
Purpose The purpose of this study is to identify the causal relationship between competitive strategy, absorption capacity and business performance of commercial fitness center and to confirm the control effect of absorption capacity between competitive strategy and business performance. Methods 330 fitness center managers and administrators were selected for the study. Out of 330, 308 questionnaires were collected and used for data analysis. The questionnaire consisted of confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis and structural equation model analysis. Finally, Ping 's two - step approach was used to verify the moderate effect of absorptive capacity. Results The results of the study are as follows. First, competition strategy of fitness center has a positive effect on absorptive capacity. Second, the competition strategy of fitness center has a significant effect on business performance. Third, the absorptive capacity did not effect the management performance. Fourth, the absorptive capacity was found to be moderate effect between the competition strategy and the management performance of the fitness center. Conclusion Based on the results, the fitness center managers and administrators of fitness center should set up competitive strategy internally and increase absorptive capacity to utilize external information by internalizing it.


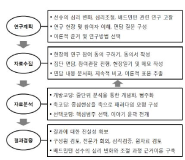
This study was purposed to explore psychological change and regulation process during badminton competition. The data were conducted using group interviews and participation observations who 18 K college badminton players. The data were analyzed using open, axial, and selective coding based on grounded theory method (Strauss & Corbin, 1998). The results were as follows: Open coding results, 89 concepts, 44 subcategories, and 18 categories emerged as psychological change and regulation process during badminton competitions. Axial coding results, the categories are showed structural relationships such as performance, score, psychological momentum, the importance of competition, court environment, physical condition, competition strategy, psychological preparation, past experience, outcome expectation, psychological disturbance, psychological skills, game situation-changing strategy, support-seeking strategy, significant others' behavior, the opponents' behavior, psychological resilience, and maintenance psychological disturbance. Selective coding results, core category of this study was revealed to maintain psychological homeostasis. Environmental context during badminton competitions causes specific situations and events that evoke psychological disturbance. In turn, a player seeks mental and behavioral strategies to maintain psychological homeostasis. There is psychological homeostasis mechanism during badminton competitions for peak performance. Development of proper interest for psychological homeostasis will be improved through this research approach in sport psychology.

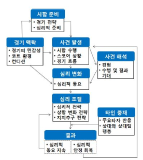

This study was to verify the structure of efficacy related to performance perceived by short-track athletes when playing a match. Therefore, 50 players answered open questionnaires and 200 players participated in construct validity verification, a total of 250 players of short-track members of national, business and university team were sampled during the research phase. The data was analyzed through the study procedures. The results were as follows: First, efficacy structure of players during the match were categorized into three groups as game managing strategy(including course management, race control, match management and selective attention ability), psychological control ability(including positive imagery, match competition, competitive spirit, ability to handle hardship, anxiety control, and patience), and physical usage of ability(including physique, endurance, and quickness). Second, the result of the first construct validity verification through exploratory factor analysis showed 7 factors in 29 items as game management, course management, psychological control, physical use, coping with hardship, speed control and psychological stability. Finally, as a result of confirmatory factor analysis, short-track self-efficacy showed the 5 factor in 15 items except for coping with hardship and psychological stability.


Purpose This study has been conducted to explore the factors that ignite the mental toughness of Taekwondo players and to compare report ratios concerning the explored factors between training and competition. Methods An open-ended questionnaire conducted 123 Taekwondo players offered raw data that stemmed the from 379 training and 369 competition situation. The raw data was categorized by an inductive approach, and the report ratios of both general and specific domain mental toughness in training and competition were compared. Results The results of this categorization were as follows. First, the mental toughness ignition factors of Taekwondo players are commonly categorized as willing to goal, external pressure, reward expectation, challenge, and social support. Second, factors were prioritized into reward expectation, challenge, willing to goal, social support, and external pressure. Third, willing to goal and external pressure were often reported in training, while reward expectation and challenge were more often reported in a competition. Social support showed similar ratios in both settings. Conclusion This study is expected to offer interesting results in the context of the ignition of mental toughness, while being utilized as a fundamental database for the development of mental social support strategies the help Taekwondo players ignite their mental toughness in competition.



