
Purpose: This study was to verify the relationship between coaching behavior(autonomy/controlling behavior), self-regulation motivation and performance. Method: 356 athletes (from middle to work and professional team) in individual and team sport completed coaching behavior scale developed by this researchers assessing autonomy and controlling coaching behavior perceived by players, Korea Basic Pyshoclogical Needs Scale (KBPNS) assessing basic psychological needs, Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire (BRSQ) assessing sports motivation level based on self-determination theory, and sport performance score. To estimate the relationship between coaching behavior, self-regulation motivation and performance, this study employed the structure equation modeling analysis. Results: The relationship between psychological needs, regulation motivation and performance showed that autonomy coaching behavior tend to reinforce competence and autonomy of player. These variables have a positive effect on more inner regulation motivation. Moreover, the intrinsic motivation through stimulation experience was a key factor leading to a positive performance by improving the performance strategy and skill of athletes. Conclusion: These results are meaningful as an empirical evidence that relationship between motivation and performance can be changed according to the type of coaching behavior, and that autonomous coaching behavior play an important role in maximizing the performance of player that provided theoretically form.

This study was to explore and confirm factors of sport psychology counseling needs in Korean elite coaches. In order to achieve this purpose, 56 elite coaches in Korean Olympic training center at Taereung and Jincheon responded on open-questionnaire and 260 coaches responded on survey. Open-ended questionnaire responses were analyzed by inductive content analysis and collected survey data were analyzed by exploratory factor analysis and confirmatory analysis. The results were as follows: Firstly, sport psychology counseling needs of elite coaches were competition preparation, negative athlete-coach relationship, athlete private problems, performance degradation, pressure on performance result, injury management, team cohesion degradation, motivation, training management, different gender athlete control, athletes drop out, pressure from outside, conflicts with colleagues, neglecting from athletes, feeling of incompetence, emotional control problem, and so on. Secondly, based on these responses, closed-ended questionnaire was developed, surveyed, and analyzed. Exploratory factor analysis illustrated that sports counseling needs of coaches were performance enhancement strategies, unreasonable pressure, negligence on training, coaching stress, competition result stress, conflicts with athletes. Finally, confirmatory factor analysis showed that construct of sport counseling needs illustrated appropriate fit indices values. The results of this study contributed to provide fundamental information on coaching education program and sport psychology counseling program development and application. Consequently, it will help coaches to control their mind at coaching in training and competitions.

