ISSN : 1598-2920
ISSN : 1598-2920
Purpose Sperm quality and function are reduced by environmental factors (e.g., obesity), leading to increased infertility worldwide. Therefore, the purpose of this review paper was to investigate the effects of obesity and exercise training on sperm quality and function in animal and human models. Methods In order to determine the effects of obesity and exercise on sperm quality, motility, morphology, testosterone, oxidative stress, inflammation, we reviewed previous literatures with MEDLINE, PubMed, and Scopus databases. Results The most important factor to control the sperm motility is calcium ion, which is performed by the protein of CatSper (Cation Channel of Sperm). Obese men showed the decrease of number, concentration, motility, and volume in sperm, resulting in delayed or failed fertility. However, regular exercise training increased sperm-mediated factors including number, motility, and morphology, and festicular function-mediated factors including sperm concentration and serum testosterone. Conclusions While obesity exacerbates sperm quality and function in men, regular exercise training with moderate intensity increases sperm number and motility and reduces oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to the improvement of men’s fertility.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the differences in physique and physical fitness according to maturity between primary and middle school baseball players. Methods Participants were 112 elite youth baseball players (49 primary school; 63 middle school). Skeletal age estimated maturity. Physique (height, arm span, thigh volume), body composition (weight, muscle mass and body fat), physical fitness (strength, power, agility, flexibility, coordination, anaerobic power and aerobic power) were measured. An independent sample t-test was used to conduct verify the difference between physique and physical fitness according to maturity. Results The results of analyzing physical and physical fitness according to maturity showed that there was a significant difference (p<.05) between the early maturation group and on-time group in primary school baseball players, body fat percentage, muscle mass percentage, sit-up, anaerobic power and reaction time. There was a significant difference between the early maturation group and the on-time group in the middle school baseball players, weight (p<.05), thigh volume (p<.05), fat mass (p<.05), muscle strength (p<.01), power (p<.05) and coordination (p<.05). Conclusions In conclusion, the maturity of a growing baseball player may be influenced by the performance, so maturity status should be considered when judging the performance of a growing baseball player, especially a middle school baseball player.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to develop a Korean Life Skills Scale for Sports (KLSSS) that original version is the LSSS developed by Cronin and Allen (2017). Methods The subjects were 899 middle school and high school students. The measurement tool was used with LSSS. The validation of KLSSS followed a three-stage of validation procedure; substantive stage, structural stage, and external stage. The result is as follows. Results First, In the substantive stage, KLSSS consisted of 47 items with 8 factors. As a result of the item clarity test, it was confirmed that all the items were appropriate. Second, in the structural stage, KLSSS was explored and confirmed as 5 factors and 18 items. Third, in the external stage, KLSSS showed discrimination and convergent validity. Conclusions KLSSS is composed of 5 factors and 18 items. The factors are teamwork (TW), goal setting (GS), time management (TM), social skills (SS), and leadership (LD). This scale can be used to obtain information on life skills in school physical education or sports.
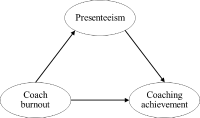
Purpose The purpose of this study was to examine the relationship among burnout, presenteeism, and coaching achievement perceived by athlete coaches in the sport field, and to identify the mediating effect of the presenteeism on the relationship between burnout and coaching achievement. Methods For this purpose, data were collected from 151 athlete coaches in South Korea through the survey. Measurement tools consisted of questionnaires on the coach’ burnout and presenteeism (SPS-13) that were designed in line with the research purpose. Collected data were analyzed using reliability testing, descriptive statistics, correlation analysis and simple mediation effect test. Results First, burnout level perceived by coaches was positively related to presenteeism, and not associated with coaching achievement. And presenteeism negatively correlated with coaching achievement. Second, the burnout level of the coach was negatively related to the coaching achievement through the presenteeism, the mediating variable. Conclusions Burnout of the athletes' coaches in the sports field has been confirmed to decrease the coaching achievement by increasing the presentations which is the work impairment due to their health problems.

