PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to understand the athletic identity of youth football players and to trace its changing trend. METHODS Participants of this study included 93 players in 2005 and 94 players in 2021, who were in middle and high schools. All participants answered open-ended questionnaires. After the results of the inductive content analysis, the changing trend of the results was assessed. RESULTS The athletic identity of youth football players were collected from 811 raw data samples collected in 2005 and 741 collected in 2021 and categorized into 19 sub-categories and 5 categories. The results show a tendency to be specific to football. The athletic identity of a football player itself is weakening, being replaced by the identity of being a student. The role of the camp is also weakening, while more privacy and autonomy are allowed to the players. As a result, efforts to secure the players’ right to study were accepted by the players, and expected to decrease as camp life with limited privacy is on the decline, and as senses toward one’s physical competence are changing. CONCLUSIONS Sociocultural contexts, including changes in the system and social modifications, are reflected in the football player's athletic identity and its changes. The athletic identity of youth football players has changed from its 2005 version of unacademic camp life with limited privacy to the 2021 version, where the player leaves camp to be provided with privacy and attend classes.
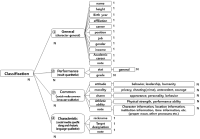
Purpose Soccer-related social media BigData includes complex information related to soccer players and is continuously and instantly generated. Text mining research is actively carried out for this kind of social media contents analysis, but it tends to be analyzed with limited linguistic characteristics such as understanding of language complexity and context, ambiguous terms, rhetoric, and new terms. This can be attributed to the fact that the tools commonly used for text mining use universal terminology dictionaries and packages that exclude the peculiarities of the analysis themes. The purpose of this study is to develop an Ontology model, which are representative tools for defining semantic ambiguity and relationships and systems between terms of text data. Methods In order to achieve the research objectives, we applied the 7-step development method of ‘Ontology Development 101: A Guide to Creating Your First Ontology’, which is useful for ontology development. Each step includes 1) Determine the domain and scope of the ontology 2) Consider reusing existing ontology 3) Enumerate important terms in the ontology 4) Define the classes and the class hierarchy 5) Define the properties of classes-slots 6) Define the facts of the slots 7) Create instances. In particular, the 3rd-step of this study, the glossary stage, is to extract core terms that make up he ontology, but since the goal of this study is to develop the ontology that can be used in social media contents analysis of soccer players, we conducted a social media text analysis related to actual soccer players and selected 484 core terms. Results The ontology which was developed in this research for social media contents analysis of soccer players consisted largely of four parts(General terms, performance results terms, common terms, and Characteristic term) and classified according to the content characteristics of the term. Conclusion Developed ontology in this study is object-oriented that defining classes and objects to define divisions and relationships between terms and also means a social media contents knowledge system of soccer players. In addition, it performs a function as a secondary tool which can be utilized for atypical data analysis.

This study was to identify the perception on retirement for professional soccer players as a basic study for the development of career transition program, Professional soccer K-League(K-League Classic, K-League Challenge), N-League(Club League), K3-League(Challenger League) league players registered in 2013 were selected as a population. Structured questionnaire surveys were utilized for the research, total of 1000 questionnaires(250 per league) were distributed and gathered. Final sample of 548 questionnaires were analyzed excluding people which do not respond properly. SPSS was used to identify the characteristics of the responder in frequency analysis. One-way ANOVA was used to find the difference in retiring causes among the leagues, Pearson Correlation analysis was used to examine the correlations among the variables. Multiple regression analysis was used to find the effect of economic and psychological preparation on plans after retirement. The results were as follows. First, among the causes of retirement, 'contract suspended', 'seek other life', 'family issues such as marriage' showed the difference in perception of retirement according to the leagues. Second, psychological preparation was more focused than economic preparation to prepare for retirement planning among players, respectively.
PURPOSE This study aimed to explore the re-socialization process of college soccer players who rejoin college soccer clubs after dropping out. METHODS A case study approach was employed, and participants were selected using the snowball sampling method. Data were collected through in-depth interviews, participant observation, and literature reviews. The authenticity of the data was validated through triangulation, member checking, and peer debriefing. All research procedures were conducted following approval from the institutional review board. RESULTS The study revealed several key findings. First, participants faced numerous challenges during the re-socialization process into sports, including interpersonal, academic, and emotional difficulties. Second, distinctive features of the re-socialization process emerged, including the determination and effort required for adapting to university life, support from socialization agents within the university, and rapid re-socialization following dropout. Third, experiences within collegiate soccer clubs indicated low barriers to entry for former athletes, academic success through complementary relationships, a hierarchical culture familiar to student-athletes, and enhanced satisfaction in interpersonal relationships and a sense of belonging. CONCLUSIONS This study underscores the importance of institutional support that enables college athletes to participate in sports clubs, facilitating the successful re-socialization of athletes who have dropped out.

[Purpose] This study aimed to examine the effects of complex physical training on exercise and football performances in youth football players. [Methods] The subjects (n=16) were randomly assigned to either a complex physical training group (CPG, n=8) or a control group (CON, n=8). CPG was performed the complex physical training for 50 minute per day, and 2∼3 times per week, for 8 weeks. Exercise performance (health related physical fitness, skill related physical fitness, Y-balance and functional movement screen; FMS) and football performance (juggling, speed dribbling, shot passing, long kick and triple hop) were measured before and after 8 weeks complex physical training. [Results] Sit-up (p=0.002), sit and reach (p=0.040), 50-m run (p=0.031), side step (p=0.005), single-leg standing with eyes closed (p=0.040), plank (p=0.023), dominant composite score (p=0.002) and non-dominant composite score (p=0.005), deep squat (p=0.009), inline lunge (p=0.042), active straight leg-raise (p=0.015), rotary stability (p=0.049), total score(p=0.001), speed dribbling (p=0.030), dominant triple hop (p=0.001) and non-dominant triple hop (p=0.032) were statistical significant interactions between group and time. [Conclusion] Our findings indicate that complex physical training has beneficial effects on performance improvement of exercise and football in youth football players.

