
Purpose This study was conducted to investigate the appropriateness of the concept of condition for athletes and to conceptualize condition in a way suitable for field and then to produce a tool to test condition that reflects usability. Methods 30 college athletes and national athletes with more than 5 years of experience were selected. In the conceptual review stage, the appropriateness of the concept of condition was verified. In the conditional element collection stage, the condition concept reflecting usability was extracted. In the development stage of the conditional questionnaire, a condition questionnaire was developed in consultation with the data provider to reflect usability. Results Previous studies on the condition of athletes were complicated and the necessity for consideration of usability was raised. As a result of conceptualization with consideration of the application to the sport scene, condition in a scene is summarized into both physical and psychological states. As a result of the appropriateness evaluation of the tool that produced the condition inspection tool reflecting the condition element based on universality and peculiarity of conditionality, the athletes evaluated that the condition inspection tool properly reflects condition, is easy to apply and can be used for condition control. Conclusion The development and application of psychological testing instruments reflecting usability will accelerate the application of sports psychology in the appropriate direction. The reflection of usability will contribute not only to the reliability and validity of the psychological testing tools used in the field of sports psychology, but also to the improvement of the possibility of intervention by leaders and athletes, the convenience of development procedures, and the utility of response results.

PURPOSE Through analysis, this study reports on occurrences of children and adolescents’ sports accidents and presents measures to prevent, cope with, and manage school sports accidents. METHODS The study used both quantitative and qualitative methods. First, a frequency analysis was conducted using 284,429 safety accident data of the School Safety and Insurance Association (SSIA). Second, the inductive analysis method was applied to in-depth interviews conducted with eight teachers. RESULTS , accidents are characterized as follows: 1) At the school level, accidents have increased significantly every year in a large proportion of elementary and middle schools. 2) The span of time spent on sports was large. 3) Accidents happened at playgrounds and auxiliary facilities. 4) Accidents happened during kindergarten play and ball sports in schools. 5) The descending order of days with the most accidents was Thursday, Tuesday, Friday, Wednesday, Monday, Saturday, and Sunday. 6) Rather than a certain month, accidents happened across the school semester. 7) Most accidents occurred from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. Second, field teachers’ stories were categorized into the following topics. 1) School accidents can occur anytime, anywhere. Whether mild or serious, they still had the burden of inevitable accidents. 2) Required: were prompt response and handling by appropriate teachers; timely treatment and recovery cost support; also procedurally simplified handling by SSIA was helpful. 3) Avoiding accidents requires the following:: regular operation of safety education programs; daily promotion of teachers’ preventive observation and close guidance; and active role reinforcement of SSIA and policy support. CONCLUSIONS Finally, measures to prevent, cope with, and manage school safety accidents were proposed.
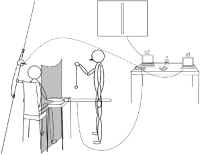
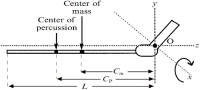
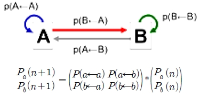
Purpose This study measured the haptic extroperception accuracy, that is, judging one hit position in a hand-held object. Especially, what factors associated the estimation of contact position when the impact is made at the grasped implement by hitting the ball. Methods Relative frequency and conditional probability based analysis verified that perceivers influenced not only the amount of pressure distinguished impressions by the coefficient of restitution but also the pressure distributions encoded impressions by the distance from the hand to the impact. Results Results conformed to previous invariant characteristic on dynamic touch in showing that perceiving the location of the impact of grasped objects, including dominant perceiving selectively modality, is constrained by inertial properties with such success requires appreciating the location of the implement’s center of percussion. Conclusion Investigated in this planes captured as a mechanical factor, we would suggest a broader hypothesis for further research into the effects of the rotational inertia related to haptic position accuracy in the hand-held object, and leading to different estimates of system function providing an account of generalization that accommodates of its varied aspects.


