 ISSN : 1598-2920
ISSN : 1598-2920

Vertical jumping is one of basic skills in many sports activities. Maximizing vertical jumping performance requires large “power”, which implies that one should generate force against the ground in a short period of time. In order to gain better understandings of how human musculo-skeletal system mechanically functions to achieve maximal power in vertical jumping, the proposed “dynamic catch” mechanism, one of “power amplification” mechanisms through the role of muscle-tendon interaction, was specifically reviewed base on the morphological and mechanical characteristics of lower limb muscle-tendon complex. By understanding basic structural and functional features of human muscle-tendon interaction, this review aims to provide basic scientific information for training and rehabilitation and promote convergence researches in related areas, such as sports biomechanics, mechanical engineering, and sports medicine.


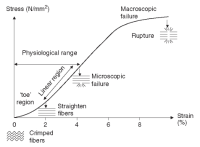

This study was aimed at investigating the effect of head-tilt angle on autonomic nerve modulation immediately after a single bout of exercise in twenty-three healthy young males(age 21.96 ± .4 yrs). Post-exercise HRV was measured on supine(SUP), -15°head-down tilt(HDT), and +15°head-up tilt(HUT) followed by 20 min aerobic exercise with moderate intensity(40% of VO2max). As results, heart rate recovery during post-exercise on each tilt angle(SUP vs. HDT vs. HUT) had no significant difference(p> .05). Also, there were no significant difference in time and nonlinear domain index of HRV. On spectral analysis; however, frequency domain index(HF, LF/HF ratio, HF/TP ratio, HF nu, LF nu) had significant difference(p< .05) on each tilt angle at recovery. Especially, PNS reactivation index (HF, HF/TP ratio, HF nu) had significant increase on HDT compared to HUT(p<. 05) while SNS activation index (LF/HF ratio, LF nu) had significant decrease on HDT compared to HUT(p<. 05). Furthermore, there were significant interaction between recovery time elapsed and each tilt angle (except for HF/TP ratio). In conclusion, -15°head-down tilt promotes the effective cardiac vagus nerve reactivation immediately after a single bout of aerobic exercise.


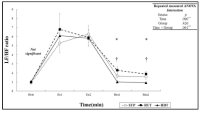
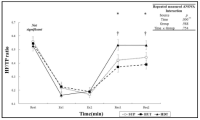

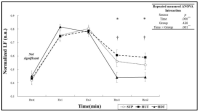

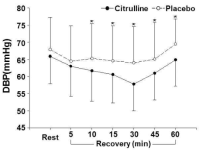
It has well known that post-exercise hypotension (PEH) after a bout of aerobic exercise was a major mechanism to reduce blood pressure though exercise training, and that citrulline supplementation reduced blood pressure by increasing nitric oxide in vivo. However, the effects of citrulline supplementation on PEH have not been fully elucidated yet. This study was designed to examine the effects of citrulline supplementation on PEH after a bout of aerobic exercise in prehypertensive and normotensive 20s males. The effects of a four-day citrulline or placebo treatment on blood pressure, cardiovascular function, and blood lactate concentration measured at rest and during recovery phase after a bout of exercise performed for 30 min at 70% VO2max were compared and analyzed. All subjects participated in a citrulline trial and a placebo trial repeatedly according to a counter-balanced order. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and mean arterial pressure measured at 10-60 min of recovery phase in citrulline trial were significantly lower than placebo trial. Rate-pressure product measured at 30 min and 45 min of the recovery phase in citrulline trial was significantly lower than placebo trial. 2) No significant differences were found in heart rate (HR), cardiac output (CO), and total peripheral resistance (TPR) measured during the recovery phase between two trials. There were significant differences in HR, stroke volume, CO, and TPR among times within a trial. 3) No significant difference was found in blood lactate concentration measured at rest and during the recovery phase between two trials. The results would be summarized that the PEH was augmented by the citrulline supplementation, and that burden to cardiac muscle as well as cardiovascular function were not affected by the citrulline supplementation. It was concluded that the short-term citrulline supplementation would be very effective to augment the PEH. A research investigating the effects of citrulline supplementation on the PEH in pre-hypertensive and/or hypertensive individuals would be warranted. In addition, a study examining the effects of citrulline supplementation during long-term exercise training on the blood pressure in hypertensive patients also would be warranted in near future.

