 ISSN : 1598-2920
ISSN : 1598-2920
Purpose Sport has become a popular platform for corporate social responsibility (CSR) campaigns. Growing numbers of athletes, teams, and organizations are engaging in CSR campaigns to promote awareness and behaviors to support CSR campaigns addressing pressing social issues (e.g., disease prevention, health promotion, etc.). However, much of the previous work has focused on whether such initiatives benefit the organization, but not the community. The present paper provides theoretical explanations on the psychological mechanism that can demonstrate how consumers respond to CSR campaigns initiated by a sport organization. Method In particular, existing literatures in moral psychology and CSR have been reviewed to identify an explanatory mechanism that promote prosocial behavior among sport consumers. Results The present paper posits that moral emotion is a central processing mechanism explaining the link between CSR and socially responsible behaviors in consumers. The paper also provides a theoretical account to explain how moral emotions are evoked in the CSR context and how they can prompt prosocial behaviors. Conclusion This paper adds to the literature by answering the call for the need to understand underlying mechanisms linking CSR with positive social outcomes (cf. Aguinis & Glavas, 2012).
Purpose The study was designed to compare physical fitness, indices of lifestyle disease, and biochemical property of muscle according to sarcopenia and obesity in elderly women. Methods One hundred elderly women were alloted to one of four groups, i.e., sarcopenia+obesity (SO: n=20) group, sarcopenia (S: n=20) group, obesity (O: n=29) group, and normal (N: n=31) group. Criterion for sarcopenia was 'appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM)/height2<5.4 kg/㎡', and criterion for obesity was 'percent body fat>35%'. Dependent variables regarding physical fitness, lifestyle disease, and biochemical property of muscle were measured and compared among four groups. Results 1) Regarding daily living fitness, grip strength, upper arm flexion, sit-and-reach, up and go, and VO2max in SO group and S group were significantly lower than N group. Regarding isokinetic function, peak torque and average power in SO group and S group were significantly lower, and relative values to body weight in SO group and O group were significantly lower than N group. 2) Regarding hypertension, resting HR and RPP in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Regarding diabetes mellitus, fasting plasma glucose and HOMA-IR in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Regarding hyperlipidemia, HDL-C in SO group and O group were significantly lower than S group and N group. Regarding atherosclerosis, TC/HDL-C ratio and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. 3) Regarding biochemical property of muscle, IL-6 in SO group and O group were significantly higher than S group and N group. Conclusion It was concluded that physical fitness was declined in sarcopenia elderly, and that relative value of isokinetic function, indices of lifestyle disease, and inflammation markers were deteriorated in obesity elderly. Especially, the decline and deterioration of physical fitness and indices of lifestyle disease were even more severe in the elderly who had the both status. Therefore, the efforts should be made to prevent and improve sarcopenia and/or obesity.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the changes of gait patterns and muscle activations according to dual tasks during stair ascending. Methods Twelve sedentary young male adults(Age: 27.0±1.8 yrs, Weight: 65.8±9.9 kg) without any lower extremity injuries participated in the study. Participants performed stair walking up 7 floors and their ascending motion on each floor was analyzed according to dual tasks. A wireless electromyography (EMG) were attached on the Rectus Femoris(RF), Biceps Femoris(BF), Gastrocnemius(GN), Tibialis Anterior(TA) muscle to calculate integrated EMG(iEMG) and co-contraction index(CI). Chest and left heel accelerometer signal were recorded by wireless accelerometer and those were used to calculate approximate entropy(ApEn) for analyzing gait pattern. All analyses were performed with SPSS 21.0 and for repeated measured ANOVA and Post-hoc was LSD. Results The results of this study indicated that dual task appeared to increase their time, CI and there were a statistically significant difference in most muscle on each floors compared to the non dual tasks. Also, ApEn were a statistically significant difference in only left and right direction than non dual task. Subjects showed more irregular pattern and instability muscle activation response during dual tasks. Conclusion Because there are many dangers often use of stairs in everyday life, in the future, we have to make a lot of efforts to prevent fall.


