PURPOSE Through analysis, this study reports on occurrences of children and adolescents’ sports accidents and presents measures to prevent, cope with, and manage school sports accidents. METHODS The study used both quantitative and qualitative methods. First, a frequency analysis was conducted using 284,429 safety accident data of the School Safety and Insurance Association (SSIA). Second, the inductive analysis method was applied to in-depth interviews conducted with eight teachers. RESULTS , accidents are characterized as follows: 1) At the school level, accidents have increased significantly every year in a large proportion of elementary and middle schools. 2) The span of time spent on sports was large. 3) Accidents happened at playgrounds and auxiliary facilities. 4) Accidents happened during kindergarten play and ball sports in schools. 5) The descending order of days with the most accidents was Thursday, Tuesday, Friday, Wednesday, Monday, Saturday, and Sunday. 6) Rather than a certain month, accidents happened across the school semester. 7) Most accidents occurred from 10 a.m. to 2 p.m. Second, field teachers’ stories were categorized into the following topics. 1) School accidents can occur anytime, anywhere. Whether mild or serious, they still had the burden of inevitable accidents. 2) Required: were prompt response and handling by appropriate teachers; timely treatment and recovery cost support; also procedurally simplified handling by SSIA was helpful. 3) Avoiding accidents requires the following:: regular operation of safety education programs; daily promotion of teachers’ preventive observation and close guidance; and active role reinforcement of SSIA and policy support. CONCLUSIONS Finally, measures to prevent, cope with, and manage school safety accidents were proposed.
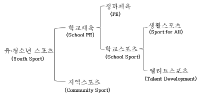
Purpose and Methods The purpose of this study is to clarify the concepts of ‘youth sport policy’ and policy areas as an alternative to school physical education concept and to provide a core conceptual framework for the development and implementation of youth sports policy in the future. Results The notion of youth sport policy is a process of seeking rational decision-making and optimal alternatives to solve the social problems associated with sports participation of youth in elementary school(aged 6 years) to high school(aged 18 years). The concept of 'youth sport' can reflect modern culture rather than 'school physical education' and it can be seen as more future oriented for lifelong participation in sports. The areas of youth sport policy are classified into physical education, school sport, and community sport. Physical education refer to the physical education classes operated by the Ministry of Education, and the school sport refers to the sports activities that take place throughout the school. Community sport is sports activities that are carried out outside the school by the choice of youth, which is the area where cooperation between the public sector and the private sector is needed. Conclusion In conclusion, healthy and active life for youth is required to establish cooperative governance of related organizations in order to ensure proper linkage between youth sport policy areas. Through this, it is necessary to solve the social problems of youth and promote their lifelong enjoyment of sport more consistently, efficiently and effectively.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the sport 5C scale of the Korean version. Methods The participants were 772 high school students from 17 to 19 who participated in sport regularly. The validation of Sport K-5C followed a three-step validation procedure through substantive stage, structural stage, and external stage. Results First, In the substantive stage, Sport K-5C consisted of 50 items with 5 factors. Second, in the structural stage, although Sport K-5C was explored as 24 items with 4 factors by EFA, but as a result of CFA, Sport K-5C was confirmed as 24 items with 5 factors. Third, the external stage provided additional validity through correlations of tests with other questionnaires which are similar concept and opposite concept, and group differentiation. Conclusions Sport K-5C is composed of 5 factors and 24 items. The factors are Caring, Character, Confidence, Competence, Connection. This scale can be used to provide an objective evaluation of positive development of youth in sport and physical education context.

PURPOSE Sport pedagogy (SP) has established itself as a subdiscipline in Human Movement Studies since the 1970s. It has become an academic labyrinth as a result of its rapid flourishing. Most researchers are extremely confused about this disorderly research complex. This study aimed to evaluate the characteristics of SP in stages in the western (mostly English speaking) countries. METHODS Analysis of literature published in English from 1990 to 2022. RESULTS The developmental versions were divided as follows: SP1.0 is positivistic in nature, SP2.0 is multi-paradigmatic as it includes all paradigms, and SP3.0 (current version). Many academic journals have been launched, and a variety of books on divergent topics are being published. Currently, research has exploded. In SP3.0, research performed by British scholars are notable in terms of number and quality, overpowering those by scholars in the USA and other countries. Youth sport and sport coaching are regarded as new legitimate areas. Additionally, signs for SP4.0 have been indicated. CONCLUSIONS In order to find way outs in the SP labyrinth, it is necessary to recognize the current research trends in international SP.
Purpose Incidence and prevalence of Korean teenager cheerleading injuries were surveyed. Methods A total of 769 junior cheerleaders who participated in National Sport Cheerleading Competitions responded to a questionnaire, and 435 reported experiences of injuries. Results Risk factors for injury included older age (p<0.001), increased experience (p<0.001), and higher BMI (p<0.05). The most frequent injury occurred at wrist, ankle, knee, shoulder and waist. And the most responded types of injury were muscular pain and contusion. Cheerleading experience affected on injury prevalence. They were injured when they perform Elevator (<0.5 yrs), Cradle (0.5-1 yrs), Cradle and Basket toss (1-2 yrs), Cradle and Pyramid (2-3 yrs). These techniques involved in bodily movements of going up and cradle. About 56% of injury was treated at home or not treated at all, and 60% of injury was either self-treated or not intervened. And only 32% of cheerleaders practiced on a formal mattress. Conclusion Safety measures for these youth cheerleaders are necessary and guidelines for securing safety and preventing and treating injuries for these population are urgent.
