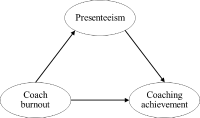
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship among burnout, presenteeism, and coaching achievement perceived by athlete coaches in the sport field, and to identify the mediating effect of the presenteeism on the relationship between burnout and coaching achievement. Methods For this purpose, data were collected from 151 athlete coaches in South Korea through the survey. Measurement tools consisted of questionnaires on the coach’ burnout and presenteeism (SPS-13) that were designed in line with the research purpose. Collected data were analyzed using reliability testing, descriptive statistics, correlation analysis and simple mediation effect test. Results First, burnout level perceived by coaches was positively related to presenteeism, and not associated with coaching achievement. And presenteeism negatively correlated with coaching achievement. Second, the burnout level of the coach was negatively related to the coaching achievement through the presenteeism, the mediating variable. Conclusions Burnout of the athletes' coaches in the sports field has been confirmed to decrease the coaching achievement by increasing the presentations which is the work impairment due to their health problems.

Purpose : The purpose of this study was to investigate coaching information with which coaches provided players during badminton competition. Methods : To this end, we generated an open-ended questions and presented it to 88 high school athletes registered in the Badminton Korea Association. The survey was conducted during a tournament and immediately after the tournament to collect the data. The collected data were categorized through inductive content analysis. Results : As a result of this study, a total of 480 raw data points collected through the open-ended survey were categorized into four general areas: psychological information, technical information, tactical information, and game operation information. Specifically, psychological information was divided into six subdivisions: concentration, confidence, relaxation/stabilization, mental toughness, play thought, and passion; technical information was broken into four subdivisions: strokes, footwork, swing and posture, and position preparation; tactical information had four subdivisions: coping to opponents, play changes, rotation, and manipulation of opponents; and, game operation information was divided into two subdivisions: taking the lead in a game and changing atmosphere. Conclusions : In other words, in badminton competition, the coaches strengthened psychological skills that promote psychological stability to attain the athletes’ peak performance and modified the athletes’ motion into the action necessary for achieving accurate techniques. Furthermore, they provided a variety of coaching information so that the athletes will respond appropriately to their opponents’ play, take the lead in games and induce a positive mood. The psychological, technical, tactical and game operation information offered by badminton coaches are the main factors influencing the performance of badminton players and suggest a need for the proper management and control of the coaches as well as athletes for the peak performance.