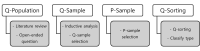
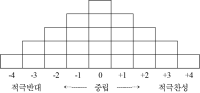
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the badminton players psychological disturbance and coping strategies types and characteristics. Methods To achieve the purpose of this study, an open-ended questionnaires were used targeting 194 badminton players, 25 Q samples were selected by collected data as the self – statement. Q samples were classified depending on their subjective experience by P samples composed of active badminton players who had more than eight years of athletic career; this data were coded and analyzed by VARIMAX rotation. Results The results revealed by the Q methodology were below. First of all, the first type is named as (Internal Disturbance - Passive Coping) type. The first type is psychologically disturbed by internal factors, and negative about external coping strategies. Second, the second type showed the higher awareness of coping strategies than the other types; It was named as (Active Coping) type. Third, The third type recognized the burden of victory and self-confidence, and it was named as the type of (Victory Obsession). Conclusion In the badminton competition, the deterioration of concentration and judgment ability because of psychological disturbance has a serious effect on the performance. Therefore, based on the results of this study, it will be possible to improve the performance by appropriate psychological intervention through the characteristics of the athletes.

PURPOSE This study examined the effects of focus of attention on beginning golfers’ competitive anxiety and motor performance. METHODS Forty-eight college students with no prior golf putting experience were selected as participants and randomly assigned to internal-focus, external-focus, holistic-focus, and control groups (12 participants each). All subjects performed 5-m golf putting in acquisition, noncompetitive, and competitive situations. RESULTS In competitive situations, the internal-focus, holistic-focus, and control groups showed golf putting accuracy and consistency similar to those in noncompetitive situations, whereas the external-focus group’s golf putting accuracy and consistency were significantly lower in competitive situations than in noncompetitive situations. In addition, the holistic-focus group showed significantly higher golf putting accuracy than the control group in both competitive and noncompetitive situations. CONCLUSIONS Holistic-focus can be used effectively as a strategy for beginners to learn motor skills and reproduce learned motor skills when state anxiety increases. However, external attention focus cannot be considered a strategy to induce effective beginners’ exercise performance when competitive state anxiety increases.
PURPOSE This study investigated weight-class-related strength parameters during pulling performance in the ssireum. METHODS Elite ssireum athletes participated, 24 divided into four weight classes of six athletes each. They performed a pulling task while gripping a tube fixed to a three-axes load cell sensor, standing on force plate platforms. The test involved 30 repetitions at maximal force with the legs bent, the ssireum’s typical posture. Maximal force (Fmax), time to maximal force (TFmax), time difference between maximal forces (TDmax), and horizontal and vertical angles at maximal force (HAmax and VAmax, respectively) were analyzed from the load cell sensors. Ground reaction force (GRF) was collected, including peak force along the three axes, the resultant force, and the center of pressure (COP). One-way ANOVA tests were conducted to compare among weight classes (α=.05). RESULTS Fmax measured by load cell showed significant difference between classes (p<.05), indicating that the second weight group (Geumgang class) generated more pulling force than the heavier classes. In GRF results, lightweight classes demonstrated larger COP difference between the left and right plates. Specifically, the Geumgang class showed more movement in the anterior-posterior (AP) direction on the left plate. The peak GRF in the right plate of the AP (p<.001) and ML (p<.05) directions showed significant differences between lighter and heavier weight classes. CONCLUSIONS The Geumgang class generated greater pulling force, and the lighter classes demonstrated more leg contribution. Force generation did not solely depend on body mass; instead, lighter athletes often relied on the lower limbs to compensate for their limitations, a strategy commonly observed in competitions.
PURPOSE Players’ nonverbal behavior during a game may be expressed through selfregulatory and intentional processes, where nonverbal cues are strategically used to achieve specific outcomes. This study aimed to observe and explore the strategic and intentional nonverbal behaviors utilized by table tennis players. METHODS The study utilized a grounded theory methodology and involved purposeful sampling of ten adult table tennis players. Semi-structured face-to-face interviews were conducted. The collected data were analyzed using open, axial, and selective coding techniques. RESULTS The findings revealed that players’ intentional nonverbal behaviors are influenced by their confidence levels, physical condition, and perceptions of others’ nonverbal cues. Throughout this process, players underwent various emotional experiences, worked to maintain a positive mental state, and experienced changes in both their behaviors and psychological states, which impacted the flow of the game. CONCLUSIONS This study’s results provide valuable insights into the role of intentional nonverbal behaviors utilized by athletes during competitions. This suggests that understanding and incorporating intentional nonverbal behavior should be a key consideration in sports psychology counseling and psychological skills training.