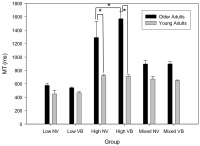
Purpose The present study was to investigate to extent that effects of sensory information distortion by muscle vibration on continuous limb movement in aging and accuracy constraint. Methods Young adult group (n=11) and older adult group (n=11) were divided. All participant were instructed to perform repetitive aiming movement to specified targets under three-accuracy constraints (i.e., low, high, and mixed accuracy constraints) in the vibration and no-vibration conditions. Kinematic data was collected by movement time and movement error frequence. Results The results showed that compared with young adult, older adult increased movement time when accuracy constraint was high under vibration condition. Older adult also was a high degree of movement errors than young adults when accuracy constraint was high under vibration condition. Conclusion The muscle vibration stimulation may influence considerably on the continuous limb movement probably due to degeneration in sensory information processing by aging.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationships among sponsorship attributes, sponsorship benefits, recognition of sponsorship value, sponsorship attitude, and sponsorship certainty through structural equation model. Methods Respondents were university students living in Seoul, Kyoungki-do, and choongchung-do. The present study was designed to identify the effect of title sport sponsorship by utilizing NH V-LEAGUE title sponsorship. By using convenience sampling method, total 400 questionnaires were distributed and gathered from samples, and among them 369 valid samples were used for further analyses. The data were recorded and analyzed using the IBM SPSSWIN Ver. 21.0 and AMOS 18.0. 18.0. Results First, sponsorship attributes had a positive influence on sponsorship benefits. Second, sponsorship benefits had a positive influence on sponsorship value recognition. Third, sponsorship attributes had no positive influence on sponsorship attitude. Fourth, sponsorship benefits had a positive influence on sponsorship attitude. Fifth, sponsorship value recognition had a positive influence on sponsorship attitude. Sixth, sponsorship attitude had a positive influence on sponsorship attitude certainty. Seventh, sponsorship certainty had a positive influence on sponsorship effects (image improvement, favorability, purchase intention).

Purpose There is a growing number of potential demand on experiential horse riding tourism due to the expand of tourism and sports industries, however the experiential horse riding clubs are operating inefficiently. Therefore the purpose of this study is to investigate implicity importance of horse riding club’s selection attributes and analyze factors affecting positive effect on market share thereby find the way to improve operating system. Methods The survey was done among 258 horse riding tourism customers of Jeju, Gyeonggi, and Gyeongbuk provinces, and conjoint analysis to figure out the relative importance of selection attributes, and simulation to predict the market share of experiential horse riding were conducted. Results The results are as follows. Cost was the most important factor when selecting horse riding club and program, location, staff were followed by. Also, “The club that serves various activities with horse riding program at 10,000won where the condition of road and parking lot are good” had the best market share. Conclusion This study suggested the effective and efficient manners to operate the horse riding club and the political implication.
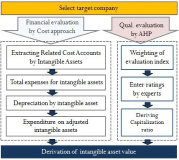
Purpose In the field of sports industry, the intangible assets of sporting companies often show discrepancies between accounting information and corporate value because of conservative current accounting standards. Therefore, this study intends to present a valuation model of intangible assets of sports industry based on cost approach, as a part of a method of capitalizing intangible property expenditures. And we tried to verify the valuation model of intangible assets derived from the research on actual sports companies. Methods To accomplish the purpose of the study, reviewing the literature on various related precedent studies and examining related valuation methodology, legal basis, and representative valuation models were utilized. And to verify the effectiveness of the derived model, Tobin q values were derived and compared. A simple regression analysis was used to verify the explanatory power of the derived model. Results The financial evaluation was conducted based on the cost approach, which enables relatively objective evaluation through the existing financial statements, and a valuation model with the procedure of duplicating the AHP evaluation to reflect the characteristics of the individual intangible assets was presented. In addition, in order to verify the proposed valuation model, the valuation was conducted by putting the accounting information of the sports companies into the intangible asset valuation model presented in this study. As a result of the statistical analysis on the evaluation results, the intangible asset value evaluation model presented in this study is proved to be significant based on statistically high explanatory power. Conclusion Therefore, if it is possible to appropriately evaluate the enterprise value of sports companies through the intangible asset valuation model based on the cost approach presented in this study, various types of technology financing will be possible in the sports industry. And this is expected to accelerate the growth of the sports industry in the future.