Purpose The purpose of this study is to explore the trend of K league exodus and its factors. Methods Qualitative case study was conducted by selecting 9 footballers and 7 their agents as the participants who have migrated from South Korea to China and the Middle East. Results The factors of migration were categorized as three push and pull factors such as economy (individual income and club's profit), policy (employment for foreign and military service) and environment (markets in home and abroad). To understand sport migration in the economic factor, there should be the environmental condition (overseas market) to pay high salaries and transfer fee to individuals and their clubs, and at the same time, the domestic market should be relatively poor environment. In addition, this study overcame limitations of economic and environmental factors by classifying Asian quota system and military service into political factor, and found the specificity (local context) of K league. Conclusions In conclusion, this study can be regarded as the first empirical work on sport labor migration in Korea and valuable as basic data of follow-up studies.
Purpose The purpose of this study was to provide basic data for spectators group of Taekwondo performance efficient marketing activities through market segmentation from characteristics, perceived values of the Taekwondo performance spectators. Methods The subjects of this research were Kukkiwon, Taekwondowon and 1,021 questionnaires were finally used for the analysis. The results of this research were drawn by frequency analysis, CFA(confirmatory factor analysis), reliability analysis, cluster analysis (hierarchical and K-means), cross-tabulation analysis and One-way ANOVA were used for data processing through SPSS 22.0 and AMOS 22.0. Results As results of the analysis, It was subdivided into three clusters (such as group of male college students, man group of low perceived value and high degreed women group of low pragmatism). Conclusions The significant differences of the characteristics and perceived value appeared from each cluster. Cluster 1: A group of male college students, and the highest perceived value for Taekwondo performance. Cluster 2: A group of male, and a low perceived value for Taekwondo performance. Cluster 3: A group of high degreed women and a low pragmatism of perceived value. Therefore, a practical marketing strategy was needed for each groups.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship among the social responsibility (economic responsibility, community cultural activity and social contribution activity), the image of the club, and the assets (image, reliability, attitude and loyalty) of the mother company. Methods The objectives of this research were the home fan in “2018 Shinhan Bank My Car KBO League.” A survey was conducted for 350 home fans of SK Wyverns who gathered in Incheon SK Happiness Dream Baseball Ground to watch the games of SK Wyverns vs. Samsung Lions held from April 6 (Fri.) to April 8 (Sun.). Data processing was done with PASW Ver. 18.0 and AMOS 18.0. Results Firstly, among the sub-factors of social responsibility, economic responsibility, community cultural activity and consumer protection had significant influence on the team image. Secondly, the team image had meaningful influence on the mother company image. Thirdly, the mother company image had significant influence on the mother company trust, mother company attitude and mother company loyalty. Fourthly, the mother company trust had significant influence on the mother company loyalty. Fifthly, the mother company attitude had significant influence on the mother company loyalty. Conclusions The mother companies of professional baseball clubs, too, will have to seek various ways for joint working with professional baseball clubs while actively supporting the activities of the professional baseball clubs being aware that professional baseball clubs give positive effect to the mother companies.


[Purpose] This study aimed to investigate the structural relationships among event quality, spectators‘ destination image, country image, and behavioral intention in the international cycle competition, Tour de Korea 2017. [Methods] The questionnaire was structured in four dimensions: event quality (three sub-dimensions and twelve items), destination image (three items), country image (three items), and behavioral intention (four items). A total of 292 spectators from six hosting cities (Yeosu, Gunsan, Muju, Yeongju, Cheongju, and Seoul) during the event participated in this study. Factor analysis, reliability, validity, correlation analysis, and structural equation modeling analysis were conducted utilizing SPSS 21.0 and AMOS 21.0. [Results] This study indicated that event quality in an international sporting event was found to be the significant factor of spectators’ destination image and country image, which, in turn, significantly influenced the spectators’ intention to revisit to the place of the event and/or the event itself. [Conclusions] The findings of the present study contribute to theoretical understandings of event quality that predicts spectators’ behavioral intention and destination image in a global sporting event. Practically, this study also provides some important suggestions for practitioners who plan marketing strategies for international sporting events.