Purpose Based on the match data of major judo world competitions in the last five years, this study identifies differences in general characteristics and environmental factors according to scoring technique and scoring times. And by exploring the factors associated with scoring technique, I would like to present a practical strategy that can be used to establish guided tactics. Methods 50,828 points were used for analysis of the entire men and women who competed from 2016 to 2020. Differences in the characteristics of the world's leading athletes according to their types of technique were used in conjunction with the chi-square test and the one-way ANOVA with Sceffe test to produce results. Results The results of this study showed that the type of skill by foot technique was the most common, and the ratio of hand skill to female player to push and foot skill was relatively high. The higher the weight class, the lower the ratio of hand technique, the higher the press rate, and the frequency of skill types also increased. At the Olympic Games, the ratio of hardening technique was higher than that of other competitions, and as the year progressed, the ratio of hand and waist technique increased, and the number of mat-hold decreased. The ratio of hardening technology was relatively high, and the ratio of hand-to-foot technology was relatively high as the semi-final and final rounds were higher. As for technical time, the male athlete's skill time appeared to be about 12 seconds longer on average, with the lowest in the heavyweight class and the longest in the lightweight class. Athletes from the Asian continent appeared to have the longest technical time, which is believed to have resulted from the characteristics of excellent physical strength, good endurance, and strong hardening technique. The skill time leading to the score by pressing and hand skill was the longest, and the waist skill and grip skill time were relatively short. Half of them appeared about 5 seconds shorter on average compared to the first round, and the more important the game (the 4th round, semi-final, and final) the longer the skill time. Conclusion In conclusion, through this study, the characteristics of the world judo players' skill types and time were confirmed, and based on this, it is necessary to analyze and systematize the technical types of the world's best athletes, including Korean athletes, in order to improve their judo performance.


This study aimed to explore elite taekwondo competitors’ imagery strategies . The study participants were 10 elite taekwondo athletes, who worked for S business team. Data were collected through open-ended questionnaires and in-depth interviews. The data were collected based on Gould et al. (1992)’s proposed qualitative research method. The inductive content analysis of the imagery was conducted following the imagery type of Paivio (1985) and Suinn (1996). The law data and case of imagery were separated by three specialists. The results were as follows. First, elite taekwondo competitors generally used the types of imagery proposed by Paivio (1985) and Suinn (1996). In particular, imagery of anxiety regulation appeared with the highest frequency among factors and ordered imagery of motivation, imagery of skills, imagery of mental skills, and imagery of competition. Second, elite taekwondo competitors mainly used imagery of skills before two weeks for competition. They mainly used imagery of anxiety regulation the day before a competition. They used imagery of anxiety regulation and imagery of motivation on the day of a competition. They used imagery of motivation after the competition. In sum, elite taekwondo competitors used individual strategies in terms of imagery in order to ensure effective training and peak performance in competition. The strategy of imagery was applied differently based on the juncture of the competition.