 ISSN : 1598-2920
ISSN : 1598-2920
The recent increases in international efforts for designing and implementing initiatives and programs about 'development though sport' have accompanied the remarkable growth of the 'sport for development and peace'(SDP) sector. This global prevalence of SDP and the resulting augmentation of its social significance have rendered a growing scholarly attention to SDP in the sociology of sport. Moreover, a grounding rationale for SDP initiatives to enhance positive individual and social changes through sport has also offered an interesting research area for the sociology of sport. This paper aims to review sport sociology literature about SDP. Major findings include a set of descriptive reports about the institutionalization of SDP and critical/reflective approaches to SDP's outcomes and limitations. It is noted that the institutionalization of SDP consists of ideological and policy endeavors, SDP organizations and institutions, and classifications of SDP project types. Despite of positive outcomes resulted from SDP programs, it has been highlighted that the ongoing issues and limitations of SDP include ambiguities of development concept, the Global North hegemony, unilateral top-down program management, and the inherent complexity and lack of program monitoring/evaluation.
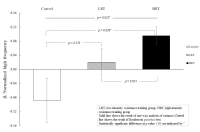
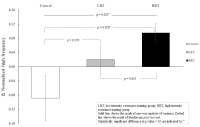
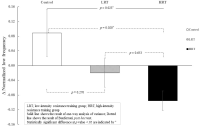
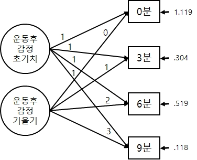
The purpose of this study is to investigate the influence of resistance training with different exercise intensities on heart rate variability(HRV) in habitual smokers. Twenty-eight healthy young smokers participated in this study were randomly divided into three groups; CON(control), LRT(low-intensity resistance training; 50% 1RM), and HRT(high-intensity resistance training; 70%1RM), respectively. LRT and HRT groups performed an 8-week resistance training(4 upper- and lower body exercises) using weight training machines, whereas CON group maintained their regular activities. All groups were evaluated basal body composition, hemodynamic parameters, HRV as autonomic nervous function, and muscular strength (1RM and isokinetic test) before and after the 8-week training. To assess the effect of 8-week training with different intensities on autonomic regulation, time and frequency domain indices of HRV were calculated from 5min R-R interval recording. As results, both LRT and HRT groups increased baseline 1RM and isokinetic strength compared to CON group. Meanwhile, high-frequency power reflecting parasympathetic activity was significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. In addition, normalized low frequency power(LF nu) indicating a shift of sympathovagal balance towards sympathetic predominance significantly decreased while normalized high frequency power(HF nu) which reflects vagal predominance significantly increased in HRT compared to CON group. Furthermore, improved cardiac autonomic regulation and parasympathetic activation had significant association with increased muscular strength. Overall, the 8-week training has enhanced muscular strength in both training groups, particularly autonomic balance improved in young habitual smokers with high intensity resistance training.

The purpose of this research is to provide the information about sports injury by surveying and analyzing a result, and to lead analytic and scientific training among the subjects being elite summer sport athletes. All sports injuries are recorded on injury report form and the following results were obtained. In Cycle sport, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees were highest. and In Table tennis sport, the prevalence of injuries of the ankle was highest due to the chronic fatigue. The prevalence of injuries of the shoulder, low back were highest due to the overuse of joints. In Badminton sport, the prevalence of injuries of low back, knees, ankles were highest by overtraining. In Gymnastics, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees, ankles were highest. In Archery sport, there is a lot of injuries to the shoulder and neck. In Weight lifting sport, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees, and ankles were highest. In Golf sport, the prevalence of injuries of knees, low back were highest. In Hockey sport, the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees, low back were highest. In Boxing sport, the prevalence of injuries of hands, shoulder, the low back were highest, In Judo sport, there are overall damage occurred in parts of the whole body, but the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees, low back were highest. In Fencing sport, the prevalence of injuries of the low back, knees were highest. In Wrestling sport, although there is a difference slightly depending on freestyle and Greco-Roman, but the prevalence of injuries of knees, ankles, low back were highest. In Handball sport, the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees were highest. In Taekwondo, the prevalence of injuries of ankles, knees, feet were highest.
The purpose of this study was to develop and validity Competitive State Anxiety Scale for Taekwondo Form athlete(CSATF). The participants were composed of the 48 Taekwondo Form athlete to explore sub-factors of Competitive State Anxiety for Taekwondo Form athlete. The data were collected by an open-ended questionnaire and interview. The participants were composed of 257 national Taekwondo Form athlete to develop Competitive State Anxiety Scale for Taekwondo Form athlete. This 157 athlete data were used for items analysis, reliability analysis and exploratory factor analysis. And 100 athlete data were utilized for confirmatory analysis. Also convergent validity, discriminant validity, predictive validity latent mean analysis of CSATF were performed The results of this study were as follows. Firstly, the results revealed that the four general dimensions were identified such as cognitive anxiety, somatic anxiety, state of confidence, environmental anxiety. Secondly, CSATF comprised cognitive anxiety(5 item), somatic anxiety(5 item), state of confidence(5 item) and environmental anxiety(6 item). Thirdly, convergent validity, discriminant validity and predictive validity, the multi-group analysis according to gender examined validity of CSATF.

