Purpose : The purpose of this study was to investigate coaching information with which coaches provided players during badminton competition. Methods : To this end, we generated an open-ended questions and presented it to 88 high school athletes registered in the Badminton Korea Association. The survey was conducted during a tournament and immediately after the tournament to collect the data. The collected data were categorized through inductive content analysis. Results : As a result of this study, a total of 480 raw data points collected through the open-ended survey were categorized into four general areas: psychological information, technical information, tactical information, and game operation information. Specifically, psychological information was divided into six subdivisions: concentration, confidence, relaxation/stabilization, mental toughness, play thought, and passion; technical information was broken into four subdivisions: strokes, footwork, swing and posture, and position preparation; tactical information had four subdivisions: coping to opponents, play changes, rotation, and manipulation of opponents; and, game operation information was divided into two subdivisions: taking the lead in a game and changing atmosphere. Conclusions : In other words, in badminton competition, the coaches strengthened psychological skills that promote psychological stability to attain the athletes’ peak performance and modified the athletes’ motion into the action necessary for achieving accurate techniques. Furthermore, they provided a variety of coaching information so that the athletes will respond appropriately to their opponents’ play, take the lead in games and induce a positive mood. The psychological, technical, tactical and game operation information offered by badminton coaches are the main factors influencing the performance of badminton players and suggest a need for the proper management and control of the coaches as well as athletes for the peak performance.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the optimal model for winning medal on vault event of men's gymnastics. Specifically, decision tree analysis was used to explore, first, for the optimal conditions for qualifying top 8th player that have high possibility into final round, and second, for the optimal model for obtaining the medal of the vault event. Methods Data were collected for five official competitions (Olympics, Asian games, and International championship, etc.) organized by the Federation of International Gymnastics (FIG) from 2013 to 2016. In this study, the data of 626 vault players were collected. Also all of these players performed 921 vault skills for qualifying round or final round. Five predictor variables for estimating for qualifying into the final round and for obtaining the medal of the vault event were selected; nationality, difficulty score, acting score, additional penalty score, final score. Results The results is as follows. Overall, it was confirmed that the optimal model for entering into the final round was the difficulty score of vault event. The optimal model for entering into the final round estimates 81.2% when condition would be the 5.6 or higher of difficulty score and 8.6 or higher of the acting score. The optimal model for winning medals was 86.7%, which means that when condition would be the 6.0 or higher of difficulty score and no additional penalty score. Conclusions This models can be used as a basic data for establishing a strategy for medal acquisition of vault event of gymnastics.



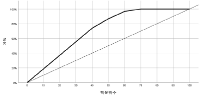
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency that can guarantee the student athletes' right to study and performance, and to derive the ranks of setting proper training duration of frequency of student athletes by school level. Consequently, to provide basic data for the development of training guidelines for the growth period of Korean student athletes. Methods Delphi and Analytic Hierarchical Process(AHP) techniques were used. The Delphi survey was conducted in three phases, and collected data through Delphi survey were computed by SPSS win ver. 22.0 and Excel, using the mean, standard deviation, median, and coefficient of variation. Using the AHP technique, we classified the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency derived through Delphi survey, and calculated the importance by using Microsoft Excel 2010. Conclusion First, elementary students should be guaranteed regular class participation, have basic after school training, and be provided with adequate rest so that they do not lose interest in the exercise. Second, middle school students are required to decide whether to continue exercise based on their ability to exercise and abundant experience. Therefore, when abandoning the exercise, students should be able to faithfully carry out their academic performance. Third, high school students are directly related to college entrance and employment, so they have to concentrate on performance rather than on academic performance.