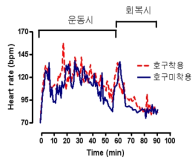
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of wearing of safeguard devices on various blood ions (i.e., Na+, K+, Ca2+) concentrations, gas parameters (PO2, PCO2, hematocrit [Hct], hemoglobin [Hb], Saturated [Sat] O2), and energy substrates (i.e., glucose, free fatty acid [FFA], lactate) concentrations during Kumdo training. Research scope extended to examine the heart rate changes during each exercise sessions. In order to achieve the research goal, 10 male elite Kumdo players, who play for G city in Gyeongsangbuk-do, were participated, and their mean maximum oxygen uptake level was 51.2(±6.1)mL· kg-1min-1. All subjects undertook Kumdo training sessions twice, which carefully pre-planned and consisted of routinely carrying out exercise program. Training period for each session was 80 min long including 10 min each for warm-up and warm-down period, but the conditions with wearing body protection devices were different following either with wearing complete set of safeguard devices or without wearing any safeguard devices except general training cloth. Heart rate was measured by every minute interval. K+ and Ca2+ showed interaction effect between the conditions with wearing safeguard devices and conditions with time of Kumdo training. Hct and Hb level significantly increased after 60 min Kumdo exercise regardless of wearing safeguard devices. Kumdo training induced dropping of blood pH independently with wearing safeguard device conditions, however the values and/or concentrations of PO2, Na+, glucose, lactate, Sat O2were significantly increased. Heart rate was maintained marginally higher values throughout exercise period when safeguard devices were worn. Based on these results, it was concluded that wearing the safeguard devices could possibly be causing a physiological metabolic changes, and this may be drawn by increased body fluid loss and energy expenditure. Further study should be undertaken to examine the effects of wearing safeguard devices on hitting intensity and hormone secretion and concentrations, that closely associated with body fluid and ion balance during Kumdo exercise and/or training.

The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on a body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate. Fifty-one elderly women were randomly assigned to aerobic training group (EX: n=12), resveratrol supplementation group (R: n=13), combined aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation group (EX+R: n=12), and control group (CON: n=14). The subjects in EX group exercised three sessions per week, 40 minutes per session for 8 weeks, the subjects in R group took 500 mg of resveratrol per day for 8 weeks, and the subjects in EX+R group received both treatments. The subjects in CON group were asked to maintain normal daily life pattern without any treatment for the same period of intervention. Body composition, physical fitness, insulin resistance, liver function, blood pressure, and heart rate were measured at pre- and post-test and the data were compared among groups and between tests by utilizing two-way ANOVA with repeated measures. Main results of the present study were as follows: 1) Physique and body composition did not change significantly in all groups. 2) Muscular endurance increased significantly in EX+R group, whereas the other physical fitness-related variables showed no significant changes in all groups. 3) Fasting glucose, fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, and HbA1c tended to be improved in EX+R group. 4) AST, ALT, and γ·GT showed no significant changes in all groups. 5) Systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure increased significantly in CON group. Heart rate tended to be decreased in EX+R group and EX group. It was concluded that the 8 weeks of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation had positive effects on muscular endurance, insulin resistance, and blood pressure in T2DM elderly women. Research investigating the effects of a longer period of aerobic training and resveratrol supplementation on the same variables would be warranted in the future.

