ISSN : 1598-2920
ISSN : 1598-2920
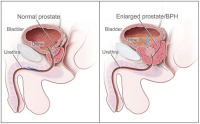
Purpose Prostate problems, such as prostate cancer, and benign prostate hyperplasia have been recognized as problems largely related to androgens and genetic factors. They affect a large fraction of the elderly population, contributing significantly to morbidity and mortality. Therefore, the purpose of this review paper was to investigate a therapeutic strategies for prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia. Methods In order to determine the therapeutic exercise strategies for prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia, previous literature was reviewed with MEDLINE, PubMed, and Scopus databases. Results Prostate cancer and its associated treatments can cause significant and lasting morbidities, such as cardiovascular and sexual dysfunctions. Various interventions have attempted to prevent or mitigate these dysfunctions. This review summarizes the available evidence concerning the effects of exercise training on male sexual health in the cancer prevalent population. Smoking cessation, regular exercise, and maintaining healthy weight are important public health targets for intervention. Importantly, several lifestyle modifications may lower the risk of developing more aggressive cancer or offer survival benefits to prostate cancer patients. Conclusions In this review article, physical exercise training can increase apoptosis markers in the prostate, suggesting exercise training as a potential novel therapeutic strategies for treating prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia. Future studies in more advanced and varied prostate cancer populations are required to ascertain the duration, intensity and frequency of exercise that optimizes the effects of exercise training on prostate cancer and benign prostate hyperplasia.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of regular vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) level, aging- and lifestyle disease-related blood components in middle-aged women. Methods The participants were recruited from a total of 19 physically healthy people aged 50-59 years, and were randomly divided into vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise (VIAE, n = 10) and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (MIAE, n = 9) group. The participants were performed vigorous- and moderate-intensity aerobic exercise three times a week for eight weeks, and body composition measurement, graded exercise test, blood collection were performed before and after. Results Mean exercise time was significantly longer in the MIAE group than in the VIAE group. The V̇O2max was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. Body weight, BMI, and body fat percentage were significantly lower than pre both groups. The BDNF concentration was significantly higher in the VIAE group than in the MIAE group. The dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-s) and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) concentration were significantly higher than pre both groups. The free fatty acid and triglyceride concentrations were significantly lower than pre both groups, and HDL-C concentrations were significantly higher than pre both groups. Conclusions Vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise not only increases maximal oxygen uptake and blood BDNF level in middle-aged women, but also induces positive changes in aging-related hormones and lifestyle-related blood variables.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between physical activity and depression according to the presence of disease. Methods A survey and basic assessment were conducted for 2,754 (Male=1,025 and Female=1,729) aged 40 and over who participated in the rural-based cohort study. The survey included physical activity, depression scale and disease preservation. The basic assessment measured height, weight, and body fat percentage. The measured data were analyzed by using logistic regression to examine the relationship between physical activity and depression prevalence. Results First, physical activity reduced the prevalence of depression by 33% and 51%, respectively, in the general population and in patients with the disease. Second, physical activity once or twice per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 51%, and at least three physical activities reduced the prevalence of depression by 37% in the general population and 33% of patients with disease. Third, physical activity less than 150 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of depression in patients with disease by 43%, and physical activity of more than 150 minutes and less than 300 minutes per week reduced the prevalence of 43% of the general population and 52% of patients with disease. Physical activity over 300 minutes per week had a 38% reduction in the prevalence of depression in the general population. Conclusions This study suggests that the level of physical activity suggested by the ACSM guidelines is appropriate to reduce the prevalence of depression. In addition, the patients with the disease was found to be effective with less frequency and amount of physical activity than the general person.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of aerobic exercise intensity on body composition, health related fitness, and quality of life in elderly women. Methods 48 elderly women over 65 years of age without physical and mental problems were assigned to four groups: control group, low intensity, moderate intensity, and high intensity aerobic training group. The aerobic exercise group applied a heart rate reserve (HRR) to low-intensity group (HRR 40-55%), moderate intensity group (HRR 55-70%), high intensity group (HRR> 70%) for 12 weeks, 3 times a week for 20 minutes a day. Subjects of the control group were to maintain their usual lifestyles during the same intervention period. Body composition, health related fitness, and quality of life were measured and analyzed using repeated two-way ANOVA. Results The main results obtained in this study are as follows. 1) There was a significant decrease in sitting forward bending in the low intensity group and a significant increase in EQ-VAS. 2) There was a significant decrease in body weight, BMI, and 6 minutes walking in the moderate intensity group, and a significant increase in grip strength and EQ-VAS. 3) The high intensity group showed a significant decrease in weight, BMI, waist circumference, sitting forward bending, and 6 minutes walking, and a significant increase in grip strength, sit and stand, functional reach, and VO2max. On the other hand, there was no significant change in all variables in the control group. Conclusions In conclusion, aerobic training was found to be effective for body composition, health related fitness and quality of life in elderly women. In particular, it can be concluded that high intensity aerobic training is effective for health related fitness, and low and moderate intensity aerobic exercise is effective for improving quality of life.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship between the track records and physical abilities in elite cyclists(keirin). Methods Twenty three elite cyclists were measured height, weight, lower body circumference(thigh, calf, and ankle), basal physical abilities(grip/back muscle strength, 25m sprint, Sargent jump test, Burpee test, shuttle run test), one-repetition maximum(1RM) strength(back squat, bench press, leg curl, power clean, dead-lift, leg press), aerobic capacity(V̇O2max, METs, HRmax), and track records(200m and 500m). Stepwise multiple regression analyses were performed to investigate which physical abilities related to track records. Results A statistically significant relationship was found between 200m track records and 2 variables which were the thigh circumference and 1RM leg press(p<.05). Also, the thigh circumference and 1RM leg press were significantly related to 500m track records(p<.05). Conclusions The results showed that the thigh circumference and maximal strength were associated with the track records in elite cyclists(keirin).



