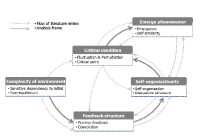
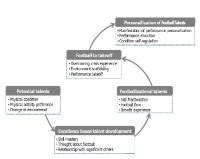
Purpose This study was aimed at interpreting the football talent development stages based on complexity theory. Methods The data for this study was gathered through literature review and in-depth interviews that were analyzed by thematic analysis. Literature review of the studies regarding complexity theory revealed the features of complexity theory and five football players participating in the K-league were interviewed. Gathered materials were analyzed by the thematic analysis. Initial codes and potential themes of football talent development stages, the conception and potential themes of the complexity theory were interpreted by metaphorical analysis. Results Results of literature review were as follows: analysis frame of complexity theory were organized environment of complexity, feedback structure, self-organization, critical condition and emergent phenomenon. The football talent development stages, interpreted as a result of literature review, were divided into Potential Talents, Excellence based Talents Development, Footballizational Talents, Football to Takeoff and Personalization of Football Talents. The stages were specifically materialized as follows: Potential Talents was materialized into physical condition, physical activity preference and change of environment. Excellence based Talent Development was materialized into skill mastery, thoughts about football and relationship with significant others. Footballizational Talents was materilized into skill fractionation, football flow and growth experience. Football to Takeoff was materialized into overcoming crisis experience, performance scaffolding and performance takeoff. Personalization of Football Talents was materialized into manifestation of performance personalization, performance evolution, condition maintenance. Conclusion Football talent development stages, interpreted by means of complexity theory, were divided into Potential Talents stage, Excellence based Talent Development stage, Footballizational Talents stage, Football to Takeoff stage and Personalization of Football Talents stage. Utilization of this study as a fundamental resource of football talents development programs and as a means to understanding football talents development is looked forward to.

PURPOSE With participants in recreational sports clubs, this study clarified positive psychological capital’s mediating effect on the relationship between exercise commitment and perceived stress. METHODS A survey conducted with individuals actively engaged in recreational sports a yielded data for statistical analysis from 296 respondents. Data processing involved frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, structural equation modeling, and testing for mediating effects using the SPSS 29.0 and AMOS 29.0 programs. RESULTS First, results showed that exercise commitment did not significantly impact perceived stress. Second, exercise commitment positively influenced positive psychological capital. Third, positive psychological capital negatively impacted perceived stress. Fourth, positive psychological capital mediated completely between exercise commitment and perceived stress. CONCLUSIONS This research encourages participation in physical activities, especially among those with low physical activity levels, because it positively affects both physical and mental well-being, ultimately enhancing social benefits and overall quality of life.
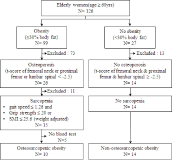
Purpose The purpose of this study were to assess physiological and biochemical characteristics in elderly women with osteosarcopenic obesity (OSO), and to analyze relationships among irisin, adipokines and bone metabolism markers. Methods 126 elderly women were selected and among them 10 women were classified into OSO group (76.9±5.2 yrs) and 14 women were classified as a NOSO group (72.9±5.6 yrs). Physique, body composition and bone mineral density were measured. Senior fitness tests were 30-s chair stand, 30-s arm curl, chair sit-and-reach, back scratch, 8-foot up-and-go, grip strength, and 2-min step test. Isokinetic muscle strength was measured by isokinetic dynamometer (Cybex 770, USA). Nutrition intake and physical activity were administered. Biochemical parameters including irisin, FNDC-5, leptin, adiponectin, CTx, 25(OH)D, osteocalcin, and PTH were measured. All data were analyzed by SAS 9.4. Independent t-test was applied to compare between OSO and NOSO groups. Multiple regression analysis was used. The level of significance was set at .05. Results The results of the study showed that there were significantly high for waist circumference, hip circumference, WHR, and BMI in OSO group compared to those of NOSO group. Higher results were also obtained for fat tissue and percent body fat but significantly low for lumbar bone mineral density. OSO group showed significant lower results for grip strength and 2-min step test compared to NOSO group. Peak torque, and relative peak torque at 60° were significantly lower for left and right knee flexion in OSO group. Protein intake was significantly low in OSO group, but no difference was obtained in level of physical activity between two groups. Irisin was significantly related to adiponectin, FNDC-5 and osteocalcin in explaining 35.2%, 81.5% and 92.1% of the variance, respectively. Conclusions This study shows that elderly women with OSO have higher results for physique and body composition parameters except body height. However, lower values were obtained for functional fitness, and isokinetic muscle strength. OSO may have more risks for metabolic syndrome, bone fractures, fall, lack of daily physical activity and limit of locomotion due to the imbalance of quadriceps and biceps femoris in non dominant leg. This study suggests that criteria and mechanism of OSO should be clarified by follow-up study.

