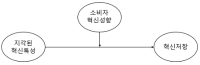
The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of sportwearable device's innovation attribute on innovation resistance and moderating effect of consumer innovativeness between sportwearable device's innovation attribute and innovation resistance. Samples were the 20, 30s who registered on undergraduate and graduate college students. They were extracted from three different universities, in Seoul. After 125 questionnaires were removed, 375 samples were used in the actual analysis; frequency analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation, and structural equation modeling. The results were as follows. First, perceived innovation attributes of sportwearble devices had a negative effect on innovation resistance. Second, consumer innovativeness was moderated in the relationship between perceived innovation attributes and innovation resistance.


The current study aimed to examine behavioral intentions of online sports products consumers using the Extended Goal-directed Behavior Model. The questionnaires were distributed to consumers who had experience of purchasing sports products online. Data collected from 282 respondents were analyzed mainly using structural equation modeling. The results were as follows: First, attitude and subjective norm had a positive effect on desire. Second, perceived behavior control did not affect desire but had a positive effect on behavior intention. Third, positive anticipated emotions had a positive effect on desire and negative anticipated emotions had a negative effect on desire. Fourth, prior knowledge did not affect desire and behavior intention. Fifth, frequency of past purchase behavior did not affect desire, but had a positive effect on behavior intention. Lastly, desire had a positive effect on behavior intention.



PURPOSE This study investigated the perceptions and experiences of collegiate student-athletes with mental health concerns who are receiving sport psychology services. METHODS A total of 196 college student-athletes (98 male, 98 female) were recruited for the quantitative phase, while 14 athletes from 7 sports participated in the qualitative phase. This integrated approach sought to provide a comprehensive perspective on the research subject. The quantitative participants answered scales for depression (CES-D), anxiety (GAD-7), social support (NCAA RSSS), and mental help-seeking attitude (MHSAS), and the qualitative participants underwent in-depth interviews using a semistructured questionnaire based on a socioecological model. Quantitative data were examined using confirmatory factor analysis, reliability measures, independent t-test, and one-way analysis of variance via SPSS 28.0 and AMOS 28.0, and qualitative data were inspected through content analysis and expert meetings. RESULTS First, higher levels of depression, anxiety, and perceived social support were reported by female athletes as opposed to male athletes. Second, athletes in individual sports reported higher levels of social support than those in team sports. Third, athletes who planned to undergo future psychological counseling reported higher anxiety, social support, and helping attitudes than those with no plans to do so. Fourth, athletes who slept for more than seven hours reported lower levels of depression and anxiety and higher levels of perceived social support than those who slept for six hours or less. Fifth, freshman athletes reported higher depression levels than sophomore athletes. Sixth, student-athletes with no scholarships had higher anxiety levels than those with partial scholarships, who then reported higher perceived social support than those with full scholarships. Seventh, a lack of accessibility was the primary barrier to psychological service access for student-athletes. Eighth, engagement in interpersonal relationships was identified as a major stressor among student-athletes. CONCLUSIONS Differences in collegiate student-athletes’ mental health status as well as perceptions of and experiences in sport psychology services depend on various factors. These findings may serve as foundational data for improving sport psychology support services for collegiate student-athletes.
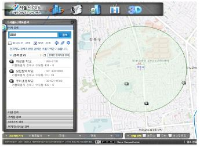
This study measured the accessibility of public exercise facilities within a residental area of a metropolitan community and examined how the accessibility can affect physical activity participation of residents. Initially, a total of 639 residents, who were aged between 19-70, visited Metabolic Syndrome Management Center of the Community Public Health Center, and registered for a Obesity Clinic Program, was listed as potential subjects. And those who responded to Physical Activity Questionnaire were selected for the analyses (n=92, 14.3% of 639). The relationships between physical activity level and accessibility to public exercise facilities were analyzed. Objective distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous physical activity(r=.209)’, 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.206)’. And perceived distance to public facility was related to ‘volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.235)’. perceived transport time to public facility was related to ‘duration of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.239)’, ’volume of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.306)’, and ‘volume of participation to total physical activity(r=.273)’. In contrast, the difference between objective distance to public facility and perceived subjective distance to the facility was negatively related to ‘duration of participation to moderate-intensity physical activity(r=-.221)’. The perceived numbers of public facility was positively related to ‘frequency of participation to vigorous-intensity physical activity(r=.237)’, ‘frequency of participation to walking(r=.273)’, ‘volume of participation to walking(r=.251)’ and 'total volume of participation to physical activity(r=.252)’. The predictor of 'total volume of participation to physical activity was perceived numbers of public facility(R2=.153, p=.046). The results revealed that the subjective accessibility to public health facilities was more influential to physical activity participation than the objective accessibility. Further research was warranted while using diverse populations as well as considering a inclusion of environmental factors.


PURPOSE This study analyzed the relationship among coaching behaviors, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance as perceived by high school athletes. Additionally, it examined whether motivational climate, competence, and effort mediate the relationship between coaching behaviors and failure tolerance. METHODS Using questionnaires measuring autonomy-supportive coaching behavior, controlling coaching behavior, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance, 365 high school athletes were surveyed. Using SPSS 28.0 and Amos 28.0 software, descriptive statistics and structural equation modeling were conducted along with the following types of analyses: reliability, correlation, confirmatory factor, convergent validity, and discriminant. Additionally, the bootstrap method was used to verify serial multiple mediating effects. RESULTS Autonomy-supportive behavior had a significant positive effect 1) on motivational climate, sports competence, and effort and 2) on failure tolerance. 3) Controlling coaching behavior had a significant negative effect on motivational climate and sports competence. 4) Motivational climate and 5) sports competence both had a significant positive effect on effort. 6) Effort had a significant positive effect on failure tolerance. Last, in the relationship between autonomy-supportive behavior and failure tolerance, motivational climate, sports competence, and effort showed partial mediating effects. CONCLUSIONS This study confirms the importance of coaches’ autonomy-supportive behavior in determining failure tolerance among adolescent athletes. Based on this information, counseling (educational) programs aimed at enhancing performance can be developed and provided in sports settings, thus fostering success among athletes.
PURPOSE This study aims to develop a coach presenteeism scale with scientifically proven reliability and validity. METHODS In order to achieve the research purpose, preliminary questions were drafted using previous studies (Lee & Kim, 2022) and existing presentation questionnaires (SPS-34, SPS-6, SPS-13). The preliminary set of questions was composed of 23 questions, which were deliberated through a meeting with subject experts. After which, a survey involving 183 coaches was conducted. In this study, statistical verification procedures were conducted through construct validation, exploratory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, internal consistency analysis, convergent validation and discriminant validation. RESULTS Finally, a 2-factor (DRA 5 items, DTP 5 items), 10-item coach presenteeism scale was developed. CONCLUSIONS In this study, a scale with verified reliability and validity was developed to support and investigate the presenteeism phenomenon experienced by coaches. These may be used by coaches themselves to check their presenteeism status and may guide future research to effectively train athletes.