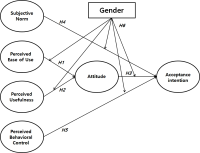
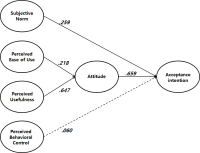
Purpose The current study was aimed to examine acceptance intention of sports wearable smart device using the Technology Acceptance Model and Theory of Planned Behavior. Methods Data were drawn from 357 consumers who had experience purchasing sports products. Data were analyzed through frequency analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 program. Results First, perceived ease of use had a positive effect on attitude. Second, perceived usefulness had a positive effect on attitude. Third, attitude had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fourth, subjective norm had a positive effect on acceptance intention. Fifth, perceived behavioral control did not affect acceptance intention. Sixth, differences of path coefficients between attitude and acceptance intention, subjective norm and acceptance intention were significant according to gender. Conclusion The significance of this research is to provide the basis of positioning strategy for domestic companies of sports wearable smart device.


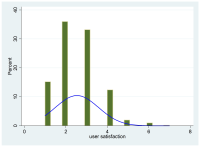
Purpose The study aims to analyze the factors affecting the Residents user satisfaction in order to improve the management of the Open School Sports Center the support facility of the National Sports Promotion Fund. Methods This data is based on Korea Institute of Sports Science(KISS)'s Open School Sports Center Usage Status and Satisfaction Survey (2016) and Open School Sports Center use performance. The analysis model is a regression model (TOBIT) that takes into account the limited characteristics of dependent variables. Results The results are as follows: the satisfaction is negatively related age, number of regulations, weekday opening hours, and usage fees. Conclusion Therefore, in order to increase the satisfaction of Open School Sports Center residents users, various supports are needed. This includes funds for PR, discounts and user-friendliness. It also requires differentiated management of each Center. In the case of regions and facilities, consumer-oriented policies need to be applied instead of collective standards.

Purpose The purpose of this study is to investigate the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency that can guarantee the student athletes' right to study and performance, and to derive the ranks of setting proper training duration of frequency of student athletes by school level. Consequently, to provide basic data for the development of training guidelines for the growth period of Korean student athletes. Methods Delphi and Analytic Hierarchical Process(AHP) techniques were used. The Delphi survey was conducted in three phases, and collected data through Delphi survey were computed by SPSS win ver. 22.0 and Excel, using the mean, standard deviation, median, and coefficient of variation. Using the AHP technique, we classified the factors for setting proper training duration of frequency derived through Delphi survey, and calculated the importance by using Microsoft Excel 2010. Conclusion First, elementary students should be guaranteed regular class participation, have basic after school training, and be provided with adequate rest so that they do not lose interest in the exercise. Second, middle school students are required to decide whether to continue exercise based on their ability to exercise and abundant experience. Therefore, when abandoning the exercise, students should be able to faithfully carry out their academic performance. Third, high school students are directly related to college entrance and employment, so they have to concentrate on performance rather than on academic performance.
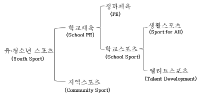
Purpose and Methods The purpose of this study is to clarify the concepts of ‘youth sport policy’ and policy areas as an alternative to school physical education concept and to provide a core conceptual framework for the development and implementation of youth sports policy in the future. Results The notion of youth sport policy is a process of seeking rational decision-making and optimal alternatives to solve the social problems associated with sports participation of youth in elementary school(aged 6 years) to high school(aged 18 years). The concept of 'youth sport' can reflect modern culture rather than 'school physical education' and it can be seen as more future oriented for lifelong participation in sports. The areas of youth sport policy are classified into physical education, school sport, and community sport. Physical education refer to the physical education classes operated by the Ministry of Education, and the school sport refers to the sports activities that take place throughout the school. Community sport is sports activities that are carried out outside the school by the choice of youth, which is the area where cooperation between the public sector and the private sector is needed. Conclusion In conclusion, healthy and active life for youth is required to establish cooperative governance of related organizations in order to ensure proper linkage between youth sport policy areas. Through this, it is necessary to solve the social problems of youth and promote their lifelong enjoyment of sport more consistently, efficiently and effectively.