This study was designed to investigate the effects of increment of physical activity for 12 weeks through aerobic exercise training or change from own vehicle to public transportation for commuting on physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function in middle-aged men. Forty-four subjects, aged 30-50 yrs, were randomly assigned to either one of three groups, i.e., aerobic exercise training group (TR: n=14), change to public transportation group (PT: n=15), or control group (CON: n=15). Subjects in TR performed aerobic exercise for 30 min per sessions, three sessions per week, subjects in PT changed from their own vehicle to public transportation for commuting, and subjects in CON maintained their life patterns during the same intervention period. Physical fitness, insulin resistance, inflammatory markers, and liver function were measured at pre- and post-test, and the data were analyzed by repeated two-way ANOVA. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) All variables related to physical fitness improved significantly in TR. Right grip strength, standing long jump, side step test, and sit-and-reach improved significantly in PT. 2) Although there were no significant changes in all variables related to insulin resistance, the variables tended to be improved in TR and PT. 3) TNF-α decreased significantly in TR and PT. IL-6 and CRP tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. 4) ALT decreased significantly in PT. AST and γ-GT tended to be improved in TR and PT; however, the changes did not reach statistical significant level. It was concluded that the 12 weeks of change to public transportation as well as aerobic exercise training would be beneficial for physical fitness and inflammatory markers. These interventions also would be possible to improve insulin resistance and liver function. The increment of physical activity through change from own vehicle to public transportation was found to be equally beneficial for health promotion compared to aerobic exercise.
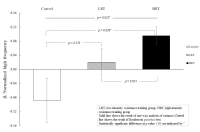
The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of resistance training with different exercise intensities on heart rate variability(HRV) in habitual smokers. Twenty-eight healthy young smokers participated in this study were randomly divided into three groups; CON(control), LRT(low-intensity resistance training; 50% 1RM), and HRT(high-intensity resistance training; 70%1RM), respectively. LRT and HRT groups performed an 8-week resistance training(4 upper- and lower body exercises) using weight training machines, whereas CON group maintained their regular activities. All groups were evaluated basal body composition, hemodynamic parameters, HRV as autonomic nervous function, and muscular strength (1RM and isokinetic test) before and after the 8-week training. To assess the effect of 8-week training with different intensities on autonomic regulation, time and frequency domain indices of HRV were calculated from 5min R-R interval recording. As results, both LRT and HRT groups increased baseline 1RM and isokinetic strength compared to CON group. Meanwhile, high-frequency power reflecting parasympathetic activity was significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. In addition, normalized low frequency power(LF nu) indicating a shift of sympathovagal balance towards sympathetic predominance significantly decreased while normalized high frequency power(HF nu) which reflects vagal predominance significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. Furthermore, improved cardiac autonomic regulation and parasympathetic activation had significant association with increased muscular strength. Overall, the 8-week training has enhanced muscular strength in both training groups, particularly autonomic balance improved in young habitual smokers with high intensity resistance training.

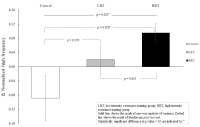
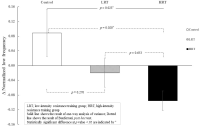
PURPOSE This study aimed to explore ways to utilize augmented reality (AR) in school sports and leisure by examining the case of an elementary school sports club using augmented reality-based e-sports. METHODS A self-study approach and Eisner's(1995) educational criticism were utilized. Data including photos, videos, literature, and memory boxes related to the elementary school AR sports club were collected weekly during the school semesters from March 2023 to January 2024, spanning a total of 30 weeks. The data were analyzed following the stages of analysis by Elo & Kyngäs(2007). RESULTS Augmented reality can act as a personalized exercise coach by visualizing physical activity information. Through posture and movement analysis, education on physical strength and expression can be provided that is linked to home; it can also expand the range of sports experiences and create a new sports culture. In order to effectively utilize AR, edtech field experts must be trained, and content must be developed through cooperation between companies and schools. The educational effectiveness of the content must be verified and the management system must be inspected, and public facilities utilizing edtech must be expanded. CONCLUSIONS AR has endless development potential in school sports and leisure, but these will require active interest and support from educational authorities.
