Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the Emotional Intelligence Scale in Sport Coaching(EISSC) based on the emotional intelligence trait model. Methods The participants were 236 professional sports coaches by the purposive sampling methods via e-mails. 48 preliminary items were developed by literature review among expert panels. Then, a total of 40 items were selected after the item-analysis. Exploratory factor analysis was conducted for construct validity and criterion validity was evaluated by Person’s correlation with coaching efficacy scale and general emotional intelligence scale. An internal consistency, Cronbach's alpha coefficient, was used to see the reliability. Results The results of exploratory factor analysis presented a six sub-structure factors (Self-awareness, Awareness of others, Optimism, Utilization of emotion, Emotion regulation, Social skills) with 20 items, which explained 68.49% of the total variance. Criterion-related validity was supported by correlations with in coaching efficacy(r=.713) and general emotional intelligence(r=.647). Reliabilities were secured with Cronbach’s alpha coefficient .854 for the total 20 items. Conclusions The EISSC can be used to provide an valid measure of emotional ability of coaches in sport.
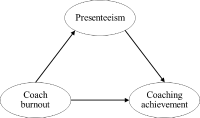
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship among burnout, presenteeism, and coaching achievement perceived by athlete coaches in the sport field, and to identify the mediating effect of the presenteeism on the relationship between burnout and coaching achievement. Methods For this purpose, data were collected from 151 athlete coaches in South Korea through the survey. Measurement tools consisted of questionnaires on the coach’ burnout and presenteeism (SPS-13) that were designed in line with the research purpose. Collected data were analyzed using reliability testing, descriptive statistics, correlation analysis and simple mediation effect test. Results First, burnout level perceived by coaches was positively related to presenteeism, and not associated with coaching achievement. And presenteeism negatively correlated with coaching achievement. Second, the burnout level of the coach was negatively related to the coaching achievement through the presenteeism, the mediating variable. Conclusions Burnout of the athletes' coaches in the sports field has been confirmed to decrease the coaching achievement by increasing the presentations which is the work impairment due to their health problems.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the relationship among emotional leadership, coach trust and athletic satisfaction of university. Methods 288 university soccer players were surveyed on the emotional leadership questionnaire, coach trust questionnaire and athletic satisfaction questionnaire through convenience sampling method. SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0 were used to achieve the purpose of this study. Frequency analysis, confirmation factor analysis, reliability verification, correlation analysis and the structural equation model analysis were performed. Results First, emotional leadership had a positive effect on coach trust of university soccer players. Second, emotional leadership had a positive effect on athletic satisfaction of university soccer players. Third, coach trust had a positive effect on athletic satisfaction of university soccer players. Finally, coach trust mediated the relationship between emotional leadership and athletic satisfaction. Conclusions Emotional leadership was a leadership that can efficiently increase coach trust, and leaders must communicate with players through emotional effort and team operations with goals of athletic satisfaction and happiness rather than wins and losses were required.

Purpose This study was to examine the effect of athletes’ personality on coach-athlete maintenance of relationship. Methods For this purpose, the data was collected by 284 athletes using personality five factor questionnaire and Coach-Athlete Relationship Maintenance Questionnaire(CARM-Q). correlation and multiple regression analysis were conducted to verify the relationship between five personality factors and maintaining coach-athlete relationship. Results The results were as follows: Personality had a significant effect on the maintenance of coach-athlete’s relationship. Firstly, the artificial neural network was analyzed to find the influence of personality that determine positive relationships with coaches. Conclusion As a result, it was confirmed that the favor was the main discriminant factor in maintaining the relationship of coach-athlete. Finally, openness and sincerity were found to maintain and develop the positive relationship with coaches.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the influence of coaches’ emotional leadership on athletic satisfaction and to investigate mediating effect of intrinsic motivation perceived by professional female basketball athletes in Korea and Japan. Methods 154 professional female basketball athletes in Korea and Japan participated in this study and responded to questionnaires which consisted of coaches’ emotional leadership, intrinsic motivation, and athletic satisfaction. The collected data were analyzed by frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, descriptive statistical analysis, correlation analysis, and structure equation analysis with using SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0. Results The results of this study were as follows; Firstly, coaches’ emotional leadership had positive effect on athletic satisfaction. Secondly, coaches’ emotional leadership had positive influence on intrinsic motivation. Thirdly, intrinsic motivation had positively affect on athletic satisfaction. Lastly, intrinsic motivation completely mediated the relationship between coaches’ emotional leadership and athletic satisfaction. Conclusion In conclusion, these findings imply that coaches’ emotional leadership and intrinsic motivation are critical factors for improving athletic satisfaction.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to understand student athletes coaches’ occupational challenges from the dual perspectives(social relationship-political system), to analyze the nature of the coping strategies for the challenges, and to provide implications for building a human rights-friendly student athletes club culture. Methods Five coaches(n=5, average career length= 19.2 years) were selected through purposeful sampling. Data were collected by semi-structured interviews with participants. The collected data were inductively analyzed(Patton, 2015). Results First, participants struggled with informal roles demanded by the interested parties(principals, athletic directors, parents, and university coaches). Second, the system for protecting student athletes’ learning rights, the 52-hour work system and the human rights system added difficulties to the coaches’ work environment. Third, the disharmony between interested parties’ demands and government agencies’ institutional ideals pushed participants to choose anti-institutional, un-ethical, un-educational coping strategies. Conclusion The findings suggest that the government, academia and the community should empower coaches as ‘the subject of reform’ who can solve the problem together rather than regarding them as ‘the object of reform.’ Furthermore, this conclusion is expected to provide implications to alleviate disharmony between interest parties’ demands and government agencies’ systems.’