The purpose of this study was to describe psychological changes and variables of injured elite athletes during sport injury rehabilitation. 5 injured elite athletes were selected as participants, and open-ended questionnaires, participant observation, and in-depth interview were used for collecting data. Results from the data were analyzed through transcription, coding, and categorization with inductive method. To validate the results of this study, triangulation, in-depth description, member checks, and peer debriefing were used, and findings of this study were as follow. The participants showed negative psychological state such as fear of return to play and anxiety during the initial rehabilitation program, but their psychological state was changed positively such as recovery of confidence and desire of return to play at the end of program. However, the specific psychological changes of each participant showed several differences according to participant's surrounding environment and situation during the rehabilitation program. All findings have important implications for implementing and developing rehabilitation program, so needs to be investigated further.
Recent research on exercise and affect has examined participants` affective changes during and after exercise with a longitudinal approach. With regard to this viewpoint, a theoretical model (Dual Mode model) has been presented to explain the different change of affect in an exercise setting and the model identified the impact of psychological factors on the affective changes. However, not only there is little empirical studies on the dual-mode model, but some relevant research has used an inappropriate statistical method (ANOVA), which cannot effectively explain the overall trends in affective change during and after exercise. Exiting research has a limitation to generalize the DM model examining only a certain gender such as active male or inactive female participants. Thus, the aim of present study was to investigate the effect of intrinsic motivation on affective change during and after exercise in participants who do not take part in regular exercise considering gender based difference. 51 inactive university students (M: 36, F: 15) responded a survey measuring intrinsic motivation for running activity and participated in moderate-intensity running exercise to examine affective change during exercise. Therefore, present study examined the influence of intrinsic motivation as a psychological variable on the trend of affective changes during and after exercise based on the dual mode model. Results from the latent curve model analysis revealed that there were decreasing trends of affect during exercise and the trends were individually different. Importantly, the decreasing trends were weaker in the participants with higher intrinsic motivation[FL=-.34, p=.000]. Additionally, participants` affective responses were positively changed after the exercise in general, but the changes were not influenced by intrinsic motivation. Therefore, the decreasing trend of affective change during exercise was weaker in the participants with higher intrinsic motivation, and the positive change in affect after exercise was not influenced by intrinsic motivation.

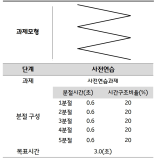
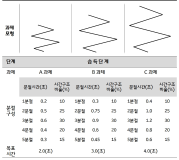
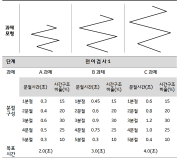
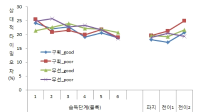
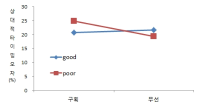
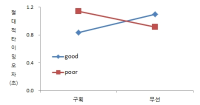
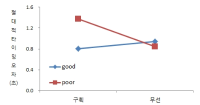
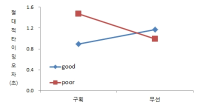
The present study was conducted to determine the effect of contextual interference (CI) and motivational properties (MP) of Knowledge of Result (KR) in learning on relative and absolute timing. Participants (N=48) were randomly assigned to one of four practice groups, which differed in practice structure on CI (blocked, random) and KR on MP (good trial, poor trial). They performed temporal timing tasks in pre-exercise and acquisition phase and went through a retention test and 2 transfer tests after approximately 24 hours. The main findings showed that first, for the relative timing error there was no significant main effect of CI and MP in the acquisition phase, retention, transfer1, and 2 test. However, there was a significant interaction effect between CI and MP in the transfer 2 test. Second, for the absolute timing error there was no significant main effect of CI and MP in the acquisition phase, retention, and transfer test 2 while there was in the transfer test 1. Moreover, there was a significant main effect between CI and MP in the retention, transfer 1, and 2 test. The findings indicated that 1) there was a significant learning effect of absolute timing between KR_good group and KR_poor group on blocked practice in the retention test, 2) random practice schedule and KR_good condition resulted in enhanced absolute timing performance relative to blocked practice and KR_poor respectively at transfer test 1, 3) there was a significant learning effect of absolute timing between KR_good group and KR_poor group on blocked practice at transfer test, 4) KR_good condition could be an useful relative timing learning strategy relative to KR_poor on blocked practice schedule at transfer test 2, effector transfer test. KR-good condition resulted in learning superior to KR_poor group on blocked practice schedule as well. However, there was no significant difference between two conditions on random practice, and 5) there was no difference in the learning effect of absolute timing error between KR_good and KR-poor group in the blocked practice, while there was not in the random practice. It indicated that motivational properties would influence the learning effect of timing in the blocked practice.