The purpose of this study was a investigate the endothelial function of prehypertensive during dynamic exercise. Hypothesis of this study was to impair the endothelial function in prehypertensive compared to normtensive during dynamic handgrip exercise. Eleven healthy prehypertension (24±2 yrs) and ten healthy normotensive (25 ± 2 yrs) were recruited in this study. Participants were performed dynamic handgrip exercise in one contraction per second at 30% of maximum voluntary contraction for three minutes. Vascular (blood vessel diameter, blood flow) and cardiar response (stroke volume, heart rate and cardiac output) were measured at rest and during exercise. Flow mediated dilation (FMD) was decrease significantly in prehypertensive less than normotensive (p<0.05) at rest, and vasodilation of prehypertensive was reduced significantly less than normitensive during exercise (p<0.05). All the cardiovascular responses were aot significantly different at rest and during exercise between prehypertensive and normotensive. These results suggest that endothelial function is impaired in prehypertensive compared to in normotensive


The present study has been carried out with a purpose of a long term estimation for the body size and BMI (Body Mass Index) of Korean children and youth using ARIMA, a time series model. In order to select an estimation model for the optimum time series, among the time series analysis method of SPSS22.0 statistic programs, a multivariate ARIMA (p,d,q) model has been selected that has an input series (physical education facility, time spent for physical education, animal source foods, GDP deflator, animal source food intake ratio), using annual average data of height, weight, and BMI data from 1965 to 2015. Among the several optimal measurements in ARIMA model with estimation variables, an optimal RMSE-based model (RMSE: Root Mean Square Error) has been selected. Using this model, the estimation model and estimated values of children’s height, weight, and BMI have been suggested for each age group. The results are as the following. The trend estimation of height follows a logistic curve, with both male and female groups showing increasing trends. The weight has a trend of increasing ratio higher than height. BMI also shows a trend curve similar to weight. The estimation model has been mostly ARIMA(0,1,0). In particular, the average BMI has been estimated as 22-23 for male students in 6th, 8th, 9th, 11th and 12th grade in 2030. This indicates the recent increasing obesity as children and youth occupy most of daily time for play culture that is far from physical activities, such as computer games, smartphone games, and video games at home.




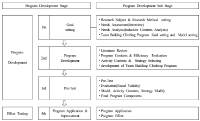
The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of team building climbing program on happiness, social development, self-esteem, stress, and depression of the youth. The participants consisted of 27 university students. The self-report instruments were compose of happiness scale, social development inventory, self-esteem scale, stress inventory, and depression scale. Qualitative data were participants’ perception about the effects of team building climbing program. Firstly, team building climbing program had positive effect on happiness of the youth, while climbing program had not significant effect on happiness of the youth. Secondly, both team building climbing program and climbing program had positive effect on social development of the youth, while team building climbing program was significant higher than climbing program in post-time. Thirdly, team building climbing program had positive effect on stress of the youth, while climbing program had not significant effect on stress of the youth. Fourthly, both team building climbing program and climbing program had positive effect on self esteem of the youth, while there were not significant between team building climbing program and climbing program in self esteem of post-time. Fifthly, both team building climbing program and climbing program had positive effect on depression of the youth, while there were not significant between team building climbing program and climbing program in depression of post-time. Limitations of this study and future implications were discussed.


To examine the flow of knowledge structure in Korean journals of sport and social sciences over the last 10 years, this study has derived a knowledge map by conducting community analysis, one of the social network analysis methods, on Korean Journal of Sports Industry Management, Korean Journal of Sport Pedagogics, Korean Journal of Sport Sociology, Korean Journal of Sport Psychology and Korean Journal of Leisure and Recreation. According to the analysis result, the integrated knowledge map for the field of sport and social sciences was classified into 5 groups and these groups were derived to be similar to the knowledge structure of the keyword groups for the research topics of the five journals targeted by this study. Along with this result, at the same time, it has been confirmed that most of the groups shared keywords with each other. Especially, some of the keywords for the research topics of sports industry management have transferred to the research topics of leisure and recreation and those of sport sociology. Sport sociology has been revealed to be closely related to sports industry management and sport psychology. In the case of sport psychology, it has been confirmed that it is related to most of the other groups and the psychological variables for understanding human behavior can be widely used. It shows that leisure and recreation is highly related to sport psychology and sport management in terms of keywords for research topics but it is suggested that it also needs its own independent research topics. Sport pedagogics, by its nature, is an isolated field but interacts with sport psychology and attempts can be made to expand its research topics through an approach based on the concept of pedagogy for physical education.