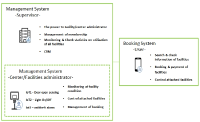
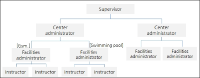
Purpose This study aims to suggest the application of IoT-based integrated management system to public sports facilities(PSF) in order to improve the utilization and management of PSF by analyzing the actual state of PSF empirically. Methods A survey was administered to managers(n=279) and users(n=500) of PSF in order to identify problems of current management and collect suggestions for improving the utilization and management of PSF. Previous research on establishing IoT-based system was also reviewed for considering the effectiveness of IoT technology. Results Generally, PSF are in low utilization and operate in a deficit. The deficit operation is caused by high labor costs and management expenses. The survey result shows that there are many problems in management and utilization such as lack of equipment, deteriorated facilities, shortage of manpower and funding, limited programs, difficulties in promotion. The result also shows that PSF need to consider developing local demand-based programs, reducing management costs, extending opening hours, improving online booking system. Conclusion To solve the problems of PSF in utilization and management, this study suggests that IoT-based integrated management system needs to be applied to PSF. It is expected that applying IoT-based integrated management system to PSF would improve operational effectiveness, ease of facility management, and user convenience.

Purpose The purpose of this study is to deeply understand what high school student athletes are doing as athletes and how they are transformed into student athletes from studying and exercising simultaneously. Through this, to understand the life of student wrestlers and to provide basic data for rational improvement of school athletic department. Methods Participants of the study selected one student in the second grade and two students in the third grade at Woosu high school in metropolitan. Data was collected through in-depth interviews, participant observation, and document analysis. The collected data was analyzed using Domain Analysis and Taxonomic Analysis by Spradley(1979). To assure the credibility of the data, additional checks and analysis were conducted with the participants, and the research process was examined by experts. Moreover, the common contents of the data were included in the research results with multilateral verification. Results Woosu high school wrestling student athletes were recognized as athletes as a training life to lose their dreams, a school life to stop their work. However, since student athletes have been studying and exercising together, they have been transformed from a trainee to a motivated active, a student who is reborn in the school community, and transformed a reflective student athlete to an immature player on a daily life. Conclusion The policy of the school athletic department to study and exercise together has a positive effect on student athletes and has a good effect. The introduction and practice of this system can expect true student athletes and establish elite physical education right away.
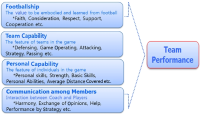
Purpose The following study was conducted to suggest and verify the validity of the concept of team performance, which has previously been considered as the total sum of individual performances. Method The concept of team performance was extracted by a conductive content analysis and an exploratory factor analysis of the data gathered from middle school football players. To verify the validity of the extracted concept, football experts' opinions were collected. Results The idea of team performance, categorized by Footballship, Team Capability, Personal Capability, Communication among Members, has been taken differently from the total sum of individual performances. Footballship is the virtue that should be materialized, and simultaneously earned during the game. Team Capability is a available resource for team's performance, Personal Capability is a available resource for a player's performance, and Communication among Members is the intimacy of communication between coaches and players. The conglomeration of experts' opinions on the concept of team performance and its components shows that team performance is evidently different from the total sum of individual performances. Conclusion The following study has been conducted to suggest and verify the validity of the concept of team performance. Team performance exists, standing distinct from the sum of individual performance, and understanding the concept of team performance will contribute not only to understanding performance, but also to improve the effectiveness of training and managing the team. Interest of the sport society is looked forward to.