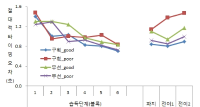
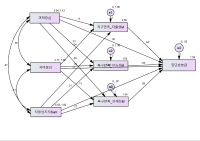
In sport context, the motivational climate created by significant others (e.g., coachs and peers) has been influences on the athletic-student's motivation, engagement, performance, and skill development. Collective efficacy is important for team performance because it influences a group's task choice, effort expenditure, persistence in the face of failure, and resistance to discouragement. This study was to examine the influence of peer motivational climate (i.e., task-involving and ego-involving motivational climate) and coach autonomous support for basic psychological need satisfaction and collective efficacy. In the study, participants were 289 athletic-students' of team sports. In the study then, questionnaire was assessed using by the correlation and path analysis. The results showed that task-involving motivational climate significantly predicted of collective efficacy, while ego-involving motivational climate were negatively predict to the collective efficacy. The results suggest the importance of considering peer influence in addition to coach influence when examining motivational climate in team sport.

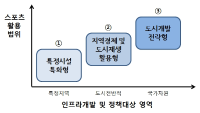
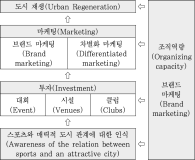
A number of global cities and local cities facilitate local economies and development by utilizing sports. However, their strategy is likely to be a short-term and one-time policy, which does not continuously strengthen their development. Therefore, the use of sports needs to be considered as more specific and longer term strategies for local development. This study examines the concept and role of sports city focused on cases of overseas sports cities, and successful and ideal cases of background and features of sports cities were analyzed to promote and lead the direction of improvement of sports cities in Korea. Consequently, strengthening a city’s sport capability and connecting it to local development need to be met to become a city into a successful sport city. To do so, it should premise recognition that sports cannot be treated separately from other urban policy area and it needs to invest in sports facilities, hosting sports events and competitions, and sports clubs based on the recognition for the importance of sports. Moreover, it needs a marketing strategy for branding and differentiation through sports of a city’s expertise. Finally, to make sports act as a catalyst to strengthen the process of an integrated city’s competitiveness, it requires a local government’s strong leadership and organization capacity of stakeholders.







The purpose of the study is to find the impact of social and economic factors in physical activity of children and youth. This study utilized the data from 4th Korean Children and Youth Panel Study(KCYPS), and the analysis were carried out based on the starting sample of 2,009 from ‘the elementary 4 panel’ and 1,978 from the ‘middle school 1 panel’ and 1,984 from the ‘high school 1 panel’, 5,971 full data were used in the final analysis. Data were processed using hierarchical regression analysis and it was statistically validated at the significance level of 0.05. First, Pearson r and Spearman ρ showed that all variables are statistically significant correlations. Second, among the first factors of personal and family characteristics, household income level(B=.113), family composition(B=-.049) and parental education (B=.060) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, parental education (B=.027) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Third, among the second factors of community-level characteristics, Gini coefficient (B=-.810), wealth concentrating (B=.120) were found on a significant impact on the movement of physical activity time, the Gini coefficient (B=-0.315) was found on a significant impact on the subjective evaluation of physical education grades. Additional factors that determine the coefficient of variation in the level 2 were found to be 0.623 and 0.001 respectively. Therefore, second factors of community-level characteristics are added such as Gini coefficient, wealth concentrating were explained to children and youth exercise time during physical activity 62.3%(p<.01) and subjective evaluation of physical education in grades 0.1%(p<.01). predictive power to