The purpose of this study was to examine the current status of school sport club(SSC) participation and to explore relationship between school sport participation and positive youth development. In order to do this, a survey was conducted with 403 elementary, middle, and high school teachers who are currently taking charge of SSCs, and also individual interviews were conducted with 22 students. In addition, the youths' developmental asset questionnaire was administered with 412 middle school students. The survey results from 403 teachers showed that SSCs have potential to contribute to positive youth development because teachers are placing an emphasis on character development as well as physical and social development through SSC activities. In addition, participants who regularly participate in physical activities had higher internal and external developmental assets than non-participants or irregular participants. Specifically, students participated in SSC more than twice a week had higher internal and external assets than students participate once a week. In addition, participants who engage more than one hour per session had higher internal and external assets except constructive use of time and social competence. Discussion and implications for organizing SSCs to provide developmental contexts and contents for positive youth development were provided.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the effects of motion analysis and image training using self-modeling with visual cues on the skill performance, imagery, and sports confidence of adolescent female soccer players. METHODS The participants were elite soccer players from two girls’ high school soccer teams divided into an experimental group (D girls’ high school, n=16) and a control group (I girls’ high school, n=13). The experimental group underwent motion analysis and image training when performing penalty kicks, short kicks, and long kicks using self-modeling with visual cues, while the control group underwent training using self-modeling videos without visual cues. Before and after the training, the evaluation score was calculated according to kick performance, and the imagery and sports confidence factors were measured. For the statistical analysis of all collected data, descriptive statistics, the Friedman test, the Mann-Whitney U test, and two-way repeated-measures analysis of variance were used. RESULTS First, on the motion analysis using self-modeling with visual cues, the experimental group’s penalty kick and short kick scores were improved and differed significantly, but no significant change was noted in long kick score. Second, as a result of image training using self-modeling with visual cues, all visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability factors of the experimental group improved except for the auditory factor, and the interaction effect was confirmed. In addition, the stated sports confidence of the experimental group was improved and the interaction effect confirmed. CONCLUSIONS The analysis of kick motion using self-modeling with visual cues was effective for the penalty kicks and short kicks of adolescent female soccer players. Moreover, this study confirmed that the analysis of kick motion improved the visual, kinesthetic, mood, and controllability sub-factors of imagery and significantly affected the players’ stated sports confidence.
PURPOSE This study aims to analyze research trends on the social capital in sports. METHODS A total of 69 papers published until December 2020 were selected as research subjects. Further, Excel, KrKwic software, and NetDraw function of the UCINET 6 program were used for analysis. RESULTS First, social capital research on sports has shown quantitative growth since 2010. Second, the studies were conducted on sports participants such as general, elderly, college students, adolescents, foreigners, and the disabled, showing the highest frequency of research subjects. Third, quantitative research conducted based on the research method were several. Fourth, single-author studies were the highest. Fifth, as the result of the analysis on the publication journal, the Journal of the Korean Physical Education Association was shown the highest. Sixth, due to frequency analysis of the thesis keywords, “social capital,” “sports participation,” “action intention,” “social capital type,” “living sports participation,” and “youth” were shown the highest. Seventh, as a result of centrality analysis between keywords through the network analysis, “sports participation” in connection centrality, “health-promoting lifestyle” in proximity centrality, and “sports participation” in mediation centrality were found as the highest. CONCLUSIONS The significance of social capital in sports is more important than others because it is a fundamental element for creating a culture where more people can enjoy sports moderately in Korea, where capitalism and liberal democracy were adopted as the governing system. Therefore, this study can be a vital resource significantly contributing to the understanding and active use of social capital, a significant factor in developing sports in Korea.
PURPOSE This study aimed to investigate the effects of COVID-19 on elite youth athletes by investigating their activities and eating habits before and after the COVID-19 pandemic. METHODS This study included 917 elite adult athletes from 19 sports and were grouped into 6. The questionnaire included items regarding demographics, physical activity, sleep, and eating habits before and after COVID-19. A total of 44 questions requiring subjective short answers were included. Statistical significance was set at p< 0.05. RESULTS After COVID-19, vigorous and moderate activity decreased across all sports; however, light activity increased in almost sports. Time spent sitting increased across all sports. The difference in the number of meals consumed varied among sports, and the number of competitions decreased in all sports. CONCLUSIONS The COVID-19 pandemic appears to be finished but has not ended yet. Athletes must determine the best way to maintain their physical, physiological, and psychological states close to their original abilities. Determining this will provide the greatest impact on the return of athletes after COVID-19; this study will be helpful.
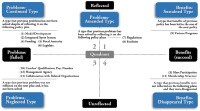
Purpose The purpose of this study is to identify policy learning in the government-led sport club policy and to analyze its type of the policy learning. Methods Sport club related documents such as policy plans, evaluation reports and journals published from 2004 to 2018 were analyzed by framework of this study. For identifying the policy learning, 12 items were determined by policy goals, policy means and policy targets. Each item was placed on four quadrants of the X-axis(benefits and problems) and the Y-axis(reflected and unreflected), and was categorized. Results This study found out the five types of policy learning. A 'benefit-sustained type' is the type that benefits of previous policy has been led to the benefits of next policy and a ‘problem-amended type’ is the type that previous problem is solved by reflecting on the following policy plans. A ‘problem-continued type’ is the type of problem that has not been solved. On the other hand, A ‘Benefit-diminished type’ and the ‘problem-neglected type’ are that previous results were not reflected. It indicates that those types have not performed the policy learning. Conclusions In order to expand the benefits of the sport club policy and to solve the problem, we should recognize the policy process and environment are not static and do policy learning. Furthermore, it suggests that there should do policy learning on what Korean sport club would be.