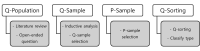
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the badminton players psychological disturbance and coping strategies types and characteristics. Methods To achieve the purpose of this study, an open-ended questionnaires were used targeting 194 badminton players, 25 Q samples were selected by collected data as the self – statement. Q samples were classified depending on their subjective experience by P samples composed of active badminton players who had more than eight years of athletic career; this data were coded and analyzed by VARIMAX rotation. Results The results revealed by the Q methodology were below. First of all, the first type is named as (Internal Disturbance - Passive Coping) type. The first type is psychologically disturbed by internal factors, and negative about external coping strategies. Second, the second type showed the higher awareness of coping strategies than the other types; It was named as (Active Coping) type. Third, The third type recognized the burden of victory and self-confidence, and it was named as the type of (Victory Obsession). Conclusion In the badminton competition, the deterioration of concentration and judgment ability because of psychological disturbance has a serious effect on the performance. Therefore, based on the results of this study, it will be possible to improve the performance by appropriate psychological intervention through the characteristics of the athletes.

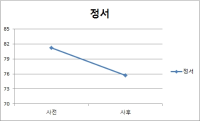
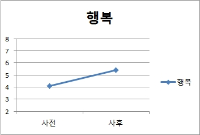
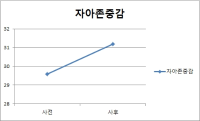
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of positive psychological intervention program on mood state, self-esteem and happiness of university student athletes. Methods The participants were 10 university student athletes. The measures utilized the Profile of Mood States(POMS), self-esteem inventory and happiness questionnaire. Positive psychological intervention program was developed by previous studies, participants interview and expert discussion. The positive psychological intervention program were managing life, self-esteem enhancing program, being optimistic, positive emotion program, gratitude, forgiveness, communication skill training program, habit/routine making program and action strategy development. The data were analyzed by SPSS 20.0. Results These results were as followings. Firstly, positive psychological intervention program decreased total mood disturbance(TMD) of university student athlete. Secondly, positive psychological intervention program improved self-esteem of university student athletes. Lastly, positive psychological intervention program increased happiness level of university student athletes. Conclusion Training and education system should be established in which a positive psychological intervention program can be applied to university student athletes.

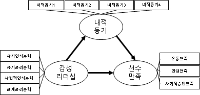
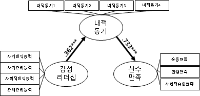
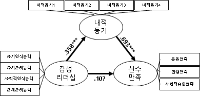
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the influence of coaches’ emotional leadership on athletic satisfaction and to investigate mediating effect of intrinsic motivation perceived by professional female basketball athletes in Korea and Japan. Methods 154 professional female basketball athletes in Korea and Japan participated in this study and responded to questionnaires which consisted of coaches’ emotional leadership, intrinsic motivation, and athletic satisfaction. The collected data were analyzed by frequency analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, descriptive statistical analysis, correlation analysis, and structure equation analysis with using SPSS 23.0 and AMOS 23.0. Results The results of this study were as follows; Firstly, coaches’ emotional leadership had positive effect on athletic satisfaction. Secondly, coaches’ emotional leadership had positive influence on intrinsic motivation. Thirdly, intrinsic motivation had positively affect on athletic satisfaction. Lastly, intrinsic motivation completely mediated the relationship between coaches’ emotional leadership and athletic satisfaction. Conclusion In conclusion, these findings imply that coaches’ emotional leadership and intrinsic motivation are critical factors for improving athletic satisfaction.

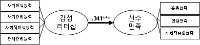

Purpose This study was designed to develop a team building program that helps freshmen student-athletes to adapt to college life and enhance team function and process and to examine the effects of this program. It could provide basic information of a team building program that effectively accelerates team function in the college team sports domain. Methods The program was developed through this process. First, an open-ended questionnaire was utilized to discover the needs of the program. Second, the results of needs of the program and important factors of team-building program were taken into consideration. Third, expert meetings were conducted. Consequently, the program consisted of three stages of total 10 sessions which was 90 min long. The questionnaires(Group Cohesion Questionnaire and Coach-Athlete Relationship Questionnaire), experience report, and program evaluation form were used as measures to identify the effects of the developed program. SPSS version 24.0 and inductive analysis were used to analyze the data. Results The results of this study are as follows. First, there was no statistically significant influence between developed program and the level of group cohesion. In contrast, the level of coach-athlete interaction was significantly increased. Second, the analysis of experience report revealed that this program reduced interpersonal conflict between team members and formed positive interpersonal relationship by mind of respect and consideration. Conclusion In conclusion, the hierarchical culture was strongly formed and team member suffered from the dual role of athlete and student in Korean college team sports. Thus, these should be resolved in order to enhance team function and process. As a results, this process could increase team performance as well as offer psychological stability to college student-athletes.