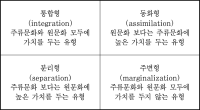
The purpose of this study is to examine acculturation strategies of expatriates in Korea in relation to spectator sport involvement. Berry's(1997) bi-dimensional model of acculturation was used as a theoretical framework to categorize the type of acculturation strategies of expatriates in Korea. Acculturation strategies of expatriates were classified into four types: integration, assimilation, separation, and marginalization. To be specific, there were 79 participants using the integration strategy, 28 using the assimilation strategy, 53 using the separation strategy, and 20 using the marginalization strategy. Research hypotheses were established to analyze differences on spectator sport involvement of expatriates between Korean spectator sport and their original cultural sport. There were significant differences in spectator sport involvement among foreigners in Korea. Firstly, the spectator sport involvement of the participants using the integration strategy was higher than that of marginalization. Second, participants categorized as using assimilation strategy were found to have lower sport involvement with Korea's spectator sport and had a higher involvement with their original cultural sport. Third, participants categorized as using separation strategy were found to have higher involvement with their original cultural sport than Korea's. Fourth, participants categorized as using separation strategy did not show significant differences with assimilation participants in comparing original cultural spectator sport. In conclusion, the result of the research indicated that expatriates living in Korea showed similar characteristics of Berry's (1997) acculturation strategies. Thus, It indicated that Berry's (1997) acculturation strategies are useful theoretical tools predicting psychological preference of expatriates in Korea. However, participants showed little difference in that all expatriates of four categories showed higher involvement with their original cultural spectator sport. Therefore, unlike Berry's (1997) theory, people with high level of acculturation showed higher levels of involvement with their original cultural spectator sport. It may provide useful information for Korean sport marketers regarding s foreign sport consumers in order to develop a market.

The current study was aimed to examine acceptance intention of sports Wearable products using the Technology Readiness and Acceptance Model. Data were drawn from 271 consumers in their 20s and 30s. Data were analyzed through frequency analysis, exploratory factor analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, simple regression analysis and multiple regression analysis using SPSS 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 program. The results were as follows: First, optimism had a positive effect on perceived usefulness but innovativeness, discomfort and insecurity did not affect perceived usefulness. Second, optimism and innovativeness had a positive effect on perceived ease of use and discomfort had a negative effect on perceived ease of use but insecurity did not affect perceived ease of use. Third, perceived ease of use had a positive effect on perceived usefulness. Fourth, perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use had a positive effect on acceptance intention.


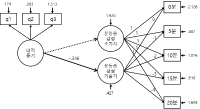
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationship between physical environment, customers' emotions, switching barriers and loyalty among water ski resort users in Gyeonggi-do and Gangwon-do province. Convenience sampling method was used, 277 of the questionnaires were selected as the ultimately valid sample. Data were analysed by SPSSWIN 18.0 and AMOS 18.0 program using frequency analysis, reliability analysis, correlation analysis, confirmatory Factor Analysis(CFA) structural equation model(SEM). The research findings are as follows. First, relations between physical environment and customers' emotions, attractiveness, cleanliness, convenience and human service had a significant positively impact on positive emotional response. convenience, attractiveness, human service, and cleanliness had a significant negatively impact on negative emotional response. Second, relations between customers' emotions and switching Barriers, positive emotional response did not have a significant impact on switching cost and interpersonal relationship, but positive emotional response had a significant impact on attractiveness of alternatives. negative emotional response had a significant impact on switching cost, interpersonal relationship and attractiveness of alternatives Third, relations between switching barriers and loyalty, switching cost did not have a significant impact on loyalty. but interpersonal relationship and attractiveness of alternatives had a significant impact on loyalty.