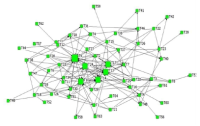
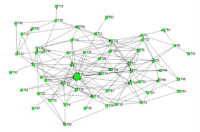
Previous work has shown that coaches sought information from several sources; however, there was a strong reliance on learning from other coaches within their social networks. There has been limited research examining the nature of these social networks with other coaches (Trudel and Gilbert 2004). Thus the purpose of this study was to examine the structures of coaches’ social networks of Korean rhythmic gymnasts. Research questions were: (1) What are the network structures of Korean rhythmic gymnasts’ coaches? (2) What structural parameters contribute to coaches’ network structures, and (3) Is there an association between coaches’ network and flow of information in their networks? A total of 37 coaches of youth rhythmic gymnasts (6-18 years old) participated in this study. Each of those coaches was asked to complete a Name Generator Questionnaire (i.e., list four names that you have a close relationship with) and general socio-demographic survey. Data were analyzed using social network analysis tools such as UCINET, p-net, and Quadratic Assignment Procedure. Analysis of network centrality, density, and strong components showed that (1) homophily was identified in the structure of coaches’ social networks (2) homophily (e.g., by gymnasts’ ranking, mentor coaches) contributed to the total social network of coaches, and (3) interacting only with close coaches in the network, coaches received information about coaches/coaching from the strong ties rather than weak ties (Granovetter, 1973). This study also has strong links to Wenger’s (1998) community of practice which posited that groups of people share a common characteristic in practice.

PURPOSE This study explored psychological experiences in long jump competitions and examined the continuity of psychological experiences over time. METHODS A total of 28 adult long jumpers, 18 men and 10 women, were provided data through in-depth interviews. Data on psychological experiences were extraced through inductive content analysis, while continuity by period was analyzed by calculating the response frequency ratio using Excel. RESULTS First, the psychological experience in the long jump competition was categorized as fundamental, competition intelligence, emotional control, and communication capacity experience. Second, in long jump competitions, results showed that jumpers experienced mixed feelings of anxiety and pressure, self-confidence, and concentration in the first period; peer communication and analysis thinking were necessary in the second period; practical intelligence and pressure control were important in the third period; learning ability and creativity were crucial in the fourth period; learning ability and coach communication were applied in the fifth period; and fighting spirit and creativity were present in the sixth period. Third, the psychological experience of long jumpers by period, basicphysical strength was maintained; competition intelligence increased in the second and fourth periods; communication skills increased until the fifth period, and decreased after; while emotional control decreased. This reflects the contextual changes over time andthe change in competition records owing to that. CONCLUSIONS In the long jump competition, psychological experience changes by period and affects competition records. This study will contribute to further understanding of psychological continuity.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine athletes’ psychological competition experiences. Methods For this study, 64 student athletes, attending universities located in Seoul and Chungcheongbuk-do, participated in the study by completing an unconstructed questionnaire. The data were analysed through content analysis method. Results As a result, 15 themes, such as morale loss, comparable performance levels, opponent irritation were collected and the themes were classified into three categories including objectives of psychological competition, requirements of psychological competition, and psychological battle. In match situations, athletes attempt to psychologically compete in order to achieve objectives such as opponent’s morale loss, induce carelessness, trigger agitation and anger, dispersion of attention, and distraction. Psychological competition among rivals is valid when the requirements, such as comparable performance levels, sensitivity to match situations, strong tenacity and confidence, understanding of opponent and oneself, mutual checks and balances, are met. Athletes attack and defend to win the psychological competition by utilizing opponents irritation, information distortion, unexpected behaviors, predicting and coping, pulling a poker face, exclusion of opponents, and self-focusing. Conclusion This study created a theoretical foundation for a profound understanding of athletes’ psychological competition, which is often found in sport fields. Furthermore, this study is meaningful in that it has raised a chance of interest concerning psychological interaction between players in match situations.

Values, such as development and social responsibilities, are added on victory-oriented Korean sport. Those change of values are along with discussions regarding improvement of players’ training environment, however, discussions on improvement of players’ training environment so far rather focused on ideological concepts, such as players’ holistic human development and human rights, therefore, there was a lack of discussion on practical training methods or teaching methods. This study focused on mental coaching as a specific method for improvement of players’ training environment. Mental coaching provides players with performance enhancement, personal growth, and self-actualization utilizing mental training, consulting, and mentoring in their training processes. This study examined a possibility of introduction of mental coaching as a training camp method for players by creating a training camp reflected on mental coaching perspectives and verifying the program effects of application. First of all, a mental coaching training camp was created through consultations with mental coaches, supervisors, and coaches. Goals of the mental coaching training camp were development of competition-routines, establishment of competition-circumstance coping strategies, comprehension of elite-players’ psychological resources, goal-setting, and motivation and the program consist of badminton competitions, mental education, a special lecture by an Olympic gold medalist, tracking, and sharing. The mental coaching training camp proceeded with middle and highschool badminton players and 31 coaches during three-days and four-nights. As results, the training camp was effective for players’ performance enhancement, personal growth, and self-actualization and team coaches realized a necessity of improvement in terms of their training and teaching behaviors. In other words, mental coaching training camp played a role as a source of long-term change as well as short-term results, thus, this study verified that the mental coaching can be introduced as a training camp method. It is anticipated that this study can provide sport fields and academic sport areas with an opportunity to consider both training contents and methods when it comes to discussion players’ training environment development.