Previous work has shown that coaches sought information from several sources; however, there was a strong reliance on learning from other coaches within their social networks. There has been limited research examining the nature of these social networks with other coaches (Trudel and Gilbert 2004). Thus the purpose of this study was to examine the structures of coaches’ social networks of Korean rhythmic gymnasts. Research questions were: (1) What are the network structures of Korean rhythmic gymnasts’ coaches? (2) What structural parameters contribute to coaches’ network structures, and (3) Is there an association between coaches’ network and flow of information in their networks? A total of 37 coaches of youth rhythmic gymnasts (6-18 years old) participated in this study. Each of those coaches was asked to complete a Name Generator Questionnaire (i.e., list four names that you have a close relationship with) and general socio-demographic survey. Data were analyzed using social network analysis tools such as UCINET, p-net, and Quadratic Assignment Procedure. Analysis of network centrality, density, and strong components showed that (1) homophily was identified in the structure of coaches’ social networks (2) homophily (e.g., by gymnasts’ ranking, mentor coaches) contributed to the total social network of coaches, and (3) interacting only with close coaches in the network, coaches received information about coaches/coaching from the strong ties rather than weak ties (Granovetter, 1973). This study also has strong links to Wenger’s (1998) community of practice which posited that groups of people share a common characteristic in practice.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop the Emotional Intelligence Scale in Sport Coaching(EISSC) based on the emotional intelligence trait model. Methods The participants were 236 professional sports coaches by the purposive sampling methods via e-mails. 48 preliminary items were developed by literature review among expert panels. Then, a total of 40 items were selected after the item-analysis. Exploratory factor analysis was conducted for construct validity and criterion validity was evaluated by Person’s correlation with coaching efficacy scale and general emotional intelligence scale. An internal consistency, Cronbach's alpha coefficient, was used to see the reliability. Results The results of exploratory factor analysis presented a six sub-structure factors (Self-awareness, Awareness of others, Optimism, Utilization of emotion, Emotion regulation, Social skills) with 20 items, which explained 68.49% of the total variance. Criterion-related validity was supported by correlations with in coaching efficacy(r=.713) and general emotional intelligence(r=.647). Reliabilities were secured with Cronbach’s alpha coefficient .854 for the total 20 items. Conclusions The EISSC can be used to provide an valid measure of emotional ability of coaches in sport.
Purpose The purpose of this study lies in: 1) clarifying what constitutes coaching ethics; 2) providing a theory to set up a coaching ethics in Korea; 3) and offer a direction to coaching ethics based on its normative traits. Methods In order to achieve this purpose, the following has been done: 1) a review of existing literature has been done to analyze the relationship between professionalism and ethics in coaching and explicate the concept and necessity of coaching ethics; 2) an effort has been made to answer such questions as “why and how much should a coach be ethical?”; “How should a coach be ethically evaluated?”; 3) An analysis of ethical responsibility embedded in coaching has been done, focusing on four ethical theories: Kantian categorical imperative, Aristotelian phronesis, Simon’s broad internalism, and Morgan’s conventionalism. Results This study reviews prior literature considering the relationship between professionalism and ethics in coaching and offers theoretical evidence to explain coaching ethics and its normative aspect. This will help resolve complicated ethical predicaments arising in the field. Conclusions This study emphasizes the role of coaches to improve fairness and wholesomeness in the field of sport, as well as suggests a coaching ethics required of a profession with internal regulations. Coaching ethics not only increases a sense of responsibility on the part of coaches but helps create a virtuous circle in which coaches’ ethical sensibility is reproduced in athletes as well. All in all, coaching ethics can stop important qualities of sport from deteriorating due to commercialism and the winner-takes-all attitude prevalent in sport today and contribute to a fair and wholesome sporting culture.
PURPOSE This study aimed to examine the mediating effect of psychological needs in the relationship between multiple coaching styles and teamwork among college football players. METHODS This cross-sectional study involved 526 elite football players. Descriptive statistics, reliability analysis, confirmatory factor analysis, correlation analysis, path analysis, and macroprocess were performed using statistical software to test the mediation effects of the data collected. RESULTS The findings suggested that autonomy-supportive and structure coaching styles positively correlated with and impacted psychological needs satisfaction and teamwork. Conversely, control and chaos coaching styles negatively correlated with and impacted psychological needs satisfaction and teamwork. In addition, autonomysupportive and structure coaching styles negatively correlated with and impacted psychological need frustration, while control and chaos styles positively correlated with and impacted psychological needs frustration. Furthermore, psychological needs satisfaction and frustration were found to partially mediate the relationships between autonomy support and teamwork, structure and teamwork, control styles and teamwork, and chaos styles and teamwork. CONCLUSIONS Autonomysupportive and structure coaching styles positively influenced teamwork by satisfying psychological needs. In contrast, control and chaos coaching styles negatively impacted teamwork by contributing to psychological needs frustration.
Purpose The purpose of this study is to conduct a typological classification of female recreational sport participants' coaching experience. Methods Q methodology was conducted using 25 Q-samples and 25 P-samples. Data were analyzed using PQmethod software. Results Four types were categorized: communication and character-oriented (I), function and immersion-oriented (II), process and fun-oriented (III), and function and inclusion-oriented (IV). These types were re-categorized as 'non-functional value-oriented (I, III)' and 'functional value-oriented (II, IV)'. Conclusion This study also made efforts to explore the value and norm that female participants expect from sport participation, which provided a variety of perspectives on social, psychological and philosophical discussions about woman sport. In addition, each type and its characteristics can be used as meaningful basic data in teaching method (coaching theory) for woman sport.