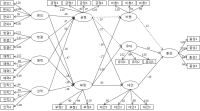
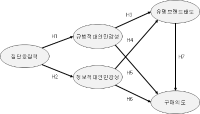
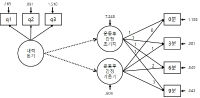
The objective of the current study is to empirically reveal the impact of self-recognized group cohesiveness and interpersonal susceptibility (normative interpersonal susceptibility and informative interpersonal susceptibility) on mountain bikers’ attitude toward name brand and purchase intents using structural equation model. In order to achieve this goal, the researchers surveyed 217 mountain bikers in six mountain bikers’ clubs in Chungcheong-do province area in South Korea. In order to validate the proposed structural model, SPSSWIN version 21.0 and AMOS 18.0 were utilized. The results showed that first, group cohesiveness had a positive influence on the bikers’ normative and informative interpersonal susceptibility. Second, normative and informative interpersonal susceptibility positively influenced attitude toward name brand. Third, normative interpersonal susceptibility did not positively influence the purchase intent, but informative interpersonal susceptibility did. Fourth, attitude toward name brand positively influenced the purchase intent.

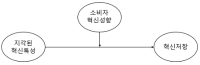
The purpose of this study was to identify the effect of sportwearable device's innovation attribute on innovation resistance and moderating effect of consumer innovativeness between sportwearable device's innovation attribute and innovation resistance. Samples were the 20, 30s who registered on undergraduate and graduate college students. They were extracted from three different universities, in Seoul. After 125 questionnaires were removed, 375 samples were used in the actual analysis; frequency analysis, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation, and structural equation modeling. The results were as follows. First, perceived innovation attributes of sportwearble devices had a negative effect on innovation resistance. Second, consumer innovativeness was moderated in the relationship between perceived innovation attributes and innovation resistance.


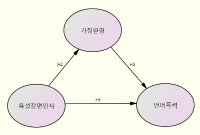
The purpose of this study is to analyse that the college students' recognition on abuse scene of sport broadcasting influences verbal violence. The subjects were college students in P municipality and this study distributed 230 questionnaires among them. And 203 questionnaires were collected except some questionnaires that didn't fill in them properly. To analyze them, this study used SPSS Win 20.0 and AMOS 20.0 and came to a conclusion as follows. First, the College students' negative recognition on abuse scene of sport broadcasting had negative influences on verbal violence. Second, home environment wasn't affected by the college students' negative recognition on abuse scene of sport broadcasting. Third, the verbal violence also wasn't much effected by the home environment of the college students. Finally, the home environment didn't intervene in the relationship between the college students' recognition on abuse scene of sport broadcasting and the verbal violence. Therefore this study considers that the abuse scene in the game on the live broadcasting needs to apply sanction properly by a broadcasting station for TV viewers, although the college students with a higher negative understanding of this abuse scene use less verbal violence.

The purpose of this paper is to map how sport sociologists and sport historians have engaged in the study of race and/in sport. Focusing on scholars with two communities of the North American Society for Sport Sociology & Sport History, it investigates themes, historical/sociological philosophy, theoretical/methodological issues that underpin their works. To be more specific, mainly four types of research are detailed: 1) popular narratives that mostly celebrate black athletes’ success in sport, 2) so-called the early academic works that highlight the positive role of sport in advancing the issue of race in relation to social justice, unification, equality, and so on, 3) a group of researches informed by the positivism, which attempt to discover, investigate, identify racially problematic phenomena, incidents, policies, or incidents and explain why they happen, what makes them problematic, and how to solve such matters, and 4) critical paradigm that orients cultural studies based researches that attempt to explore the relationship between sport and race with focus on interpretive, theoretical, and reflective approaches. In conclusion, it is discussed why I pay attention to the critical paradigm, what it’s emergence means to the sporting academy, and in what ways we can embrace it into the Korean sporting academy.
Recent studies focus on Metabolic Equivalent Task (MET) to measure levels of and areas of peoples’ physically active lifestyle because MET more readily translate peoples ’subjectively perceived physicality into standardized scores. MET also allows researchers to clearly understand the relationships between peoples’ physicality and psychological variables. Thus, the purpose of this study was to understand the levels of and areas of MET among Korean middle school students and to analyze the relationships between MET scores and physical self-efficacy. A total of 278 questionnaires were analyzed using SPSS 18.0. Exploratory factor analysis, descriptive analyses, and regression analyses indicated that middle school students’ physically active lifestyle occurred in the order school, leisure, housework, and transportation areas. Female students did more physical activity in the areas of housework and transportation, compared to male students. In contrary, male students did the majority of physical activity in the areas of school and leisure. Physical self-efficacy affected students’ MET scores, especially for vigorous intensity activity. With regard to gender differences, physical self-efficacy affected male students’ MET scores in the area of leisure while female students’ MET scores were affected in the areas of school and housework. The results were discussed in light of methodological and pedagogical perspectives, and future research suggestions were provided in the discussion.