Purpose The purpose of this study is to empirically inquire into the relationship between a indoor swimming pools employee’s group cohesiveness, swimming pool identification & communication and job satisfaction, customer orientation, long-term orientation, and positive word of mouth through structural equation model analysis. Methods For this purpose, For this purpose, the survey targeted 221 workers working at 10 swimming pools in Seoul for over three months. For sampling method, convenience sampling method was used, while the questionnaire was self-administered. In an effort to verify the proposed structural model, this study used IBM SPSSWIN Ver. 21.0 and AMOS 18.0. Results First, group cohesiveness, swimming pool identification & communication has positive influence on the job satisfaction. Second, job satisfaction has positive influence on the customer orientation. Third, job satisfaction has positive influence on the positive long-term orientation. Fourth, customer orientation has positive influence on the positive word of mouth. Fifth, long-term orientation has positive influence on the positive word of mouth.

Purpose This study reviewed the seriousness of the Match-fixing through the mixed research methods of the big data analysis (quantitative) and the focus group interview (qualitative) using the keyword, ‘Match-fixing’ and discusses the cautious and comprehensive basic direction for coping with negative issues and preventing recurrence. Methods For the quantitative research method, Naver and Daum were used as the analysis channel and the main keywords selected for the data search were ‘Match-fixing’ and ‘Match-fixing+(measures/eradication/solution)’. The data collection period was limited from January 1, 2010 to December 31, 2016. In addition, for the qualitative research method, 6 homogeneous groups (experience, interest, knowledge) related to the research topic were constructed and interviewed using purposive(intentional) sampling. Results First, five factors (emotion, participant, cause, punishment, countermeasure) were categorized by big data analysis. Second, through Focus Croup interview, additional keywords for three factors (emotion, participant, countermeasure) were derived. Conclusions Therefore, it is required that various preventive measures such as emotional reward for negative emotion, preventive and ethical education, advancement of sports, establishment of Match fixing committee, Expert training are needed.


Purpose The purpose of this sequential mixed-method study is to compare the levels of Moderate to Vigorous Physical Activity (MVPA) between the students with intellectual disabilities and students without disabilities in different types of inclusive physical education classes and to understand why different levels of MVPA occur. Methods For this purpose, 17 students with intellectual disabilities and 102 students without disabilities participated in this study, and the levels of MVPA in inclusive physical education classes were accessed using thee dimensional accelerometers. The collected data were analyzed using independent sample t-test. To understand the different levels of MVPA identified in quantitative analysis, four teachers were interviewed. Results Results showed that different levels of MVPA were found in inclusive physical education classes, and this is because the students with intellectual disabilities had participation constraints and teachers did not have knowledge to deal with those constraints. Considering gender difference, only different levels of MVPA were found among male students, which could be stemmed from few opportunities of cooperative works between male students with intellectual disabilities and male students without disabilities. Considering types of inclusive physical education classes, significant different levels of MVPA were identified in tee ball classes. The reason for this could be that the rule of tee ball is too complicated and too many team tasks for the students with intellectual disabilities to understand and to execute. Conclusions Based on the results, practical teaching strategies to increase levels of MVPA of the students with intellectual disabilities are provided in the discussion section.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to further understand how out-of-school adolescents’ self-esteem and interpersonal relations have changed in a peer mentoring basketball program and what they have experienced for the program It was action research of qualitative research method. Methods 4 out-of-school adolescents in the adolescents Center of C-si were selected as the participant. The data was collected by in-depth interviews, participant observation, and research journal. The collected data was then analyzed by an inductive categorical system. Results The findings were summarized as follows: the out-of-school adolescents showed somewhat low self-esteem and difficulties of interpersonal relations at an early stage participating in the peer mentoring basketball program. However, their self-esteem and interpersonal relations have been gradually changed during the program. First, they participated in various mentoring activities and self-expression activities. Their self-esteem has been improved as they found their real values, communicated with others, and lived with their confidence. Second, they overcame personal relations with fear and indifference of others, extended personal relations, and sympathized with others to solve the problem that they had as interpersonal relations. Conclusions The out-of-school adolescents has positively changed their self-esteem and interpersonal relations through the peer mentoring basketball program. We expect that out-of-school adolescents could overcome their difficulty and live well their life in the future.



Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate differences among perfectionism, anxiety, and aggression in contact and non-contact sports and verify the structural relationship model of perfectionism, anxiety, and aggression in the field of sports. Methods Male college athletes (N=299) participated in the study and perfectionism, anxiety, and aggression questionnaires were utilized after their verification of validity and reliability were conducted. The descriptive statistical analysis, the multivariate analysis, the correlation analysis, the structural equation analysis, and the multi-group analysis were conducted. Results The results are as follows: First, the level of perfectionism, anxiety, and aggression were significantly different between contact and non-contact sports (F=4.316, p<.001). Additionally, subfactors of aggression such as hostility, physical aggression, and verbal aggression factors in contact sports showed a higher average than non-contact sports. Second, perfectionism positively affected anxiety (t=6.936, p<.001) and anxiety positively affected aggression (t=3.380, p<.001). Moreover, the complete mediation effect of anxiety was found in the path from perfectionism to aggression (β=.152, p<.01). Finally, we compared path coefficients between contact and non-contact sports. As a result, positive causal relationships was indicated in the path from anxiety to aggression (β=.511, p<.001) in contact sports. However, it was not discovered in non-contact sports (β=.149, p>.05). Conclusions In conclusion, perfectionism causes anxiety and anxiety is a mediator leading to aggression in sports. Such effect is more predictable and observable in contact sports in which aggression is more favorable and encouraged. Implications and suggestions for future research are discussed.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of training methods on body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power in female judo players. Methods Subjects performed weight training (n=10) and circuit weight training (n=10) consisting of 10 sports items for 12 weeks. In order to analyze the effects of training, body composition, isokinetic strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function, and anaerobic power were measured and the effect of training was verified. Results First, the comparison of body composition between WT and CWT groups showed that significant interaction effect between group and period was found in all variables (weight: F=1082.694, p=.001, body fat mass F=199.999, p=.001; skeletal muscle mass F=2481.698, p=.001, and percentage body fat: F=496.246, p=.001). Second, there was a significant interaction effect between group and duration in shoulder muscle strength and knee endurance (EPTL: F=6.598, p=.019; EAPL: F=12.860, p=.002). Conclusions The result of this study showed that the interaction effect between period and group was not significant according to the training method but the overall effect of the circuit weight training group was more positive than the weight training group. Therefore, it can be concluded that the 12 weeks circuit weight training can contribute to improve the performance of female Judo players by improving body composition, strength and muscle endurance, cardiopulmonary function and anaerobic power.

Purpose The purpose of this study was to explore the optimal model for winning medal on vault event of men's gymnastics. Specifically, decision tree analysis was used to explore, first, for the optimal conditions for qualifying top 8th player that have high possibility into final round, and second, for the optimal model for obtaining the medal of the vault event. Methods Data were collected for five official competitions (Olympics, Asian games, and International championship, etc.) organized by the Federation of International Gymnastics (FIG) from 2013 to 2016. In this study, the data of 626 vault players were collected. Also all of these players performed 921 vault skills for qualifying round or final round. Five predictor variables for estimating for qualifying into the final round and for obtaining the medal of the vault event were selected; nationality, difficulty score, acting score, additional penalty score, final score. Results The results is as follows. Overall, it was confirmed that the optimal model for entering into the final round was the difficulty score of vault event. The optimal model for entering into the final round estimates 81.2% when condition would be the 5.6 or higher of difficulty score and 8.6 or higher of the acting score. The optimal model for winning medals was 86.7%, which means that when condition would be the 6.0 or higher of difficulty score and no additional penalty score. Conclusions This models can be used as a basic data for establishing a strategy for medal acquisition of vault event of gymnastics.