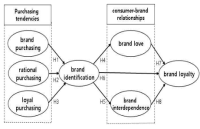
The purpose of this study was to investigate the relationships among purchasing tendencies, brand identification, consumer-brand relationships, and brand loyalty by analyzing structural equation model. A survey was conducted by using members(n=220) of 8 sport clubs located in Chungcheong Province. The data were recorded and analyzed using the SPSSWIN Ver. 21.0 and AMOS 18.0 to analyze the structural equation model. The findings of this study were as follows: First, brand purchasing had a significantly negative effect on brand identification. Second, rational purchasing was found to impact significantly on brand identification. Third, loyal purchasing did not show significant impact on brand identification. Firth, brand identification was found to significantly influence on brand love, brand interdependence, and brand loyalty. Fifth, brand love had no positive impact on brand loyalty. Finally, interdependence was found to impact significantly and positively on brand loyalty.


The purpose of this study was (1) to develop instructional contents for teaching and learning sportsmanship and (2) to examine the perceptions of sports instructors on that contents. Instructional contents based on sympathy was constructed from Youtube clips. Final version was developed to apply situated learning in class and was comprised of twenty-sportsmanship video clips and worksheets. Participants were sports instructors (N=208) in elementary and middle schools. Open-ended question and interview on call were used to collect the data. Qualitative content analysis was used to analyze the instructors’ perception regarding instructional contents. Results of this study showed that sports instructors responded to the contents as thoughtful experience (1) making myself realize the value of opponent, (2) making myself realize the value of sports, (3) making myself realize the value of judge, (4) making myself realize the value of coach/athlete. This study concluded that instructional contents was touching and emotional. Implication of instructional contents for teaching and learning sportsmanship, pros and cons of the contents and teaching tips were discussed.




The purpose of this study was to examine whether β-alanine ingestion for 8 weeks can regulate isokinetic knee strength, and 3km record in middle-long distance woman cyclists. Fourteen middle-long woman cyclists participated in this study and were divided into two groups; training group with beta-alanine ingestion and training group with placebo ingestion. All subjects took in beta-alanine or placebo supplement three times per a day for 8 weeks. Physical activity was evaluated by measuring the isokinetic muscular strength and 3km record before and after intervention for 8 weeks. As a results, in isokinetic test, there were significant interrelationships in peak torque of the right and left flexors at 60°/sec, peak torque of the right and left extensors at 180°/sec, peak torque of the right flexors at 180°/sec. In 3km record, result showed a significant interrelationship by groups and time. The results of present study provide evidence that beta-alanine supplement may be effective to increase physical activity and competition record in middle-long woman cyclists.
The purpose of this study is to analyze relationship between game result and foul, yellow card, red card, penalty kick in soccer match. For the study, the sample used corresponded to 2,654 matches from the 2005 season to the 2014 season of the Korean Professional football League. One-way ANOVA and frequency analysis was used to elucidate the relationship between game result and each element. The results were as follows. First, it was more foul when both home team and away team win the game. Second, home team received more yellow card when home team win the game. Third, it received less red card when both home team and away team win the game. Fourth, home team got more penalty kick when home team win the game.

This study aims to visualize the data regarding the entire rally and the final 5 strokes in a badminton single match and to present its analysis method using the parallel coordinate system. For this study, were used the videos of three games of the final, semifinal, quarterfinal in the '2014 National Fall Badminton Championship’ where the L Player of Gyeonggi C university won championship. Herein, the data was collected utilizing a tagging technique of Dartfish (Ver 8.0), in terms of shuttlecock ball direction, judgment of final kill stroke, and used technique. The data collected were classified and condensed using Excel 2013 program, and the parallel coordinates, which is provided with free open source through D3js.org, was utilized as a data visualization tool. As the results; first, the entire rally of single matches in badminton was visualized; second, as an analysis method of data visualization in relation to final 5 strokes, game pattern analysis, attack success course analysis by players and techniques, attack failure course analysis by players and techniques, and a plurality of selected condition analysis by players and techniques could be presented. In future, when processing subsequent studies that can provide us together with numerically analyzed data as well as visualization through a parallel coordinate system, it is expected that this study could be applicable to a variety of events and utilized in the actual sports games.