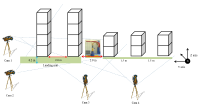
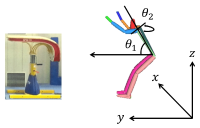
Purpose The purpose of the study was to perform a comparative analysis of the YANG Hak Seon technique carried out by "K" athlete with the kinematical data of "Y" athlete and propose a method to improve the YANG Hak Seon technique of "K" athlete. Method The subject recruited for the study was a male athlete from Korean national team (Age: 21, height: 1.65 m, body weight: 59.6 kg, and career: 11 years). Four high - speed cameras were used to analyze the 3D motion of the YANG Hak Seon technique performed by "K" athlete. The variables selected for analysis were the velocity of COM, displacement of COM, the rotational & torsional angle of the trunk and rotational & torsional angular velocity of the trunk. The results obtained were compared to the preexisting data of the "Y" athlete (data set from the published research). Results Firstly, the horizontal displacement of the YANG Hak Seon technique of the "K" athlete was observed to be shorter along with lower vertical displacement during landing compared to “Y” athlete. In addition, the overall horizontal velocity was low and vertical velocity was not generated which rises during the BC (board contact) phase. Although the rotational angular velocity of the trunk was lower during the BC, HC (horse contact) phase and LD (landing) phase, torsional angular velocity was higher during the LD. Conclusion In order to improve the completeness of the YANG Hak Seon technique of the K player, it is necessary to enter with a fast and low posture on the footplate during the initial phase. In the BC phase, it is essential to raise the COM simultaneously while landing on the footplate and increase the rotational angular velocity of the trunk.


Purpose The purpose of this study is to analyze the performance contents of men's floor exercise and to provide basic materials for achieving excellent results at world competitions. Methods Teams ranked 1 - 12 who participated in the World Championships' floor movement group competition selected a total of 59 players by the convenience sampling method and carried out technical statistics, frequency analysis, member variable variance analysis, and post hoc analysis. Results First, as a result of frequency analysis of the difficulty of each group, all the teams ranked 1 to 12 liked the most difficulty of C and found that they do not like the F difficulty the most. Secondly, there was a difference in average for each group's start score, ranking 1st to 4th> 5th to 8th> 9th to 12th place. Thirdly, there was a difference in average of difficulty levels for each group B, C, E, and it became very significant with E difficulty.Results of post hoc analysis B difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th, 5th to 8th), C difficulty (9th to 12th> 1st to 4th), E difficulty (1st to 4th> 5th to 8th ·9th to 12th). Conclusion These results show that in floor exercise, the art of more than C difficulty and the connection technology of A, B, C, difficulty, E and F, difficult difficulty such as difficulty, creative and dynamic performance composition is excellent It clearly states that it is a condition for getting results.
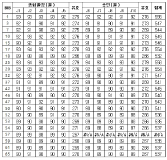
Purpose The purpose of this study is conducted to analyze the objectivity of the ski technical championships hosted by Korea Ski Instructor Association (KSIA) and to identify the error sources that affect the score of the competition. Methods To this end, we used the data from the 25th(2009) to 33rd(2017) ski technical championships held by the Korea Ski Instructor Association (KSIA). The data provided by Win Excel 2010 was used to sort out the missing data, such as abandonment, according to the data processing method. The collected data were analyzed by using SPSS 22.0 to calculate the mean and standard deviation of each season, event, and judges, and the Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC). In addition, by using the single facet crossed design(p*j) of the generalizability theory’s G study, the variance component estimates for the participant(p) and the judges (j) are calculated, and the influence (%). Results As a result of the research, it was confirmed that the results of all the seasons and events from the 25th to the 33th events were very consistent, with the objective of .845~.986 higher than the recognition level of .80. In addition, the results show that the relative ratio of the judges to the error of the judging score is very low as a result of the error analysis through the dispersion component estimates. Conclusion In summary, the results of the KSIA evaluation are highly evaluated objectivity and have very low impact on the judges' errors.