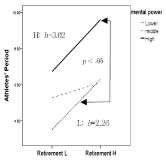
Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare the differences between the three simple control models of Hayes (2012) and to determine whether there were Moderating Effects depending on the level of self-esteem, willpower and belief that are psychological factors in the relationship between athlete's retirement and Athlete's period. Methods To achieve this objective, a total of 259 retirees were collected from data on retirement and psychological factors. The data processing method presented the reliability and feasibility of the measuring instrument through technical statistics, frequency analysis, confirmation factor analysis, and reliability analysis. In addition, we conducted a hierarchical regression analysis using the PROCESS command statement in IBM 20 to examine the regulatory effects. Results The results of the study are as follows: The first was the significant model of Hayes (2012)'s three simple control models. It is up to the researcher to choose which model to choose, but when selecting the model, the justification of the variables must be established on the basis of theoretical basis, and the reliability of the variables must be put in to produce reliable and reasonable results. The second was to verify that the relationship between the retirement factor(10) and the Athlete's period has an adjustment effect based on self-esteem, willpower and belief. Among the psychological factors, the Moderating Effects was greatest in the influence of belief on the Athletes' period, and the more reasons for retirement, the longer the Athletes' period than the weaker. The combined mental strength of all three psychological factors combined shows that the combined effect of control also significantly increases the player's ability to survive by combining with the retirement factor. In particular, sportsmanship has resulted in a better mix of retirement factors than the sense of Self-esteem and will, resulting in a longer increase in the capacity. Conclusions Therefore, players who long for a player always keep their dreams of becoming a big star in mind, and ask me to always keep the belief in hope that I will enjoy my career for a long time.






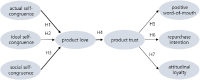
Purpose The purpose of this study was to analyze the relationships among sport-products self-congruence, product love, product trust, and purchase behavior of sports-for-all club members through structural equation model analysis. Methods A survey was conducted targetting 227, men & women in their twenties who are members of MTB, Tennis, Badminton, Golf in at the 8 in Seoul metropolitan area. For sampling method, convenience sampling method was used, while the questionnaire was self-administered. In an effort to verify the proposed structural model, this study used IBM SPSSWIN Ver. 21.0 and AMOS 18.0. Results First, actual self-congruence has positive influence on the product love. Second, ideal self-congruence didn't have positive influence on the product love. Third, social self-congruence has positive influence on the product love. Fourth, product love has positive influence on the product trust. Fifth, product trust has positive influence on the positive word-of-mouth. Sixth, product trust has positive influence on the repurchase intention. Seventh, product trust has positive influence on the attitudinal loyalty.


Purpose The purpose of this study is to classify the subjectivity of re-socialization barriers among retired footballers. Methods Q methodology was conducted to identify constraint factors contributing to social adjustment and reemployment perceived by 28 P-samples. Results Re-socialization barriers were classified as ‘Type I: Internal-constraint’, ‘Type II: External-constraint’, ‘Type III: Internal-conflict’, and ‘Type IV: External-conflict’. These types provided a variety of academic and practical discussions, depending on where the barriers are taken from (internal and external) and what depends on them (objective conditions and subjective ideas). Conclusions This study focused on the subjective structure of retired footballers and complemented traditional methodology focusing on hypothesis testing. Therefore, each type found in this study provides useful information not only in follow-up study on retired athletes, but also in policy-making decision such as support projects.