Purpose: The purpose of the present study was to identify the difference of overall putting accuracy and/or distance control among three visual conditions; executing putt focusing vision on the near target(ball), focusing on the far target(hole), and with no vision. In order to satisfy ecological validity, the test was held not on the synthetic putting green in a laboratory, but on the outdoor real putting green. Methods: A putting green with slight slope and minimal break was selected as the test site. The test was held at 8.5m uphill, 13m uphill, 8.5m downhill, and 13m downhill. Twenty participants were asked to putt the ball as close to the target as possible. They were also asked to adhere to their own pre-putt routine having enough time of visual fixation toward the hole to get distance and direction cues. Each Participant putted a total of 12 balls putting 3 balls on each distance-slope experimental condition. Overall putting accuracy score represented actual distance (in meter) from the far target(hole) to the ball rest. Distance control score represented it from the near target(original ball position) to the ball rest. Repeated measure ANOVA was used to verify the raw data. Results: Putt from 8.5m uphill and putt from 13m downhill were revealed to have statistically significant difference only in distance control by visual focus conditions. Putt focusing vision on the ball was the best at 8.5m uphill. Putt focusing vision on the hole was the best at 13m downhill. However, there was no significant difference in overall putting accuracy by visual conditions. Discussion & Conclusion: The results of our study are interesting and valuable from two aspects. First, the presumption is that overall putting accuracy on the real putting green has no significant difference by visual conditions because it is affected by various factors, i.e. memory of distance, slope, break, turf condition, impact quality, body alignment, etc. Second, no consistent evidence was detected that specific visual condition, especially executing putt focusing vision on the hole, was the best for distance control.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to determine the effectiveness of six-weeks intermittent hypoxic training at 3,000 m hypobaric hypoxic condition on aerobic and anaerobic exercise capacity in competitive swimmers. Methods South Korean swimmers (n=20) were randomly assigned into training at sea-level (n=10, intermittent normoxic training group; INT) and training at 526 torr corresponding to 3,000 m hypobaric hypoxic condition (n=10, intermittent hypoxic training group; IHT). The participants completed an aerobic continuous treadmill training (30 min) within 80%HRmax and anaerobic interval bicycle training (10 times; 2 min of exercise and 1 min of rest) for 30min within 90%HRmax in each environment. We compared their aerobic and anaerobic exercise capacity before and after six-weeks of training. Exercise frequency was 1 hour, 3 days per a week, and during 6 week. Results In aerobic exercise capacity, PWC at 75%HRmax, estimated VO2 max, and exercise time were increased by training in only the IHT group. Estimated VO2 at 75%HRmax was increased by training in both groups, but presented a larger increase tendency in the IHT group compared with the INT group. In anaerobic exercise capacity, peak anaerobic power and fatigue index were increased by training in only the IHT group. Blood lactate level after wingate test were decreased by training in both groups, but the IHT group have a lower blood lactate level in after training compared with the INT group. Conclusion In our study, we did not measure to various dependent variables for support to enhancement of aerobic and anaerobic exercise performance. However, these results showed that the IHT method may be effective in improvement of exercise performance in competitive swimmers who participates in a variety of events from short to long distance.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate conditioning management and perception in Korea Ladies Professional Golf Association golfers and elite amateur female golfers. METHODS Physical characteristics and performance-related factors were investigated through a short version of the conditioning questionnaire consisting of 16 questions on five factors, surveying 129 female professional golfers and 174 elite amateur female golfers. The components of the questionnaire included physical fitness (four questions), injury (four questions), nutrition (three questions), mental (three questions), and performance strategy factors (two questions). Data were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics ver. 23.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). An independent t-test was used for comparison between groups. RESULTS Physical fitness-related factors showed significant differences in all four questions between groups (p<0.001–0.031), injury-related questions showed significant differences between groups in three questions (p<0.001–0.003), and one nutrition-related question was different between groups (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS Differences were seen in conditioning management factors recognized between professional and elite amateur female athletes. Future research on conditioning questions and differences in effects according to actual performance will be needed.