PURPOSE This study examined the effect of sports life skills and life skills transfer of student-athletes and coaches, applying Actor-Partner Interdependence Model (APIM). METHODS Korean student-athletes and coaches from middle and high school sports teams participated in this study. There were 300 student-athletes (Mage=15.44, SD=1.64; male=218, female=82), with an average of 5.46 (SD=2.40) years of athletic career. Meanwhile, 33 coaches were (Mage=39.70, SD=8.36; male=26, female=7), with an average of 13.52 years of coaching career (SD=10.01). Measures included the Life Skills Scale for Student-Athletes (LSSSA; Jang et al., 2020) and Korean Life Skills Transfer Survey (KLSTS; Lim et al., 2018). Descriptive analysis, correlation, and APIM were undertaken by using the SPSS and AMOS programs. RESULTS First, the correlation between athletes’ and coaches’ life skills was not significant. Second, athletes’ life skills significantly affected their life skills transfer, similar to coaches’ life skills significantly affecting their life skills transfer. Fourth, coaches’ life skills did not significantly influence athletes’ life skills transfer, and the converse was not true either. CONCLUSIONS This study verified the effect of life skills development for two groups of athletes and coaches, on transfer in sports, and attempted statistical verification of whether it affects sports life skills and transfer between athletes and coaches. Although no statistically significant results were found in the partner effect, it is meaningful in that, it provided important implications for conducting a follow-up study on the relationship between athletes and coaches. In other words, it is expected to be a cornerstone for research on building a new model, along with investigating the interactive relations between athletes and coaches on life skills in the sports field.
PURPOSE This study aimed to provide evidence for improving the working environment by exploring the phenomenon of presenteeism experienced by coaches. METHODS Ten coaches experiencing presenteeism were selected as participants of the study using the snowball sampling method, and in-depth interviews were conducted. The in-depth interviews were conducted for about 50 to 60 min using semi-structured questions organized through pre-expert meetings, and inductive content analysis was conducted. RESULTS First, the health problems that developed while coaching were categorized into two detailed areas (physical and psychological symptoms). Second, the causes of presenteeism were categorized into four general areas (policy and institutional problems, poor job environment, athlete problems, and human relations). Third, performance loss due to presenteeism was categorized into two general areas (coach-athlete relationship damage and poor training performance). Finally, coping with presenteeism was categorized into three detailed areas (private time spending, joining acquaintances, and changing training methods). CONCLUSIONS The result of this study confirmed that coaches are currently experiencing the phenomenon of presenteeism for various reasons, and the symptoms and coping method for this differ with each individual. However, the phenomenon of presenteeism experienced by coaches requires further future research since it is not easily observed and the coping method is not efficient.
PURPOSE For student-athletes to be able to successfully dedicate themselves to training and competition, the following key factors play an important role: The coach, team climate, and individual motivational characteristics. To test this hypothesis, the structural relationships between having a perceived autonomy support, a caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment were analyzed. METHODS Participants were 297 high school athletes registered with the Korea Olympic Committee (203 males, 94 females, Mage=17.88 years). Data were collected using sports climate questionnaires for autonomy support, caring climate scale, basic psychological needs scale, and sport commitment measurement. The collected data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling. RESULTS The model’s fitness was indicated by x2/df=2.797 (x2=106.288, df=38), CFI=.977, TLI=.967, RMSEA=.078 (90% CI=.061, .096). Examining the various path coefficients revealed that coach autonomy support had a positive effect on the athlete’s caring climate, basic psychological needs, and sport commitment. The caring climate had a significant effect on basic psychological needs, but did not have a statistically significant effect on sport commitment. Finally, basic psychological needs had a positive effect on sport commitment. CONCLUSIONS Coach autonomy support fosters a caring climate, and athletes who are able to perceive this are able to dedicate themselves to their sport since their basic physiological needs are met. Therefore, coaches should use appropriate coaching strategies to enhance athletes' autonomy and foster a caring climate, as both are essential factors for meeting athletes' psychological needs and promoting sport commitment.
Purpose The purpose of this study lies in: 1) clarifying what constitutes coaching ethics; 2) providing a theory to set up a coaching ethics in Korea; 3) and offer a direction to coaching ethics based on its normative traits. Methods In order to achieve this purpose, the following has been done: 1) a review of existing literature has been done to analyze the relationship between professionalism and ethics in coaching and explicate the concept and necessity of coaching ethics; 2) an effort has been made to answer such questions as “why and how much should a coach be ethical?”; “How should a coach be ethically evaluated?”; 3) An analysis of ethical responsibility embedded in coaching has been done, focusing on four ethical theories: Kantian categorical imperative, Aristotelian phronesis, Simon’s broad internalism, and Morgan’s conventionalism. Results This study reviews prior literature considering the relationship between professionalism and ethics in coaching and offers theoretical evidence to explain coaching ethics and its normative aspect. This will help resolve complicated ethical predicaments arising in the field. Conclusions This study emphasizes the role of coaches to improve fairness and wholesomeness in the field of sport, as well as suggests a coaching ethics required of a profession with internal regulations. Coaching ethics not only increases a sense of responsibility on the part of coaches but helps create a virtuous circle in which coaches’ ethical sensibility is reproduced in athletes as well. All in all, coaching ethics can stop important qualities of sport from deteriorating due to commercialism and the winner-takes-all attitude prevalent in sport today and contribute to a fair and wholesome sporting culture.

Purpose This study was to explore construct of fear and courage behavior overcoming the fear and relationship between fear and courage in competition. Methods Total 65 national athletes of combat sports(Judo, Boxing, Taekwondo, Fencing) responded to open questionnaire about fear and courage behavior in competition. The data was analyzed by triangle verification and content analysis. Results Firstly, the fear of combat sports athletes consisted of five factors, which were negative consequences, lack of preparation for a game, concerns of performing one’s best, expectation of significant others, and internalized ego threat. Secondly, courage behaviors to overcome fear were self-effort, self-suggestion, self-conviction, selfish self-regulation, social self-control, self-analysis, and acceptance of experience. Finally, there were the relationship between fear and courage in competition. Conclusion These results will contribute to provide useful information for combat sport athletes and coaches in different level to cope with competition fear.