PURPOSE This study investigated the associations between physical fitness and fall efficacy with thigh circumference in elderly women with osteopenia/osteoporosis. METHODS A total of 166 female participants aged 76.3±5.0 years with –1.0≥T-score of femur neck bone mineral density were voluntarily recruited from local community centers. The participants were classified as low 25%, middle 50%, and high 25% groups based on their thigh circumference. Physical fitness measurements, including strength, flexibility, aerobic endurance, and balance were measured with a standardized protocol. The Korean version of the fall efficacy scale (K-FES) was used to assess fall efficacy. Logistic regression analysis was used to estimate odd ratio (OR) of poor physical fitness and low fall efficacy according to thigh circumference levels. RESULTS In terms of physical fitness, the middle 50% group (OR=0.430, 95% CI=0.194-0.953) and high 25% group (OR=0.129, 95% CI=0.049-0.343) had significantly higher linear trend for poor physical fitness compared to the low 25% group (reference), (p<0.001). In fall efficacy, the middle 50% group (OR=0.279, 95% CI=0.119-0.656) and high 25% group (OR=0.100, 95% CI=0.036-0.275) had significantly higher linear trend for low fall efficacy compared to the low 25% group (reference) (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS The current findings suggest that maintaining high thigh circumference via regular physical activity and diet may contribute to attenuation of decreased risk for poor physical fitness and low fall efficacy in elderly women with osteopenia/osteoporosis.
Purpose The purpose of this research is to provide implications for the study of the physical education curriculum in Korea and China by comparatively analyzing the revised high school physical education curriculum in the two countries. Methods Using Bereday(1964)’s four steps of comparison model in education, this study focuses on the format and content of the general high school physical education curricula of Korea and China, each curriculum having been revised respectively in 2015 and 2017. Results First, in terms of format, both countries consider PE a necessity and share similarities in regard to course structure, credit allocation and document format. Nevertheless, though both countries are oriented toward competency-centered education, there are some differences with respect to official education curriculum documents, numbers of subjects and hours of study based on the reality and situation of each country. Second, in terms of content, both countries present various teaching methods and evaluation principles for the sake of acquiring core competence. However, the Korean curriculum prefers to advocate learning of the value of physical activity to achieve core competencies, while the Chinese curriculum prefers to focus on acquiring athletic skills and health knowledge for achieving core competencies. Conclusions After comparing physical education curriculum in both countries, two implications could be obtained. One is that the consistency problem in Korea should be solved between the core competency, the teaching and learning methods and evaluation standards. The other is that, in China, integrated value of physical education should be paid more attention and core competency as well as teaching and learning methods should be considered.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a Korean Life Skills Scale for Sports (KLSSS) that original version is the LSSS developed by Cronin and Allen (2017). Methods The subjects were 899 middle school and high school students. The measurement tool was used with LSSS. The validation of KLSSS followed a three-stage of validation procedure; substantive stage, structural stage, and external stage. The result is as follows. Results First, In the substantive stage, KLSSS consisted of 47 items with 8 factors. As a result of the item clarity test, it was confirmed that all the items were appropriate. Second, in the structural stage, KLSSS was explored and confirmed as 5 factors and 18 items. Third, in the external stage, KLSSS showed discrimination and convergent validity. Conclusions KLSSS is composed of 5 factors and 18 items. The factors are teamwork (TW), goal setting (GS), time management (TM), social skills (SS), and leadership (LD). This scale can be used to obtain information on life skills in school physical education or sports.
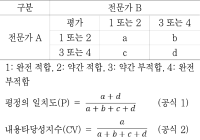
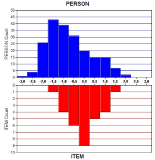
Purpose Common content knowledge(CCK) is composed of rules, techniques, and tactics. Such knowledge is a requirement for effective teaching of physical education (PE). There are, however, few validated tests of CCK. Thus, the purpose of this study was to develop a CCK test of soccer and evaluate the validity and reliability of the test using Rasch modeling (Rasch, 1980). Methods We developed thirty item common content knowledge test for soccer. Then, we used Rasch modeling to evaluate the validity and reliability of a test of soccer. Pre-service teachers (N=92) majoring in physical education and non-PE major (N=111) participated in this study. Results Thirty questions demonstrated good item-model fit. Moderately high internal consistency for person-ability and high internal consistency for item-difficulty are reported. Both Infit and Outfit statistics showed a good fit between the data and the Rasch model. Conclusions The analysis provides evidence to support the validity and reliability of this instrument as a CCK test of soccer. Limitations of the study were discussed and suggestions were provided to improve the test.