PURPOSE This study aimed to provide evidence for improving the working environment by exploring the phenomenon of presenteeism experienced by coaches. METHODS Ten coaches experiencing presenteeism were selected as participants of the study using the snowball sampling method, and in-depth interviews were conducted. The in-depth interviews were conducted for about 50 to 60 min using semi-structured questions organized through pre-expert meetings, and inductive content analysis was conducted. RESULTS First, the health problems that developed while coaching were categorized into two detailed areas (physical and psychological symptoms). Second, the causes of presenteeism were categorized into four general areas (policy and institutional problems, poor job environment, athlete problems, and human relations). Third, performance loss due to presenteeism was categorized into two general areas (coach-athlete relationship damage and poor training performance). Finally, coping with presenteeism was categorized into three detailed areas (private time spending, joining acquaintances, and changing training methods). CONCLUSIONS The result of this study confirmed that coaches are currently experiencing the phenomenon of presenteeism for various reasons, and the symptoms and coping method for this differ with each individual. However, the phenomenon of presenteeism experienced by coaches requires further future research since it is not easily observed and the coping method is not efficient.
PURPOSE In this study, in-depth interviews were conducted with track-and-field athletes and leaders who participated in the Tokyo Olympics. The study aimed to present practical measures for the development of Korean track and field, which people at the forefront of Korean track and field thought. METHODS In-depth interviews were conducted using semi-structured questions for a total of five track-and-field national athletes and four track and field coaches. RESULTS A total of 39 subcategories and 104 concepts were derived with regard to four research questions: the process up to the Tokyo Olympics, the actual condition of Korean track and field, a comparison with track-and-field power nation, and practical measures for becoming track-and-field power nation. CONCLUSIONS Practical measures are needed to improve and develop the competitiveness of Korean track and field, which is expected to improve its competitiveness and help develop Korean track and field in the future.
PURPOSE This research explores the underlying mechanism that determines how people perceive their goal progress and its relation with their motivation and self-efficacy. METHODS Three hundred and sixty Koreans who participated in an online survey were given salient individual exercise goals (11 workouts), and they reported their self-efficacy, goal progress perception, and motivation. We conducted dummy variable multiple regression analysis (2 [absolute progress-low (27%) vs. high (73%)] X 2 [categorization vs. no-categorization]) and multiple moderated mediation analysis based on Process Model 7 and 21 (Hayes, 2017). RESULTS The findings showed significant interaction between categorization and absolute progress on progress perception. In low progress condition, the categorization group perceived more progress than no categorization group and contrary effect in high progress condition. For motivation, in low progress condition, categorization group was more motivated than no categorization group, and inverse effect in high progress condition. Moreover, there was no direct effect, but only low self-efficacy group played the moderating role between perceived progress and motivation in conditional indirect effect. Lastly, the result indicated significant multiple moderated mediation effect. CONCLUSIONS This research theoretically contributes to the domains of categorization and motivation. Sport marketers can utilize categorization as a strategy by breaking down yearly memberships into monthly categories based on consumers perceptions. Future research can include subsequent motivation after a superordinate goal is completed.
PURPOSE This study aimed to identify the lower limb muscle activity based on direction prediction presence or absence and gender during side cutting in healthy college students. METHODS The study participants included 14 healthy males and females (8 males; 6 females). All participants ran at full speed for a distance of 12m, and side-cutting was carried out at 45 degrees in a randomly indicated direction and in a fixed direction. Simultaneously, data regarding vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris muscle activity of the dominant leg were collected using an electromyography sensor, and data regarding vertical acceleration were collected using an inertial sensor attached to the pelvis. A sync webcam was used for obtaining the initial contact of side cutting and the stance period time. During the 10 milliseconds (pre-activation) prior to the initial contact and 50% of the stance phase (loading phase), vastus medialis, vastus lateralis, semitendinosus, and biceps femoris average muscle activity and hamstring to quadriceps ratio included as variables. RESULTS During the pre-activation and loading phase, the vastus medialis muscle activity of the male group was higher in the unexpected condition than in the expected condition. Furthermore, hamstring to quadriceps ratio was confirmed to be lower under unexpected condition compared to under expected condition during on loading phase. CONCLUSIONS The study results suggest that the risk of anterior cruciate ligament injury may increase with side cutting under unpredictable conditions. It is expected to provide useful information for identifying factors related to knee injury in the general population.