PURPOSE This study analyzed the relationship among coaching behaviors, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance as perceived by high school athletes. Additionally, it examined whether motivational climate, competence, and effort mediate the relationship between coaching behaviors and failure tolerance. METHODS Using questionnaires measuring autonomy-supportive coaching behavior, controlling coaching behavior, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance, 365 high school athletes were surveyed. Using SPSS 28.0 and Amos 28.0 software, descriptive statistics and structural equation modeling were conducted along with the following types of analyses: reliability, correlation, confirmatory factor, convergent validity, and discriminant. Additionally, the bootstrap method was used to verify serial multiple mediating effects. RESULTS Autonomy-supportive behavior had a significant positive effect 1) on motivational climate, sports competence, and effort and 2) on failure tolerance. 3) Controlling coaching behavior had a significant negative effect on motivational climate and sports competence. 4) Motivational climate and 5) sports competence both had a significant positive effect on effort. 6) Effort had a significant positive effect on failure tolerance. Last, in the relationship between autonomy-supportive behavior and failure tolerance, motivational climate, sports competence, and effort showed partial mediating effects. CONCLUSIONS This study confirms the importance of coaches’ autonomy-supportive behavior in determining failure tolerance among adolescent athletes. Based on this information, counseling (educational) programs aimed at enhancing performance can be developed and provided in sports settings, thus fostering success among athletes.
PURPOSE This study aimed to develop a team building program for a middle school soccer team in order to verify its effects. METHODS A total of 50 middle school soccer players participated in the needs analysis, and 10 middle school soccer players participated the preliminary program. In addition, a total of 37 ‘S’ middle school soccer players and 2 coaches participated the final team building program to identify its effects. The team building program was developed through the following sequence: program goal setting, organization of program activities, and the pretest. Three types of questionnaires and a self-report were utilized to verify the effects of the team building program. RESULTS The team building program was developed based on interpersonal relationships, goal setting, and communication. The level of team cohesion, team communication, and coach-athletes interaction significantly increased through this program. Furthermore, the effects of stress relief and self-improvement were revealed through the self-report. CONCLUSIONS The team building program was determined to be effective and has various benefits. It is expected to contribute to the growth of middle school soccer players if coaches actively participate in the program with their athletes.
PURPOSE This study aimed to apply a capacity building program to sport life skill leaders and to provide cases of this process. METHODS The study participants included four leaders (male=2, female= 2, Mage=37.5) who were managing a sport life skills program at a university. They participated in a capacity building program, which consisted of (a) understanding (leader seminar), (b) application (managing the sport life skills program), and (c) evaluation (leader’s self-reflection), which were conducted in eight sessions. Four leaders conducted self-evaluations using program quality assessment (PQA) during every session, and quantitative and qualitative data were collected. Qualitative data were derived using a cross-case analysis, and quantitative data were used for calculating the effect size after performing the paired t-test. RESULTS Analyzing the reported cases of sport life skill leaders, the use value of the capacity building program was identified. Furthermore, the cases reported by the four leaders enabled observation of how the leader’s capabilities were strengthened. In the paired t-test, the effect size of physical and psychological safety, appropriate structure, supportive relationship, opportunities to belong, support for efficacy mattering, opportunities for life skill building, excluding integration of family, school, and community effort, were all significant. All effect sizes were found to have “very large effects.” CONCLUSIONS The capacity building program played a positive role in strengthening the leaders’ life skill coaching capabilities. These findings have practical implications—chiefly, it is important to strengthen leaders’ or coaches’ capabilities in order to foster life skill development and transfer of student-athletes.

Purpose This study was designed to develop a team building program that helps freshmen student-athletes to adapt to college life and enhance team function and process and to examine the effects of this program. It could provide basic information of a team building program that effectively accelerates team function in the college team sports domain. Methods The program was developed through this process. First, an open-ended questionnaire was utilized to discover the needs of the program. Second, the results of needs of the program and important factors of team-building program were taken into consideration. Third, expert meetings were conducted. Consequently, the program consisted of three stages of total 10 sessions which was 90 min long. The questionnaires(Group Cohesion Questionnaire and Coach-Athlete Relationship Questionnaire), experience report, and program evaluation form were used as measures to identify the effects of the developed program. SPSS version 24.0 and inductive analysis were used to analyze the data. Results The results of this study are as follows. First, there was no statistically significant influence between developed program and the level of group cohesion. In contrast, the level of coach-athlete interaction was significantly increased. Second, the analysis of experience report revealed that this program reduced interpersonal conflict between team members and formed positive interpersonal relationship by mind of respect and consideration. Conclusion In conclusion, the hierarchical culture was strongly formed and team member suffered from the dual role of athlete and student in Korean college team sports. Thus, these should be resolved in order to enhance team function and process. As a results, this process could increase team performance as well as offer psychological stability to college student-athletes.
