Purpose This study conducted legal, institutional and pedagogical consideration on C0rule in Korean collegiate sport. Methods (1) Systematically examined the unconstitutional elements of C0rule in terms of the basic rights of student-athletes, and (2) reviewed pedagogical validity in terms of higher education, college credit system and physical education. Results First, C⁰rule adopted the result (the credit) of the uniform education as the standard of sanctions. Providing discriminatory educational opportunities according to academic credit is regarded as the infringement of equal rights. Second, since the college sports league is the only place to prepare for vocational education and employment for student-athletes, restricting their opportunities according to the credit is also against the freedom of happiness and choice of profession. Third, C0 credit, the minimum standard, overlooked purpose and level of higher education and rigorous evaluation. Last, C0rule has resulted in overlooking the academic significance and status of college education, especially physical education. Conclusions This study is meaningful in that it brought the subjects to discourse field and provided opportunities to review the fundamental problem of the school sport and the basic rights of student-athletes. At the present stage of the transition of the school sport system due to the introduction of various regulatory systems, we should be careful about oligopoly and unilateral flow of knowledge and production of other alienation.
The purpose of this study was to describe the epidemiology of Korean collegiate injuries during 2015. Collegiate student-athletes(n=167) in six sports (badminton, baseball, basketball, rugby, taekwondo, and volleyball) participating in all practices and games during pre-season, in-season, and post-season were tracked via the injury surveillance system(rate, location, type, and cause of musculoskeletal injury). Injury rate for 1000 athlete-exposure(AE) and 1000 time-exposure(TE) were calculated with 95% confidence intervals(CI). We captured a total of 961 injuries, a rate of 19.29/1000 AE(95% CI=18.07, 20.51) and 0.16/1000 TE(95% CI=0.15, 0.17). Commonly injured body locations were knee(17.5%, n=168), thigh(16.1%, n=155), ankle(12.1%, n=116), and finger(8.4%, n=81). Injuries were mostly diagnosed as contusion(40.1%, n=385), ligament sprain(21.1%, n=203), and laceration/abrasion/skin injury(13.5%, n=130). Common causes were contact with another athlete(44.6%, n=429), contact with moving object (12.7%, n=122), overuse/atraumatic(11.9%, n=114), and contact with non-yielding object(9.4%, n=90).
PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to explore the effects of the student-athlete and student peer mentoring program as a collegiate class. METHODS The peer mentoring program, conducted at A University in the first semester of the 2023 school year, was evaluated using practical action research (Zuber-Skeritt, 1996). RESULTS In the introduction stage, ‘relative and absolute evaluation’, ‘member ratio’, and ‘definition of professor role’ were categorized as challenge issues. In the progress stage, ‘de-formalized lecture method’, ‘student athlete’s coaching experience’, and ‘student’s experience of football culture’ were discovered as possibilities, while ‘vacancy and absence of mentor-mentee’, ‘limited group activities and limitations of team sports’, and ‘lack of objective evaluation’ required improvement. At the end stage, student-athletes experienced changes in values such as self-identity, football, and human relationships, as well as quantitative and qualitative changes in sports participation. CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the potential of the peer mentoring program as a collegiate class as well as its practical significance for guaranteeing student-athletes' learning rights and for forming sports culture on collegiate campuses.
PURPOSE This study aimed to explore the re-socialization process of college soccer players who rejoin college soccer clubs after dropping out. METHODS A case study approach was employed, and participants were selected using the snowball sampling method. Data were collected through in-depth interviews, participant observation, and literature reviews. The authenticity of the data was validated through triangulation, member checking, and peer debriefing. All research procedures were conducted following approval from the institutional review board. RESULTS The study revealed several key findings. First, participants faced numerous challenges during the re-socialization process into sports, including interpersonal, academic, and emotional difficulties. Second, distinctive features of the re-socialization process emerged, including the determination and effort required for adapting to university life, support from socialization agents within the university, and rapid re-socialization following dropout. Third, experiences within collegiate soccer clubs indicated low barriers to entry for former athletes, academic success through complementary relationships, a hierarchical culture familiar to student-athletes, and enhanced satisfaction in interpersonal relationships and a sense of belonging. CONCLUSIONS This study underscores the importance of institutional support that enables college athletes to participate in sports clubs, facilitating the successful re-socialization of athletes who have dropped out.