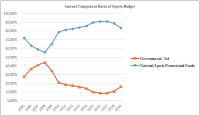
Purpose This study focused on analyzing the policies regarding operation of Sportstoto, a sole legal sports betting business in Korea. Methods In order to fulfill the research goal, literature review on reports, articles, and statistics from Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism, National Gambling Control Commission, Korean Sports Promotion Foundation, and other precedent studies was conducted. Results Currently Sportstoto fails to maintain its competitiveness due to inconvenient betting process, lack of product diversification, and low payout rate, resulting in the growth of illegal sports gambling. In addition, governmental aid for sports budget has diminished consistently, while at the same time the revenue cap regulation for betting industry restrains the development of Sportstoto and disturbs the gathering of sports budget, which appears to be a policy contradiction. Moreover, there are no specific guidelines for the expenditure of Sportstoto revenue which function as a budget. Conclusions This study suggests three ideas to overcome these problems. First is the alleviation of regulation in non-monetary area so that Sportstoto can improve its competitiveness against illegal sports gambling. Second is the clear establishment of policy regarding sports budget, either to foster Sportstoto as a fundraising business, or to enlarge governmental allocation for the budget. Lastly, institutional management must be provided for the expenditure of Sportstoto revenue as to follow government’s sports policies.

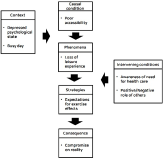
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the alienation and the overcoming process of the physical activity participation of people with Adventitious Visual Impairment(AVI) Methods 21 Adults with AVI were recruited and one on one semi-structured interview was conducted. Ground theory was used to analyze the data. Member check, peer debriefing was conducted to enhance the trustworthiness of this study. Results As a result, a total of 203 concepts were derived. This consisted of 21 subcategories and the common themes of the subcategories were categorized into nine categories. Specific results are as follows. First, the physical activity of people with AVI was directly affected by the sports facilities, physical activity programs, and professional instructor. This causal condition resulted in the loss of leisure experience in the context of the busy daily life and the depressed psychological state. Second, due to the perceived need of health care and the positive involvement of others, people with AVI came to expect the effect of exercise. Third, people with AVI participated in physical activity again as a tool to achieve the purpose of health improvement. This type of physical activity has a limitation that it can not guarantee the continuity of physical activity due to the limitation that it does not contain autonomy and interest of people with AVI. Conclusions Based on these results, the following suggestions were made. First, it is necessary to improve the environment for ensuring participation in physical activity of people with AVI. Moreover education and promotion of the effects and values of the exercise should be carried out for people with AVI and their guardians. Second, it is necessary to diversify physical activity types and reconstruct existing exercise programs.

The purpose of this study was to critically interpret a certain sports-related idea, "Integrated Korean Team," which was an issue at the PyeongChang Winter Olympics. The idea emerges as a specific political agenda under the conditions of domestic politics and the special environment of Korean national affairs and discourse. To this end, we investigated media texts on the relationship between sports, political dynamics and views on related discourse that were produced in 1990-1991 and 2018. The main findings are as follows: First, sports functions as a political socialization tool for political power as it forms public opinion. Second, sports exchanges work as a kind of international politics. Specifically, political power controls sports as certain political situations arise and political elites' needs change. Third, mega sports events have tended to become politicized in recent years as they become more effective. Fourth, North Korea’s sports under political power cannot be easily dealt with by the private sector, and it has limitations because it is not politically independent. The analysis showed that the negotiation process and realization of the Integrated North and South Korean Team seemed to be a turning point in politics and sports. Here are the conclusions drawn from discussing the two unifying events in 1991 and the situation in 2018. First, both South and North Korea pulled the Integrated Korean Team card when political needs arose. Second, when the two Koreas did not need to reconcile due to changes in the political situation between the two Koreas, they did not want to make efforts to integrate Korean Team. Third, the position of the political elite was directly represented by the position of the South-North Korean team. Fourth, the supporting public opinions of the Integrated Korean Team are gradually diminishing as the power gap between the two Koreas widens and sports players' human rights issues emerge.
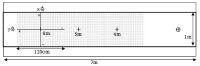
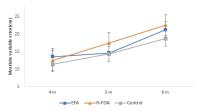
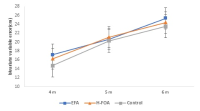
Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the effectiveness of the holistic focus of attention(H-FOA), presented as an alternative attention concept, to explore effective attention focus for the skilled performer. Methods KPGA's experts (N = 24) were selected and randomly assigned to external focus, overall focus and control groups. Experiments were conducted in the putting competition of the target distance (4m, 5m and 6m). Performance was measured for accuracy. Results Interestingly, the control group showed the high putting performance accuracy (MRE). In addition, the holistic focus of attention group was able to identify performance similar to the control group. The effect of external attention focus could not be confirmed. Conclusions Results of this study indicate that external focus may be unnecessary for skilled golfers. Rather, holistic focus of attention is highlighted for the improvement of players’ attentional focus under pressure.