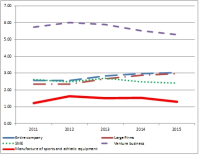
Purpose In recent years, competition among companies has become more and more important to maximize the competitiveness of companies by improving their productivity through technological innovation. Increasing competitiveness through technological innovation is becoming an essential requirement for survival of companies. In order for companies to innovate, it is necessary to spend R&D investment and the government is strengthening various policy supports to do this. Athletic equipment industry classified as manufacturing industry in sports industry. In this study, considering the fact that manufacturing industry occupies a large part of Korea's R&D investment, we compared R&D intensities with athletic equipment industry and other industries. We also examined whether R&D investment has affected firm performance. Methods The data used in the analysis were extracted from KIS-DATA with KSIC codes of companies classified as sports and athletic goods manufacturing industry in the 9th Korean Standard Industrial Classification of National Statistical Office. The analysis period is five years from 2011 to 2015 to look at the current status. Looking at the number of companies extracted by year, it was 42 in 2011, 45 in 2012, 46 in 2013, 48 in 2014, and 39 in 2015. Results Research showed that the intensity of R&D of athletic equipment industry was 1.22% in 2011, 1.63% in 2012, 1.51% in 2013, 1.53% in 2014 and 1.30% in 2015. This was lower than the manufacturing industry, which was a category of athletic equipment industry, and lower than that of similar small and medium sized enterprises. The correlation between R&D intensities and the sales growth rate of firms showed a positive correlation in 2011 and 2015, but the correlation is not strong. Conclusion R&D investment in athletic equipment industry was not actively taking place, and R&D investment did not have a significant effect on the performance of the company.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the differences in physique and physical fitness according to maturity between primary and middle school baseball players. Methods Participants were 112 elite youth baseball players (49 primary school; 63 middle school). Skeletal age estimated maturity. Physique (height, arm span, thigh volume), body composition (weight, muscle mass and body fat), physical fitness (strength, power, agility, flexibility, coordination, anaerobic power and aerobic power) were measured. An independent sample t-test was used to conduct verify the difference between physique and physical fitness according to maturity. Results The results of analyzing physical and physical fitness according to maturity showed that there was a significant difference (p<.05) between the early maturation group and on-time group in primary school baseball players, body fat percentage, muscle mass percentage, sit-up, anaerobic power and reaction time. There was a significant difference between the early maturation group and the on-time group in the middle school baseball players, weight (p<.05), thigh volume (p<.05), fat mass (p<.05), muscle strength (p<.01), power (p<.05) and coordination (p<.05). Conclusions In conclusion, the maturity of a growing baseball player may be influenced by the performance, so maturity status should be considered when judging the performance of a growing baseball player, especially a middle school baseball player.
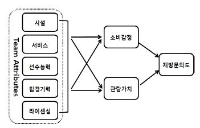
The purpose of this study was to provide managers and owners of Korea professional baseball teams with the necessary information for improving managerial performance by fan acquisition and retention. This paper chose LG, Nexen, and SK fans over the age of 17 as population of this study who visited at least twice home games held in the Jamsil, Mokdong, and Munhak baseball stadium. For the analysis of data, 413 questionnaires were used using SPSS 15.0 Windows and Amos 7.0. To examine respondents demographics traits, frequency analysis was processed and reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis and correlation analysis for relationship among the variables were conducted. Also, convergent validity analysis and discriminant validity analysis were made. Finally, path analysis was made for the verification of model suitability and of research hypotheses through structure equation modeling. The research results are as per the below. First, team attributes like physical facilities, team performance and licensing had significantly positive influence on consumption emotion. Second, team attributes like service and team performance significantly positive impact on viewing value. Third, consumption emotion had significantly positive impact on revisit intention. Fourth, viewing value had significantly positive impact on revisit intention.