Purpose Recently, studies associated with the negative physical and mental effects of athletes’ pain have received extensive attention. This study confirmed the validity of the pain catastrophizing scale (PCS) developed in clinical settings and is widely used in the sports field, and examined their relationship between the perceived stress levels and fear of pain. Methods The pain catastrophizing consisted of 13 items of three factors which are Helplessness (6 items), Rumination(4 items), Magnification(3 items). To verify the validity, PSC was revised by following the recommended revision guideline procedures. To test the validation of pain catastrophizing, 206 adult athletes were recruited including the collegiate, professional, and national levels. The participants were instructed to complete questionnaires to assess the level of pain catastrophizing, perceived stress, and fear of pain. Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) to test the fit of measurement model was adopted to examine three higher-order three-factor measurement models. Results In results, confirmatory factor analysis indicated that the Korean version of the pain catastrophizing scale demonstrated a good model fit of measurement when removing one item with a significantly lower factor load as well as the reliability of the scale was reasonable. The pain catastrophizing had a meaningful positive direct relation with perceived stress level and fear of severe pain. In addition, construct validity and predictive validity of PCS showed valid. Conclusions Based on the results of this study, the Korean sports pain catastrophizing scale can be used to measure the subjective pain intensity of Korean athletes. In addition, it is expected to provide fundamental information for evaluating athletes’ post-injury rehabilitation processes.
PURPOSE This study assessed elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness and developed reference standards for both their basic and specialized physical fitness. METHODS Data for analysis were collected from 870 athletes: from national teams, 123 elite Taekwondo athletes from the Performance Analysis and Assessment System (PAAS) administrator website (1999–2020); from regional sports centers, 731 collegiate and general division elite Taekwondo athletes (2015–2019); and from Y University, 16 elite Taekwondo athletes. Through measurement items’ selection and categorization, 20 physical fitness items were selected for the reference standards’ development, including 9 for basic fitness and 11 for specialized fitness. Taekwondo weight classes were divided into two: light + middle (fin, fly, bantam, feather) and middle + heavy (light, welter, middle, heavy). RESULTS Descriptive statistics for basic and specialized physical fitness items were categorized by gender and athletes’ fitness level. The reference standards’ development was aligned with existing standards, integrating the Cajori physical fitness 5-levels. It also introduced minimum physical fitness reference standards and target achievement reference standards for evaluating elite Taekwondo athletes’ physical fitness. CONCLUSIONS The reference standards proposed here can serve as objective indicators in selection of national representative athletes and also provide foundational data to establish fitness goals and evaluate future elite athletes’ physical fitness.
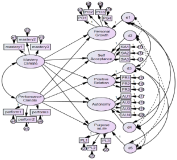
Purpose This study identified the influence of perceived motivational climate on psychological well-being in ballet majors. Methods Participants were 211(male=25, female=186) collegiate students enrolled in ballet department. Measures were The Perceived Motivational Climate in Sport Questionnaire(PMCSQ) and Psychological Well-being Questionnaire. Data were analyzed by using descriptive statistics, reliability test, correlation, and structural equation modeling. Results Results were as follows. First, mastery climate who ballet majors perceive significantly influenced on the five subscales of their psychological well-being: Mastery climate was positively related to personal growth, self-acceptance, positive relation with others, autonomy, and purpose in life. Second, performance climate who ballet majors perceive significantly influenced on the five subscales of their psychological well-being: Performance climate was negatively related to personal growth, self-acceptance, positive relation with others, autonomy, and purpose in life. Model fit indices were acceptable(RMSEA=.070). Conclusion In conclusion, this study indicated that motivational climate who ballet majors perceive was a important situational factor on their psychological well-being.