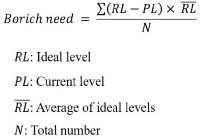
Purpose This study was designed to develop a curriculum for pre-service golf coaches at universities to enhance the coaches’ competencies to counsel athletes on the field. Methods This study was conducted in accordance with the revised and supplemented procedures for the national competency standard (NCS) based curriculum development outline under the level of application of individual instruction-level classes among the types of curriculum development. Results The results were as follows: First, the elements of the counseling competence were guided by conflict resolution counseling, psychological skills training, guidance counseling, coordination and Intervention, and relationship formation. Second, the curriculum was adopted as a curriculum for sports psychology, theory and practice of counseling, counseling practice and super-vision, and psychological skills training, and non-disciplinary activities were participation in group and personal counseling, and an open counseling case study. Third, the feasibility of the curriculum was calculated in the range of 0.8 to 1.0 for all areas to be reasonable. Conclusions The results of this study have structured the counseling competencies required for pre-service golf coaches. Based on this, the results of the study suggest counseling courses in the curriculum of university. This is expected to ultimately seek to improve the coaching field by enhancing the capacity of the coaches.
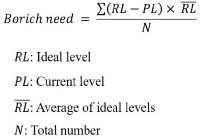


PURPOSE The purpose of this study is to explore the effects of the student-athlete and student peer mentoring program as a collegiate class. METHODS The peer mentoring program, conducted at A University in the first semester of the 2023 school year, was evaluated using practical action research (Zuber-Skeritt, 1996). RESULTS In the introduction stage, ‘relative and absolute evaluation’, ‘member ratio’, and ‘definition of professor role’ were categorized as challenge issues. In the progress stage, ‘de-formalized lecture method’, ‘student athlete’s coaching experience’, and ‘student’s experience of football culture’ were discovered as possibilities, while ‘vacancy and absence of mentor-mentee’, ‘limited group activities and limitations of team sports’, and ‘lack of objective evaluation’ required improvement. At the end stage, student-athletes experienced changes in values such as self-identity, football, and human relationships, as well as quantitative and qualitative changes in sports participation. CONCLUSIONS This study confirmed the potential of the peer mentoring program as a collegiate class as well as its practical significance for guaranteeing student-athletes' learning rights and for forming sports culture on collegiate campuses.
Purpose Based on Haidt's social-intuitionist theory, this study analyzes the differences in ethical decision-making between sport athletes and the general public in order to understand the ethical judgment tendencies of athletes and examine the determining factors influencing their judgment from the perspective of their environment. In so doing, this study hopes to motivate education for enhancing ethical consciousness as well as institutional policy. Methods To this end, 200 elite athletes in their twenties registered for more than 10 years at the Korean Sports Association and 200 college students in their twenties from five universities in Seoul were selected for comparison. Response trends for each item were analyzed by percentage, and differences between groups were confirmed by the χ2 test method. Results The results are as follows. First, in general ethical situations, athletes usually showed a compulsory ethical view that emphasized principles, whereas in a sports situation, they showed a double consciousness and revealed a very strong consequential ethical view which put much emphasis on outcome. Second, athletes strongly maintained a Confucian ethical view that recognized ethics as a norm compared to the general public and, as a result, it was found that paternalism was relatively stronger than rationalism in their ethical decision making. Third, athletes regarded other people's thoughts and group interests as important criteria for ethical decision-making rather than individual thoughts and interests, and showed a group-centered mindset which emphasized group harmony and relationship. Fourth, while the general public viewed excellent athletes as those with excellent skills and good personality, and valued their morality, athletes thought relatively little of the influence and importance of morality in their success. Finally, it was found that coaches and managers were fundamental to the formation of the athlete’s moral view. Conclusion An in-depth understanding of sports participants' ethical awareness should come first in order to enhance ethical consciousness in sport. I hope this study will work as a catalyst for research which approaches athletes' ethical consciousness from a socio-cultural context.