PURPOSE This study aimed to develop physique and basic physical fitness evaluation criteria for middle school soccer players, providing a foundation for training and player development to be used by coaches in the field. METHODS The study involved 440 middle school soccer players (Grade 1=178, Grade 2=132, and Grade 3=130). Measurements were conducted on seven physique and ten basic physical fitness factors. Measurement results were organized using Windows Excel 2021 and descriptive statistics were performed using Windows SPSS 26.0. Based on the descriptive statistics of the measurement results, the Cajori 5-Grade evaluation method was applied to establish evaluation criteria for each grade and fitness component. RESULTS The study results provide evaluation criteria for middle school soccer players based on the measured data, considering grade, physique, and basic physical fitness. CONCLUSIONS The criteria established in this study are expected to be widely utilized by coaches in the field to set training goals for areas such as player selection, development, injury prevention, and rehabilitation.
It has been known that β-alanine supplementation induce the increment of carnosine in vivo and was effective in delaying fatigue by buffering the hydrogen which was formed during exercise. This study was designed to investigate the effects of 4 weeks of β-alanine supplementation on physical fitness and blood lactate concentration in middle school soccer players. Nineteen middle school soccer players were randomly assigned to either one of two groups, i.e., β-alanine group (n=10) and placebo group (n=9). Subjects in β-alanine group consumed β-alanine 2 g/day during 1st and 2nd week, as well as 3 g/day during 3rd and 4th week, whereas subjects in placebo group consumed maltodextrin in the same manner. All subjects ate same menu and trained same amount at the same training camp during the intervention period. Body composition, aerobic capacity, anaerobic capacity, isokinetic function, and blood lactate concentration during maximal GXT were measured at pre- and post-test. Main results of the present test were as follows: 1) Fat mass and percent body fat decreased significantly in β-alanine group. 2) No significant changes were found in variables related to aerobic capacity in both groups. 3) Average power increased significantly in β-alanine group. 4) Isokinetic muscular endurance increased significantly in β-alanine group. 5) Blood lactate concentration did not change in eithet group; however, blood lactate concentration immediately after maximal GXT in β-alanine group tended to be increased more than placebo group. It was concluded that β-alanine supplementation would have positive effects for improvement of body composition, anaerobic capacity, and muscular endurance in middle school soccer players.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the relationship among emotional leadership, coach trust and athletic satisfaction of university. Methods 288 university soccer players were surveyed on the emotional leadership questionnaire, coach trust questionnaire and athletic satisfaction questionnaire through convenience sampling method. SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 were used to achieve the purpose of this study. Frequency analysis, confirmation factor analysis, reliability verification, correlation analysis and the structural equation model analysis were performed. Results First, emotional leadership had a positive effect on coach trust of university soccer players. Second, emotional leadership had a positive effect on athletic satisfaction of university soccer players. Third, coach trust had a positive effect on athletic satisfaction of university soccer players. Finally, coach trust mediated the relationship between emotional leadership and athletic satisfaction. Conclusions Emotional leadership was a leadership that can efficiently increase coach trust, and leaders must communicate with players through emotional effort and team operations with goals of athletic satisfaction and happiness rather than wins and losses were required.
PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to explore the effects of the student-athlete and student peer mentoring program as a collegiate class. METHODS The peer mentoring program, conducted at A University in the first semester of the 2023 school year, was evaluated using practical action research (Zuber-Skeritt, 1996). RESULTS In the introduction stage, ‘relative and absolute evaluation’, ‘member ratio’, and ‘definition of professor role’ were categorized as challenge issues. In the progress stage, ‘de-formalized lecture method’, ‘student athlete’s coaching experience’, and ‘student’s experience of football culture’ were discovered as possibilities, while ‘vacancy and absence of mentor-mentee’, ‘limited group activities and limitations of team sports’, and ‘lack of objective evaluation’ required improvement. At the end stage, student-athletes experienced changes in values such as self-identity, football, and human relationships, as well as quantitative and qualitative changes in sports participation. CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the potential of the peer mentoring program as a collegiate class as well as its practical significance for guaranteeing student-athletes' learning rights and for forming sports culture on collegiate campuses.
Purpose This study aims to explore migration factors of Korean male footballers who have moved from South Korea to Southeast Asian countries. Methods Qualitative case study was conducted with 9 footballers, 4 their agents and 2 K-league staffs as the participant. Results As a result, by regarding their migration as involuntary decision, this study could provide academic and practical discussion on sport labor migration. First of all, this study established theoretical framework for involuntary migration of the participants through ‘Push-Pull Theory’ which focuses on demand and supply on the labor force. Second, this study found that a local rule (FA compensation system) of Korean professional football league (K league) and hierarchical collectivist culture contributed to their migration, which has not been reported by previous studies focused on the voluntary migration of mainstream players and it reflected local context of K league. Conclusions In conclusion, this study confirmed that sport labor migration was also considered as social phenomenon and reflected a cross section of a particular society. Through the migration of athletes, we can provide a variety of viewpoint on economic (market) structure, related policy and system in a particular society, and understand migration motives in terms of agency (subculture).