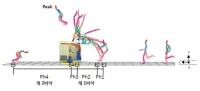
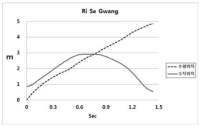
The aim of this study was to acquire essential information regarding Ri Se Gwang motion(element group Ⅱ, difficulty 6.4 point, double Tsukahara with tucked 1/1 twist), which Ri Se Gwang of North Korea performed during the final vault event of artistic gymnastic at Incheon Asian Game 2014, by analyzing motional characteristics. Firstly, Ri Se Gwang technique had second jump airborne time of 1.07 seconds and airborne height of 2.91m, which have great influences on the success of technique while having horizontal and vertical velocity of 2.73 m/s and 3.87 m/s, respectively, at the takeoff. These were sufficient jump motion for successful accomplishment of the technique however flight pattern was somewhat small which was mainly oriented vertically when compared to previous studies of Yeo and YANG Hak Seon 2 techniques. Secondly, blocking angle of vault contact was small at 9 degrees while having very small takeoff angle of 79 degrees. However, it had fast average trunk rotational velocity of 545 deg./s at the vault contact phase by rapidly bending trunk from the board takeoff until approaching the vault leading to achieve fast trunk rotational velocity of 452 deg./s after the take off in order to complete the airborne rotation successfully. Thirdly, the preparation phase of Ri Se Gwang technique had a distinct characteristics that the trunk was rapidly bent during the approach to the vault attempting aggressive blocking which leads to vertically oriented flight. It showed that this characteristic assists the motion of thigh snatch and the regulation of twist which strengthen airborne rotation for airborne rotational motion. And it also showed that sufficient landing and twist angles at the landing phase are possible with free rotational motion if the height of second jump reaches 3 m.








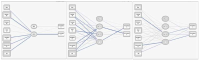
This study examined whether or not regulatory focus can predict motivation level. 141 Ssireum player completed Korean self-regulatory focus of Hong(2005)assessing their self-regulatory focus, and Behavioral Regulation in Sport Questionnaire(BRSQ) of Lonsdale, Hodge & Rose(2008) accessing motivation level based on self-determination theory. Artificial neural network analysis was utilized to find motivation factors that determine the regulatory focus, and the option was multi-layer perception. The result represented promotion focus predicted intrinsic motivation. Also, the prevention focus predicted extrinsic motivation. This result provided that self-regulatory focus can predict player’s motivation level and promotion focus related to intrinsic motivation.


This study aimed to explore the types of traumatic event experienced by Volleyball players and then prepare to take-off the serial process of posttraumatic growth to schematize a causal network by organizing the factors for overcoming adversity. Participants experiences were collected by distributing open-ended questionnaires to 77 professional Women's volleyball players in 2013-2014 and collected data was categorized by inductive content analysis. These results were schematized by the causal network. As a result of the study, according to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: member conflict, competence loss, physical injury, and coach conflict and the emotions relative to the trauma were categorized into four general areas: powerlessness, pressure, dejection, and hostility also coping factors were categorized into three general areas: social support, intervention strategies, and psychological control. Finally, positive growth emerged as psychological leap, performance improvement, psychological maturity, and emotional stability. And as a result of the categorized study, bring about a better understanding to the posttraumatic growth by causal network. Based on the study results, that volleyball players experienced a positive development on themself after overcoming the problem that they had suffered psychological scars from a traumatic event. In doing so, they contributed to the formation of resources that helped them in their positive lives. In this regard, this study expects to provide the players who have been scratched in mind because of the traumatic experience.