The purpose of this study was (1) to develop a archery lesson using forced connection method-sportcasting for cultivating collaborative problem-solving competencies, and (2) to apply and to examine the responses of students after physical education(PE) lesson. A archery lesson of Understanding-Performance-Appreciation step was developed according to LfPE(Lee, 2014) using backward curriculum design. Participants were tenth grade students (N=148) in a high school. Open-ended question used to collect the data. The analysis of data indicates that students expressed features in lessons. Six features are (a) 朋友信之, (b) 君子不器, (c) 能竭其力, (d) 觀其所由, (e) 溫故知新, (f) 思而不學. In-depth interviewers were carried out for further analysis of the answers to the questionnaires. The results are as follows. First, 朋友信之 means lesson cultivating collaborative problem solving competencies. Second, 君子不器 means pleasant and funny lesson. Third, 能竭其力 means lesson cultivating self management ability. Fourth, 觀其所由 means lesson cultivating appreciativeness for archery. Fifth, 溫故知新 means lesson improving the status of PE teacher and school. This study concluded that a archery lesson generated fun and interest for students. Implication for developing lesson using LfPE, utilize and transform forced connection method-sportcasting in PE were discussed.


There has been a growing advocacy for a critical approach to physical education teacher education(PETE) in the era of globalization and ubiquitous society. Drawing on critical pedagogy, the purpose of this paper was to explore the meanings and methods for developing critical professionalism in PETE through identifying the definitions and features of critical professionalism. The notion of critical professionalism includes four crucial components: critical reflection, social sensitivity, critical thinking, and practicability. This paper suggests an inquiry-oriented physical education teacher education to develop per-service teachers’ critical professionalism in terms of providing a range of teaching methods centered on microteaching, discussion-based lessons, critical reading and writing, and using media materials. Building on findings, it was concluded that there is a need of programs for the development of policy literacy understanding complex social and cultural contexts of school physical education. Furthermore, PETE should focus on the processes of critical reflection on the teaching and learning act itself within wider social contexts, by using an inquiry-oriented approach to PETE, which will contribute to fostering teachers’ critical capacities needed to guard the educational aims of physical education against political interference.

Sportscasting in Physical Education (Lee, 2011) is a class activity that students simulate sports broadcasting (e.g., students report, analyze, and comment on game play). It encourages problem solving (PS) learning for students. Scaffolding is the support with the intention of helping the student achieves his/her learning goals and contributes to problem solving. However, limited studies have examined if sportscasting with scaffolding is effective instructional strategies for PS. The purpose of this study was to examine effects of sportscasting with scaffolding on PS abilities, and on academic achievement. Participants were 46 college students. The static-group comparison design was used: an experiment group (N=26) with supportive scaffoldings (e.g., conceptual explanation, terminology dictionary, visual materials) and a control group (N=20) with reflective scaffoldings (e.g., organizing the environment, using appropriate cues to guide behaviors, and modeling). The results revealed that students in reflective scaffoldings had higher PS abilities than students in supportive scaffoldings. However, two groups were not statistically different in academic achievement. Sportscasting with instructional scaffolding promote a deeper level of cognitive skills and male students performed better than female students. The effective scaffolding types (Lewis, 2010) for sportscasting were discussed to help students to foster PS skills.


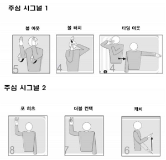
Impact of 9-week strength training of racing cyclist candidate during training camp on body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was examined. Two by two (cyclist experience, y/n and strength training (ST) participation, y/n) experiment design was employed. A total of 20 candidates participated and divided evenly into four groups; 1) experienced cyclist participating ST (CST), 2) non-experience cyclist participating ST (nCST), 3) experienced cyclist no participating ST (CnST), and 4) non-experience cyclist no participating ST (nCnST). Two programs were introduced; 1) non ST containing, pre-existing program emphasizing on sprint and acceleration training and 2) new-program containing ST and sprint and acceleration training. CST and nCST participated the latter program. Before and after the 9-week training, body composition, racing cyclist specific fitness, and racing cycle performance was tested. After 9 weeks, all groups decreased body weight(p<0.05), body fat content(p<0.05), body mass index, and CST and nCST increased lean body mass(p<0.05). Muscular strength measures such as grip strength, low back strength, 1RM of bench press, 1RM of squat, and anaerobic capacity improved after 9 weeks in all groups(p<0.05). The magnitude of changes was greater in order of CST, nCST, CnST, nCnST. Time trial of 200 meter sprint was faster after 9 weeks in all groups except CnST while 500 meter sprint was improved only in nCnST(p<0.05). After 9 weeks, regardless of previous cyclist experience, those who participated in ST ranked high places at racing cycle competition. Both training programs for the candidates improved body composition and racing cyclist specific fitness. When strength training was added to pre-existing training program emphasized on sprint and acceleration, the racing cycle performance was enhanced. Strength training for racing cyclist is highly recommended to improve their racing performance.