Purpose The present study explores educational values of professional coaches from perspectives as educators while they are giving the players sports coaching. Since free agent system was introduced in 1999 at Korean Baseball Organization(KBO) league, the socio-economical differences between players and coaches are getting bigger and bigger. In this situation, professional coaches tend to have more difficulties in interacting with the players. The study focuses on looking into professional coaches' educational agony and reward. Also, it highlights their educational values as educators rather than coaches. Methods Two professional baseball coaches and a TV commentator participated in the study: all past professional players, and professional coaches for more than 10 years. The researchers collected data through semi-structured in-depth interviews; each participant was interviewed three times. The researchers recorded and transcribed all of the interviews; then, the researchers reread the interview transcripts and inductively produced codes for themes whenever emergent codes appeared. Verbatim quotations from the interviews are excerpted in the present research report. Results The findings indicate that, first, the participants are all highly motivated in giving lessons to the players. They all helped the players overcome the difficulties and be good players. They emphasized the importances of endeavors and attitudes during their lessons to be well-received by the players. Second, the participants agreed that good coaches should have the ability to find the potentials of the players and have personality to gain the players' trust. They always have to work and study hard to keep expertises. Conclusions This study argues that the participants are playing their roles in a sport coaching area not only as coaches, but also as educators.


Values, such as development and social responsibilities, are added on victory-oriented Korean sport. Those change of values are along with discussions regarding improvement of players’ training environment, however, discussions on improvement of players’ training environment so far rather focused on ideological concepts, such as players’ holistic human development and human rights, therefore, there was a lack of discussion on practical training methods or teaching methods. This study focused on mental coaching as a specific method for improvement of players’ training environment. Mental coaching provides players with performance enhancement, personal growth, and self-actualization utilizing mental training, consulting, and mentoring in their training processes. This study examined a possibility of introduction of mental coaching as a training camp method for players by creating a training camp reflected on mental coaching perspectives and verifying the program effects of application. First of all, a mental coaching training camp was created through consultations with mental coaches, supervisors, and coaches. Goals of the mental coaching training camp were development of competition-routines, establishment of competition-circumstance coping strategies, comprehension of elite-players’ psychological resources, goal-setting, and motivation and the program consist of badminton competitions, mental education, a special lecture by an Olympic gold medalist, tracking, and sharing. The mental coaching training camp proceeded with middle and highschool badminton players and 31 coaches during three-days and four-nights. As results, the training camp was effective for players’ performance enhancement, personal growth, and self-actualization and team coaches realized a necessity of improvement in terms of their training and teaching behaviors. In other words, mental coaching training camp played a role as a source of long-term change as well as short-term results, thus, this study verified that the mental coaching can be introduced as a training camp method. It is anticipated that this study can provide sport fields and academic sport areas with an opportunity to consider both training contents and methods when it comes to discussion players’ training environment development.



PURPOSE This study analyzed the relationship among coaching behaviors, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance as perceived by high school athletes. Additionally, it examined whether motivational climate, competence, and effort mediate the relationship between coaching behaviors and failure tolerance. METHODS Using questionnaires measuring autonomy-supportive coaching behavior, controlling coaching behavior, motivational climate, sports competence, effort, and failure tolerance, 365 high school athletes were surveyed. Using SPSS 28.0 and Amos 28.0 software, descriptive statistics and structural equation modeling were conducted along with the following types of analyses: reliability, correlation, confirmatory factor, convergent validity, and discriminant. Additionally, the bootstrap method was used to verify serial multiple mediating effects. RESULTS Autonomy-supportive behavior had a significant positive effect 1) on motivational climate, sports competence, and effort and 2) on failure tolerance. 3) Controlling coaching behavior had a significant negative effect on motivational climate and sports competence. 4) Motivational climate and 5) sports competence both had a significant positive effect on effort. 6) Effort had a significant positive effect on failure tolerance. Last, in the relationship between autonomy-supportive behavior and failure tolerance, motivational climate, sports competence, and effort showed partial mediating effects. CONCLUSIONS This study confirms the importance of coaches’ autonomy-supportive behavior in determining failure tolerance among adolescent athletes. Based on this information, counseling (educational) programs aimed at enhancing performance can be developed and provided in sports settings, thus fostering success among athletes.