The primary purpose of the study was to identify the characteristics of Korean national youth soccer players’ functional movements. The secondary purpose was to examine whether certain tests of Functional Movement Screen (FMS) meaningfully achieve goodness-of-fit for the soccer-specific movements. Korean national youth soccer players (30 male players, 18.37 ± 0.67 yrs, 178.7±7.09 cm, 70.2±6.46 kg), performed FMS tests [deep squat (DS), hurdle step (HS), in-line lunge (IL), shoulder mobility (SM), active straight leg raise (ASLR), trunk stability push-up (TSP), and rotary stability (RS)]. The mean (±SD) FMS composite score and each test score were calculated. Rasch analysis, which was used to determine the goodness-of-fit for the tests, was applied to examine the item difficulty of the FMS tests. The mean FMS composite score was 10.2± 1.79; the mean DS, HS, IL, SM, ASLR, TSP, and RS score were 1.13±0.35, 1.27±0.45, 1.4±0.56, 1.6±0.77, 2.07±0.69, 1.43±0.82, and 1.3±0.47 respectively. According to the results of Rasch analysis, 4 tests (DS, IL, ASLR, and RS) were shown to be within the acceptable range (infit & outfit > 0.5 ~ < 1.5). The other 3 tests (HS, SM, and TSP) were shown to be out of acceptable range. The additional analysis revealed the DS (logit = 2.08) as the most difficult test and ASLR (logit = -3.16) the least. The results of the study showed that the players’ FMS composite score was lower (< 14) than the cut-off points used by previous studies for different athletes. The further study is warranted to examine the relationships between the scores of the tests appeared to be soccer-specific in the present study and the level of performance variables.

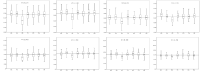
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the physical performance and develop the criteria of 4243 middle and high school students across 5 provinces (Busan, Gwangju, Daejeon, Gyeongi and Jeonbuk) in Korea that took part in the talent development project. The data was collected between 2011 and 2014. The criteria was divided by gender and age across different grades, and the mean, standard deviation and 5 evaluation levels were calculated and analyzed.

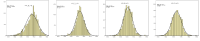

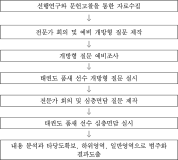
Values, such as development and social responsibilities, are added on victory-oriented Korean sport. Those change of values are along with discussions regarding improvement of players’ training environment, however, discussions on improvement of players’ training environment so far rather focused on ideological concepts, such as players’ holistic human development and human rights, therefore, there was a lack of discussion on practical training methods or teaching methods. This study focused on mental coaching as a specific method for improvement of players’ training environment. Mental coaching provides players with performance enhancement, personal growth, and self-actualization utilizing mental training, consulting, and mentoring in their training processes. This study examined a possibility of introduction of mental coaching as a training camp method for players by creating a training camp reflected on mental coaching perspectives and verifying the program effects of application. First of all, a mental coaching training camp was created through consultations with mental coaches, supervisors, and coaches. Goals of the mental coaching training camp were development of competition-routines, establishment of competition-circumstance coping strategies, comprehension of elite-players’ psychological resources, goal-setting, and motivation and the program consist of badminton competitions, mental education, a special lecture by an Olympic gold medalist, tracking, and sharing. The mental coaching training camp proceeded with middle and highschool badminton players and 31 coaches during three-days and four-nights. As results, the training camp was effective for players’ performance enhancement, personal growth, and self-actualization and team coaches realized a necessity of improvement in terms of their training and teaching behaviors. In other words, mental coaching training camp played a role as a source of long-term change as well as short-term results, thus, this study verified that the mental coaching can be introduced as a training camp method. It is anticipated that this study can provide sport fields and academic sport areas with an opportunity to consider both training contents and methods when it comes to discussion players’ training environment development.


